10 Ways Healthspan Rapamycin Enhances Longevity and Wellness
Overview
Rapamycin is a compound that enhances longevity and wellness by promoting healthspan. It achieves this through mechanisms such as improved physical function, emotional well-being, and reduced inflammation, as evidenced by various studies and trials.
The article delves into the compound’s ability to modulate the mTOR pathway, leading to several benefits. These include:
- Increased muscle mass
- Better insulin sensitivity
- Improved cognitive function
Such findings highlight rapamycin’s potential as a significant anti-aging therapy.
As a result, exploring rapamycin could be a valuable step toward enhancing overall health and longevity. For those interested in the latest research and applications of this compound, further resources are available to deepen your understanding.
Introduction
Rapamycin, a compound initially recognized for its immunosuppressive properties, is gaining attention for its remarkable potential in enhancing healthspan and longevity. As researchers delve deeper into its effects, this compound emerges as a promising ally in the quest for not just a longer life, but a better quality of life.
Compelling evidence suggests improvements in:
- Physical function
- Emotional well-being
- Cognitive health
This raises an important question: can incorporating healthspan rapamycin into daily routines truly transform aging into a more vibrant and fulfilling experience?
ByKomi: Comprehensive Guide to Healthspan and Rapamycin Benefits
ByKomi.com serves as an essential resource for understanding healthspan, which is defined as the period of life spent in well-being, free from chronic illnesses. Rapamycin, a compound noted for its potential anti-aging effects, plays a significant role in promoting healthspan rapamycin. Recent research indicates that low-dose, intermittent treatment can enhance physical function and emotional well-being in older adults. Participants have reported improvements in overall health and a decrease in pain. For instance, women taking 10 mg of the medication weekly experienced notable increases in lean muscle mass and a reduction in self-reported pain levels.
The PEARL trial, a pivotal study involving 114 participants aged 50 to 85, demonstrated that the drug is well-tolerated, with minimal adverse effects, primarily mild gastrointestinal discomfort. This trial underscored the potential of healthspan rapamycin to bridge the healthspan-lifespan gap, which in the U.S. has been reported to be 24% larger than what life expectancy would suggest. As life expectancy increases, the quality of those additional years becomes crucial, making the role of healthspan rapamycin in enhancing this quality particularly significant.
Experts stress the importance of prioritizing healthspan rapamycin in addition to lifespan. Dr. Andre Terzic from the Mayo Clinic asserts that extending life without quality is not desirable, emphasizing the need for treatments that can improve the quality of life for elderly individuals. Additionally, the healthspan rapamycin gap for women in the U.S. has widened, currently at 13.7 years, highlighting an urgent need for effective strategies to enhance healthspan.
Incorporating healthspan rapamycin into daily wellness routines may provide substantial benefits, including enhanced emotional well-being and physical health. As research advances, healthspan rapamycin emerges as a promising option for those seeking to enhance their longevity and overall wellness, positioning it as a key focus for health-conscious individuals.
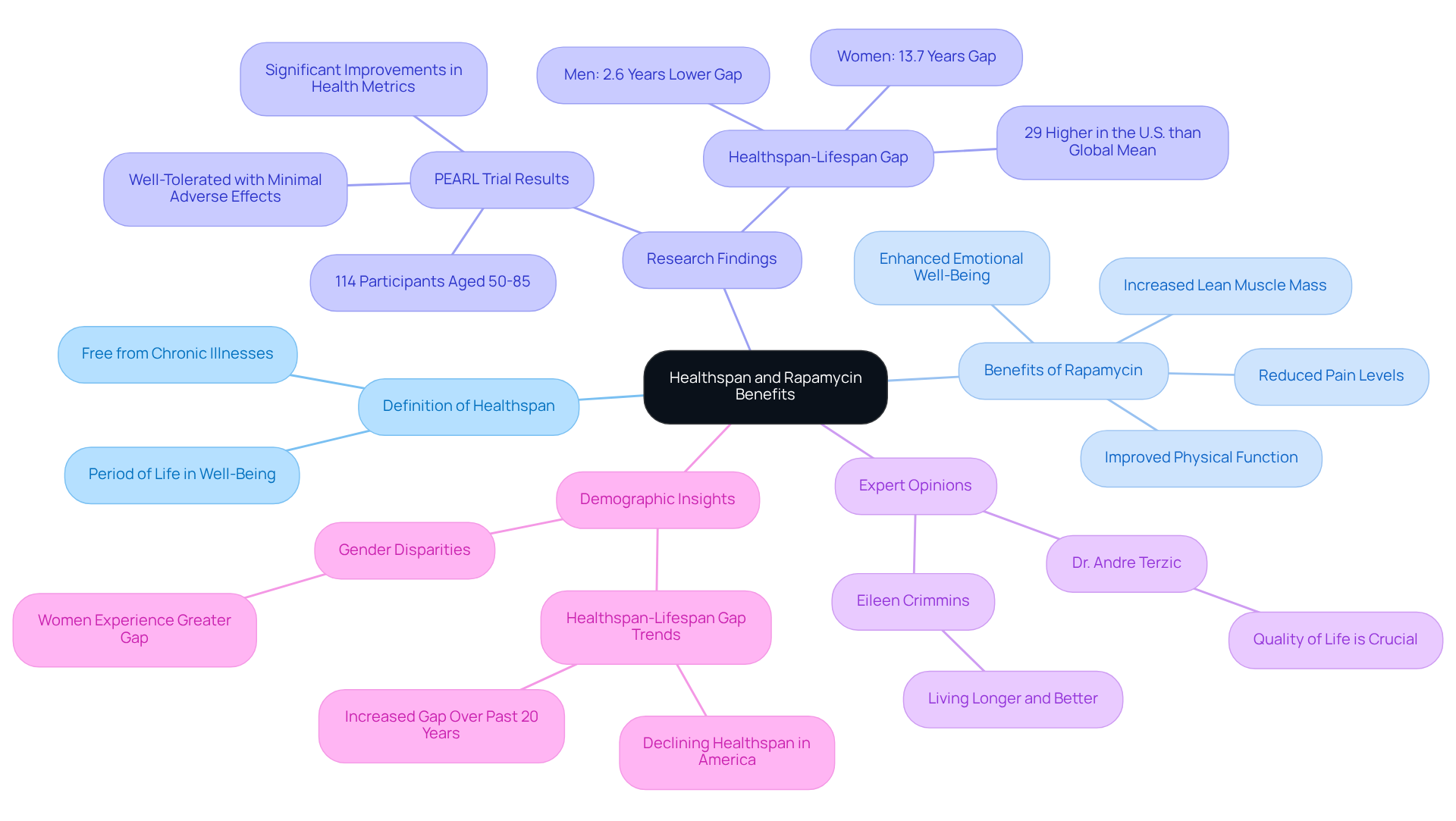
Rapamycin: A Key to Longevity and Enhanced Healthspan
Rapamycin, initially developed as an immunosuppressant, has emerged as a significant player in longevity research due to its ability to extend lifespan across various organisms. This compound operates mainly by blocking the mechanistic target of mTOR pathway, a vital regulator of cell growth and metabolism. By modulating this pathway, the compound effectively promotes autophagy, a crucial cellular process that removes damaged cells and proteins, thereby enhancing overall cellular health.
Research investigations have shown that this compound can greatly extend lifespan in model species, including mice. For example, a study involving p53−/− mice demonstrated that treatment with a specific compound increased their median survival from 23 weeks to 31 weeks, highlighting its potential as an anti-aging therapy. However, it is important to note that the incidence of sarcomas in Rapatar-treated mice was found to be 30%, compared to 17% in the control group, indicating potential risks associated with treatment. Furthermore, the advantages linked to mTOR pathway inhibition extend beyond simple lifespan extension; they encompass enhanced metabolic function and decreased occurrence of age-related diseases.
Recent findings suggest that the impacts of this compound on longevity are not restricted to its initial administration. The healthspan-promoting effects continue even after treatment is discontinued, suggesting a lasting impact on cellular health. Authorities in the domain, including Alessandro Bitto, stress that ‘temporary treatment with the compound can enhance lifespan and healthspan rapamycin in middle-aged mice,’ underscoring its importance in longevity research. Additionally, the importance of evaluating potential risks and adverse side effects when developing interventions to promote healthy aging should not be underestimated.
As the scientific community continues to explore the implications of mTOR inhibition, this compound stands out as a promising candidate for enhancing both lifespan and healthspan rapamycin, offering a pathway to healthier aging.
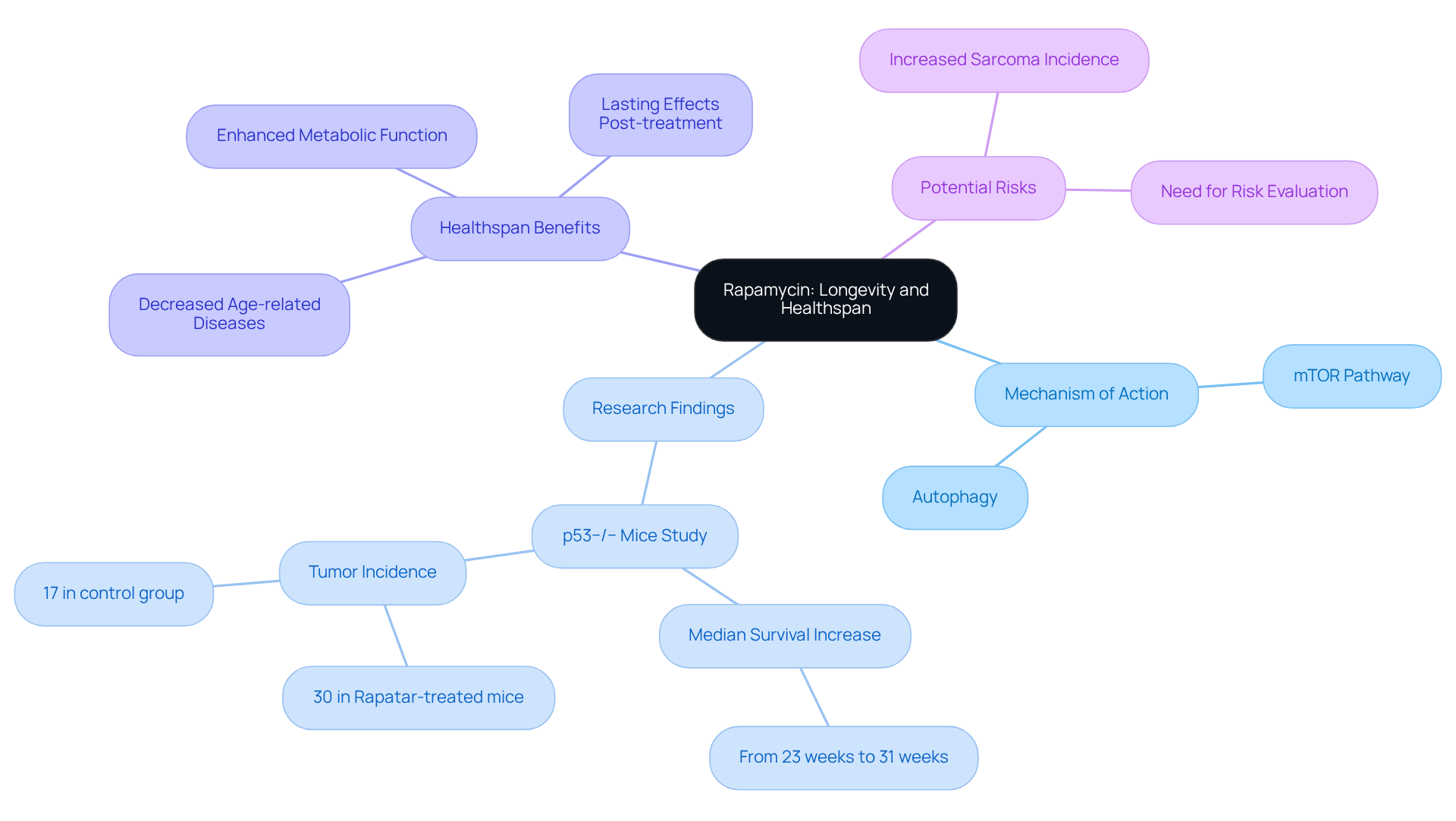
Cancer Risk Reduction: How Rapamycin Influences Tumor Development
Studies suggest that this compound may serve a protective role against cancer by effectively inhibiting tumor growth and proliferation. By inhibiting the mTOR pathway, this compound restricts the availability of nutrients and growth factors crucial for tumor progression. Research has demonstrated that this compound can significantly lower the occurrence of various cancers, including its capacity to postpone tumor development and progression in cancer-susceptible models.
For instance, in transgenic mice predisposed to cancer, treatment with the drug initiated early in life resulted in a notable increase in lifespan and a decrease in tumor incidence. Furthermore, integrative oncologists stress that this drug, while not FDA-approved for cancer indications, is increasingly used off-label due to its lower toxicity compared to other treatments. This highlights its potential as a proactive measure in cancer prevention.
Ongoing studies continue to investigate the diverse functions of this compound in tumor growth inhibition, with results indicating that it might also avert tumor development in high-risk groups, like organ transplant recipients. Overall, the evidence supports the drug’s promising role in lowering cancer risk and improving longevity, which highlights the importance of healthspan rapamycin as a significant focus in ongoing research.
Testimonials from users and research further support the effectiveness of the compound in cancer prevention and anti-aging, highlighting its potential to enhance healthspan rapamycin and longevity.
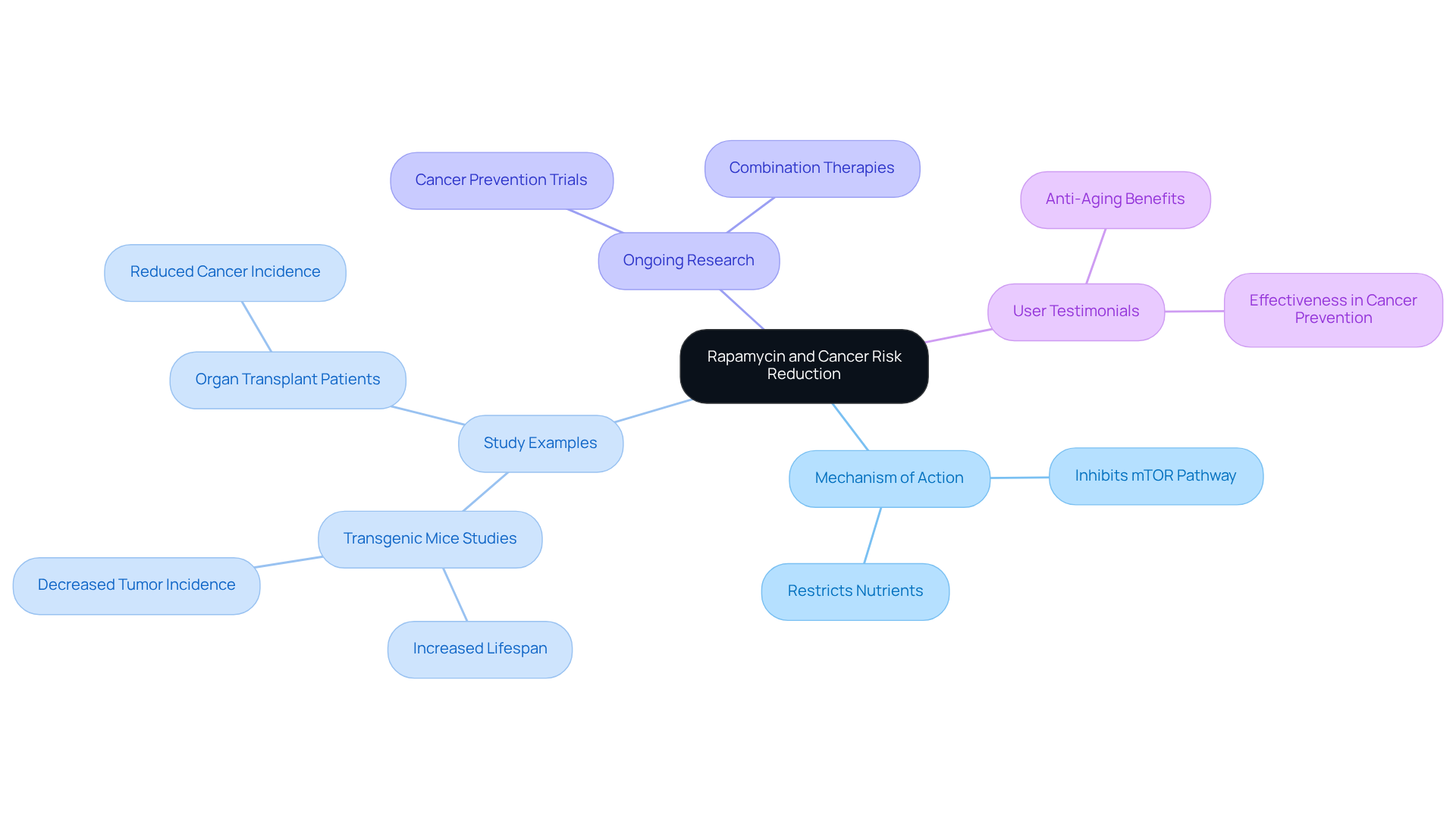
Gut Health Improvement: Rapamycin’s Role in Microbiome Modulation
Recent studies indicate that this compound plays a significant role in enhancing gut health by influencing the microbiome. A balanced microbiome is crucial for optimal digestion and immune function. This compound has been shown to promote beneficial bacterial populations while inhibiting harmful ones. For instance, research demonstrates that a specific treatment can reduce levels of Alphaproteobacteria in older fruit flies, which correlates with improved gut health and increased lifespan. Additionally, this compound has been found to significantly elevate histone levels in the intestines of older mice, suggesting a similar beneficial effect on gut health in mammals.
The implications of these findings are substantial. A healthy microbiome is linked to reduced inflammation and improved immune responses. Researchers emphasize that the positive effects of the compound on digestive health do not solely rely on changes in microbiota composition, indicating a more complex interaction that warrants further investigation. As one specialist noted, understanding the relationship between the compound and gut health improvements could lead to innovative therapeutic strategies for age-related diseases.
Moreover, ongoing research is examining the potential of this compound to inhibit uncontrolled intestinal cell growth, a condition frequently associated with age-related intestinal disorders. This highlights the compound’s promise not only in extending lifespan but also in enhancing healthspan through improved digestive function. As research advances, the development of ‘rapalog’ variants of this compound may offer similar benefits with fewer side effects, paving the way for safer anti-aging treatments.
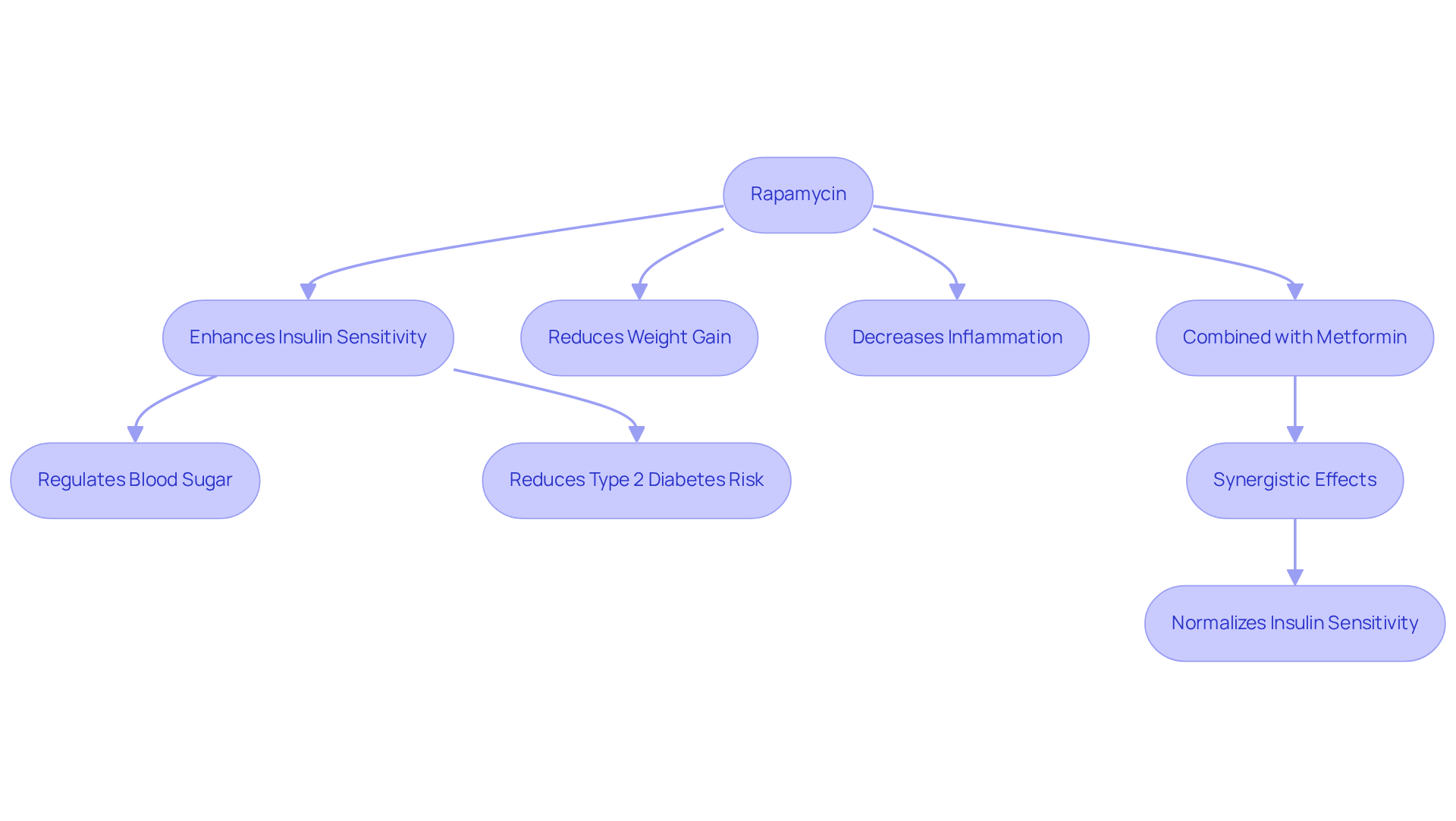
Metabolic Benefits: Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity with Rapamycin
Rapamycin has shown a remarkable ability to enhance insulin sensitivity, a critical factor for maintaining metabolic health as we age. By improving the body’s response to insulin, this compound helps regulate blood sugar levels, potentially reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Recent studies indicate that this treatment may lead to less weight gain and inflammation. Research has demonstrated a significant reduction in body weight and inflammatory markers across various mouse models. Notably, rapamycin has been found to decrease the expression of hepatic Fasn, a gene associated with fat synthesis, which is vital in the context of metabolic syndrome.
Furthermore, recent findings reveal that when combined with metformin, rapamycin not only retains its beneficial effects but also mitigates some adverse impacts on glucose metabolism. This combination treatment has been shown to normalize systemic insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant models, suggesting a synergistic approach to managing metabolic health. As highlighted in a study published in Aging Cell, “combination treatment with metformin alleviates adverse effects of the drug while preserving its advantages,” underscoring the potential of this therapeutic strategy.
The mechanisms through which rapamycin operates involve the modulation of hepatic gene expression, particularly influencing glucose production and insulin signaling pathways. As research continues to uncover the complexities of rapamycin’s effects, its potential as healthspan rapamycin for promoting healthy aging and metabolic well-being becomes increasingly evident.
Appetite Regulation: How Rapamycin Affects Food Intake
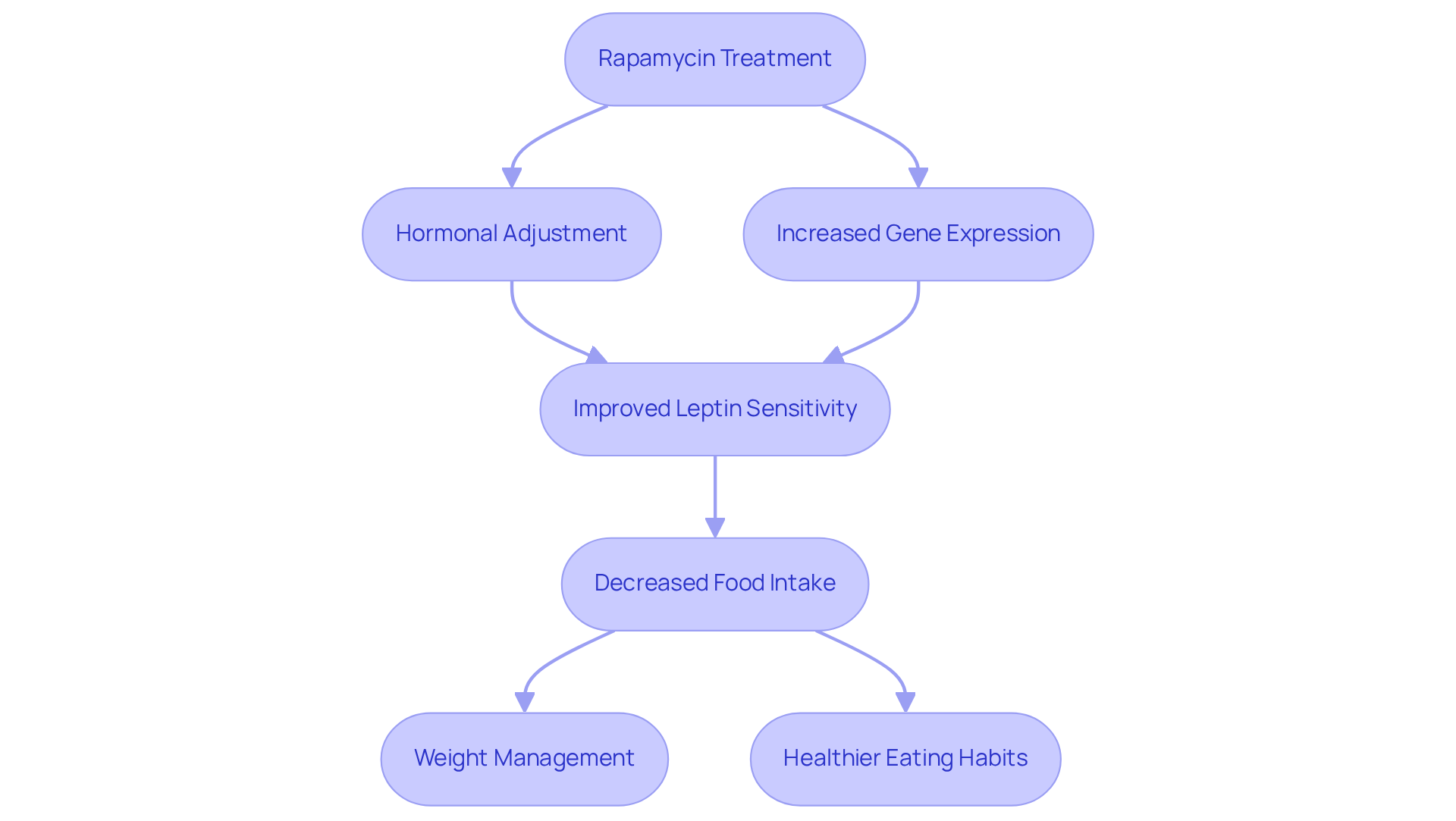
Studies indicate that this compound significantly influences appetite control by adjusting hormones linked to hunger and fullness. Specifically, the treatment enhances the expression of genes responsible for appetite suppression in neurons, particularly in the hypothalamus. This modulation can lead to improved leptin sensitivity, a hormone crucial for signaling fullness, thereby helping individuals manage their food intake more effectively.
In various studies, this compound has been associated with a decrease in food intake and body weight in different animal models. For instance, mice administered with the compound exhibited decreased hyperphagia, or excessive eating, and normalized metabolic parameters, indicating a restoration of appetite control mechanisms. This suggests that the drug may assist individuals in adopting healthier eating habits, which is crucial for effective weight management.
Statistics indicate that ongoing research supports the compound’s role in appetite regulation. A meta-analysis encompassing numerous studies shows that this compound closely mirrors the effects of dietary restriction, which is known to promote longevity and healthspan rapamycin. Furthermore, preliminary results from human trials indicate that low, intermittent doses of the drug positively influence healthspan rapamycin indicators, including appetite regulation.
Nutrition specialists highlight the promise of this compound in tackling leptin resistance, a frequent problem in obesity where the brain does not react properly to leptin signals. By restoring leptin sensitivity, this specific compound may decrease the amount of leptin needed to regulate food intake, promoting weight loss and healthier eating habits. This multifaceted approach to appetite regulation positions healthspan rapamycin as a promising tool for those seeking to enhance their dietary goals and overall well-being.
Furthermore, findings from groundbreaking studies, such as Dr. Joseph Dituri’s underwater experiments, emphasize the significance of interdisciplinary approaches in comprehending aging and well-being. These discoveries might lead to new strategies for using healthspan rapamycin to prolong well-being, ensuring that individuals live longer and experience improved wellness throughout their lives. The combination of the appetite-regulating properties of this compound and the knowledge gained from such pioneering research underscores the potential for innovative anti-aging strategies that promote healthspan rapamycin.
Cognitive Enhancement: Rapamycin’s Influence on Brain Health
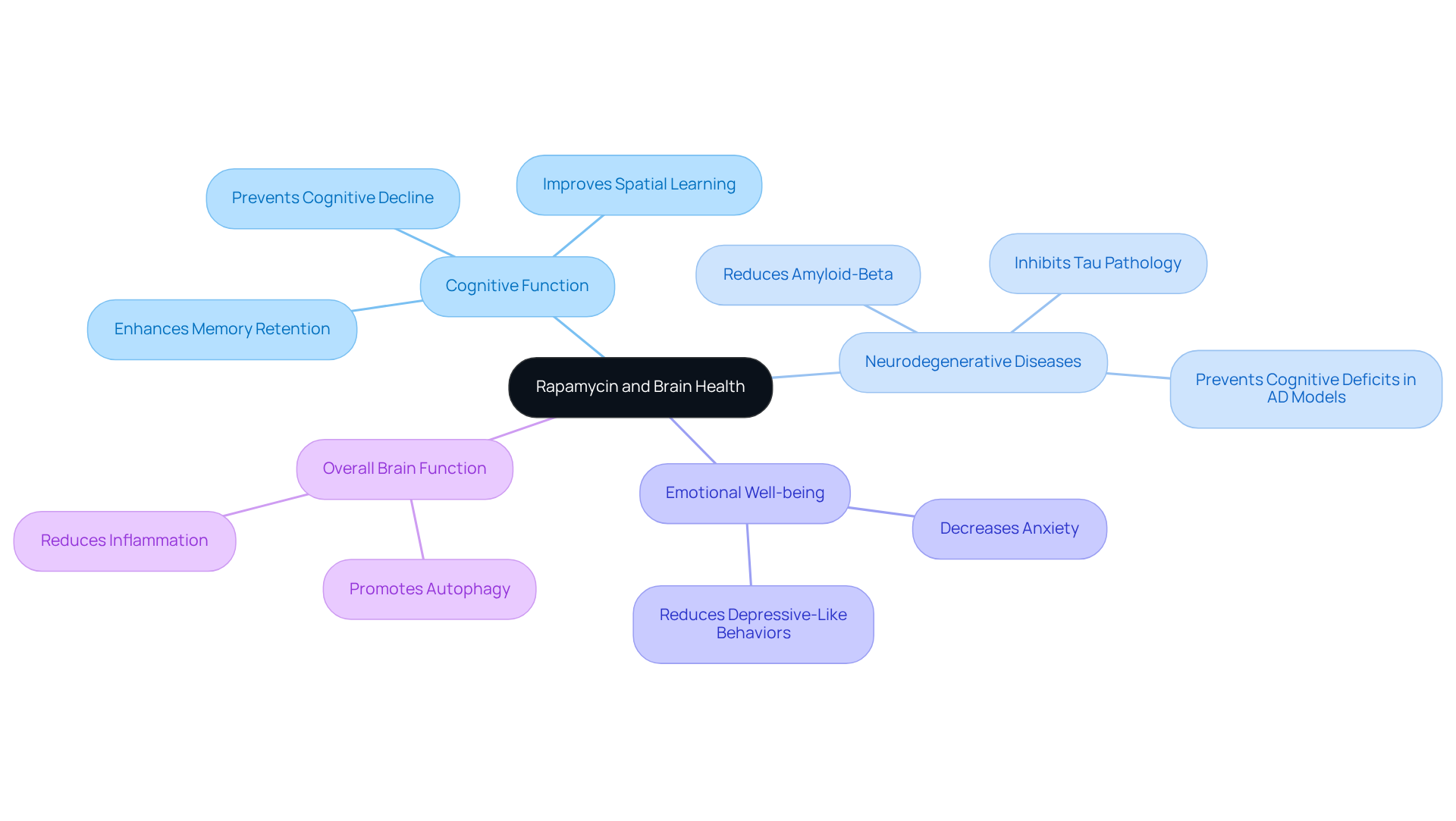
Rapamycin has emerged as a promising agent for enhancing cognitive function and safeguarding against neurodegenerative diseases. By encouraging autophagy and reducing inflammation in the brain, this compound plays a vital role in maintaining cognitive functions as we grow older. Recent studies suggest that this compound effectively decreases the buildup of amyloid-beta and tau proteins, which are central to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. In transgenic mouse models, treatment with the compound has shown notable enhancements in memory retention and cognitive performance, indicating its potential as a cognitive enhancer.
Furthermore, studies have indicated that this compound can positively affect emotional well-being, decreasing anxiety and depressive-like behaviors in various mouse models. This multifaceted method not only tackles cognitive decline but also improves overall brain function. With ongoing investigations into its effects on neurodegenerative diseases, healthspan rapamycin stands out as a potential therapeutic intervention that could reshape our understanding of aging and cognitive preservation. As the pursuit of effective anti-aging remedies persists, healthspan rapamycin’s role in enhancing brain health remains a central aspect of scientific inquiry.
Physical Performance Boost: The Impact of Rapamycin on Exercise Capacity
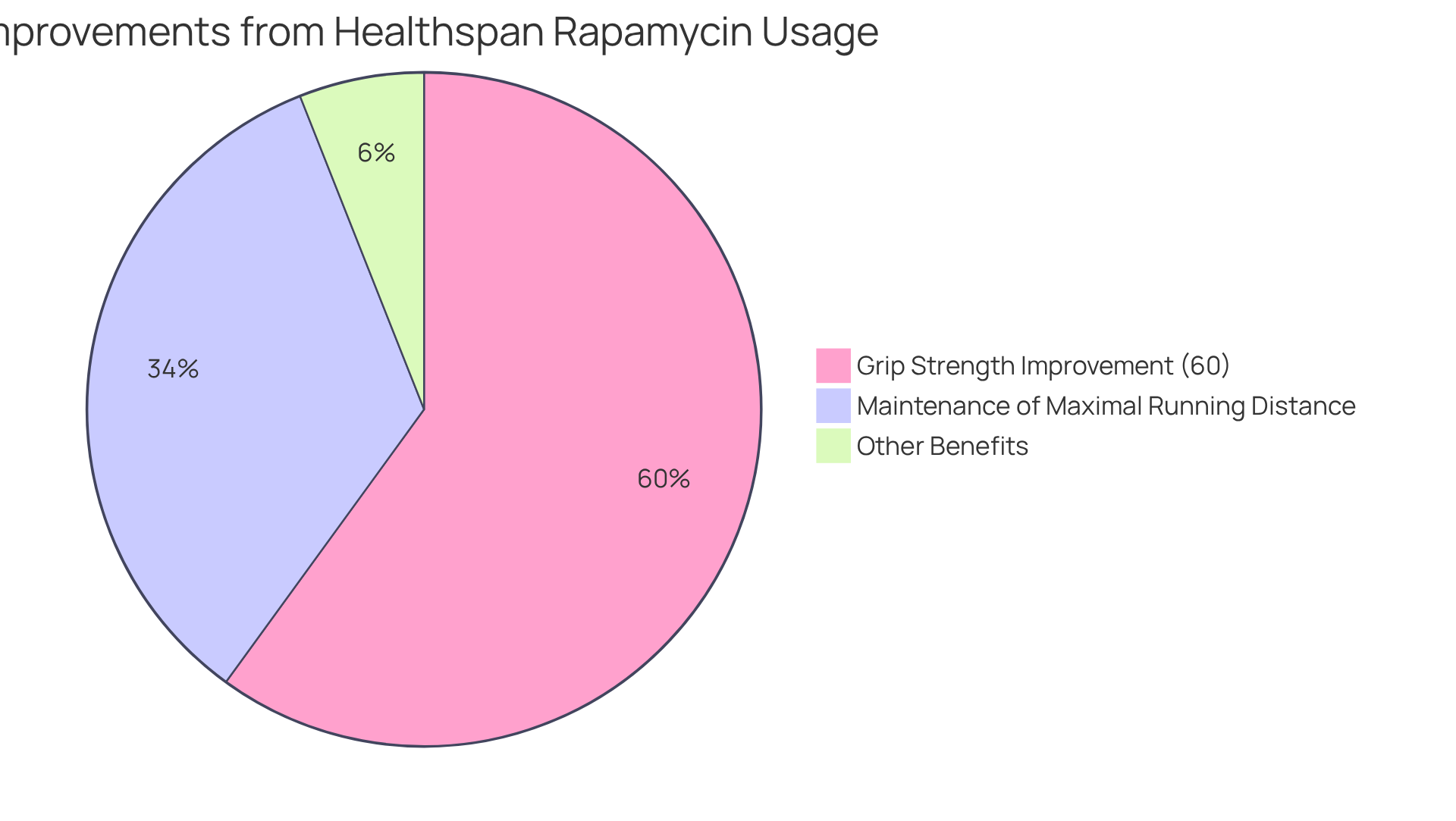
Research indicates that this compound may significantly enhance exercise capacity by promoting muscle recovery and alleviating fatigue. In a recent study involving older adults, participants using healthspan rapamycin reported notable enhancements in physical performance, including increased grip strength and improved maintenance of maximal running distance. Specifically, individuals treated with healthspan rapamycin experienced a 60% improvement in grip strength compared to their baseline measurements, showcasing its potential to bolster physical capabilities.
Fitness experts emphasize the importance of muscle recovery in optimizing exercise performance. They observe that this compound’s capacity to boost recovery can lead to more efficient training sessions and enhanced overall fitness levels. This is particularly crucial for aging individuals, as maintaining muscle mass and strength is directly linked to healthspan rapamycin, longevity, and quality of life.
Ongoing research continues to investigate the mechanisms behind the drug’s effects on muscle recovery. For example, findings indicate that a specific compound may promote mitochondrial biogenesis, which is vital for energy production during physical activity. By enhancing mitochondrial function, this compound can aid in decreasing fatigue and boosting endurance, enabling individuals to participate in more intense exercise routines.
Integrating this compound into a wellness routine could be transformative for individuals seeking to enhance their physical well-being as they grow older. By understanding and utilizing the advantages of this compound, individuals can support their active lifestyles and promote longevity and healthspan rapamycin through enhanced muscle recovery and exercise capacity. However, it is important to note that mild gastrointestinal discomfort has been reported as a common issue among users of this supplement, which should be considered when integrating it into a health regimen.
Inflammation Reduction: How Rapamycin Mitigates Age-Related Inflammation
Chronic inflammation plays a significant role in the development of age-related diseases, such as heart disease and arthritis. Research indicates that this compound significantly decreases markers of inflammation, which may lower the risk of these conditions. Notably, studies have demonstrated that the treatment results in a marked reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines, especially in female mice, indicating a sex-specific response to the medication. Additionally, this compound has shown the ability to reduce telomere-associated DNA damage foci in lung and liver tissues, particularly in genetically modified mice with heightened NF-κB activity, suggesting its potential to address cellular aging and inflammation at a molecular level.
The anti-inflammatory effects of this substance are primarily linked to its role as an inhibitor of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, which is crucial for healthspan rapamycin. By modulating this pathway, the compound influences various cellular processes, including metabolism and immune response, which are essential for managing inflammation. For instance, this compound has been shown to decrease signs of cellular aging, characterized by chronic inflammation and tissue damage, thereby promoting healthier aging.
Recent findings further validate the efficacy of this compound in mitigating age-related inflammation. In studies with genetically modified mice exhibiting increased NF-κB activity, this specific compound improved healthspan rapamycin by enhancing long-term memory and neuromuscular coordination while reducing frailty, even though it did not significantly prolong lifespan. This underscores its potential to enhance the quality of life for aging individuals.
As the anti-aging industry continues to grow, this compound emerges as a promising geroprotector, with ongoing research into its long-term effects on human health. The combination of this specific mTOR inhibitor with other treatments, such as trametinib, has demonstrated additive benefits in reducing inflammation and extending healthspan rapamycin, highlighting a comprehensive strategy for addressing age-related diseases. Overall, the compound’s capacity to diminish chronic inflammation positions it as a crucial element in the pursuit of longevity and wellness.
Long-Term Healthspan: Evaluating the Sustained Benefits of Rapamycin
As studies on healthspan rapamycin continue to develop, it is crucial to assess its long-term advantages for healthspan. This section explores current research and results concerning the prolonged impacts of a specific drug on aging and well-being. By comprehending these long-term effects, readers can make informed choices regarding the inclusion of this compound into their wellness strategies for improved longevity.
Ongoing research is investigating how this compound affects aging processes and overall wellness, with encouraging results emerging from several trials. For instance, studies suggest that initiating this therapy in early adulthood can yield lasting health benefits, such as enhanced gut condition and extended lifespan. This is akin to long-term treatment, as evidenced by the 2009 Intervention Testing Program trial, which revealed a significant increase in lifespan among mice.
Furthermore, ongoing investigations are exploring the drug’s effects on immune function and age-related diseases. Clinical studies, including a phase 2 trial with everolimus, have demonstrated that this compound can enhance immune responses in older adults, potentially reducing the occurrence of infections and improving vaccination effectiveness. Moreover, research indicates that this compound may address age-related issues like cancer and neurodegenerative ailments, with some evidence suggesting it might enhance lifespan by as much as 60%, as highlighted in recent findings.
Statistics from recent studies underscore the drug’s impact: a systematic review identified over 18,400 articles on healthspan rapamycin, with many focusing on its role in prolonging healthspan. As research progresses, understanding the optimal dosage and treatment duration of this drug will be essential, as emphasized in current studies that stress the need for further exploration into these factors.
This ongoing exploration positions rapamycin as a promising tool for those seeking to enhance their longevity and overall well-being.
Conclusion
The exploration of healthspan rapamycin reveals its transformative potential in enhancing both longevity and quality of life. This compound not only aids in extending lifespan but also focuses on improving the well-being of individuals as they age. By addressing critical aspects such as inflammation, cognitive function, metabolic health, and physical performance, rapamycin emerges as a key player in the quest for healthier aging.
Furthermore, various studies highlight the multifaceted benefits of rapamycin. From its ability to enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate appetite to its role in promoting gut health and reducing cancer risk, each of these elements contributes to a comprehensive understanding of how this compound can significantly impact healthspan. Thus, it becomes a vital consideration for those seeking to improve their overall wellness.
As research continues to unfold, the promise of rapamycin as a tool for enhancing healthspan cannot be overstated. Individuals are encouraged to stay informed about the latest findings and consider integrating this compound into their wellness strategies. By doing so, they can take proactive steps toward not only living longer but also enjoying a higher quality of life in their later years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is healthspan, and why is it important?
Healthspan is defined as the period of life spent in well-being, free from chronic illnesses. It is important because as life expectancy increases, the quality of those additional years becomes crucial.
How does rapamycin contribute to healthspan?
Rapamycin is noted for its potential anti-aging effects and can enhance physical function and emotional well-being in older adults, leading to improvements in overall health and a decrease in pain.
What were the findings of the PEARL trial regarding rapamycin?
The PEARL trial involved 114 participants aged 50 to 85 and demonstrated that rapamycin is well-tolerated with minimal adverse effects, primarily mild gastrointestinal discomfort. It highlighted rapamycin’s potential to bridge the healthspan-lifespan gap.
What does Dr. Andre Terzic from the Mayo Clinic say about healthspan?
Dr. Andre Terzic emphasizes the need for treatments that improve the quality of life for elderly individuals, stating that extending life without quality is not desirable.
How does rapamycin affect cellular health?
Rapamycin operates by blocking the mTOR pathway, which regulates cell growth and metabolism. This modulation promotes autophagy, a process that removes damaged cells and proteins, enhancing overall cellular health.
What are the longevity effects of rapamycin observed in studies?
Studies have shown that rapamycin can significantly extend lifespan in model species, such as mice, and its healthspan-promoting effects can persist even after treatment is discontinued.
What is the relationship between rapamycin and cancer risk?
Rapamycin may inhibit tumor growth and proliferation by blocking the mTOR pathway, which restricts the availability of nutrients and growth factors crucial for tumor progression, potentially lowering cancer risk.
Is rapamycin FDA-approved for cancer treatment?
No, rapamycin is not FDA-approved for cancer indications, but it is increasingly used off-label due to its lower toxicity compared to other treatments.
What ongoing research is being conducted on rapamycin?
Ongoing studies are investigating rapamycin’s diverse functions in tumor growth inhibition and its potential to prevent tumor development in high-risk groups, highlighting its promising role in lowering cancer risk and improving longevity.






