7 Key Differences Between NMN vs NAD for Health Benefits
Overview
This article delves into the essential differences between Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), particularly focusing on their health benefits in the realms of aging and metabolic wellness. NMN acts as a precursor to NAD and has demonstrated potential in boosting energy metabolism and promoting cellular health. Furthermore, it underscores the importance of personalized supplementation approaches tailored to individual health goals, alongside ongoing research into the distinct effects of these compounds.
As we explore these topics, consider how NMN and NAD could fit into your wellness journey. What specific health goals do you have in mind? Understanding these differences can empower you to make informed decisions regarding supplementation. With the continuous evolution of research, staying updated on these developments is crucial for optimizing your health strategies.
Introduction
In the pursuit of longevity and optimal health, the significance of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) has captured considerable interest. These compounds are not merely trends within the wellness community; they play vital roles in the complex processes of cellular function and energy metabolism.
- NMN acts as a precursor to NAD, making it essential to comprehend their unique functions and benefits, particularly for those contemplating supplementation in relation to aging and metabolic health.
- As research continues to reveal NMN’s potential in addressing age-related decline and boosting vitality, individuals are increasingly eager to understand how these compounds can influence their health strategies.
This comprehensive guide explores the distinctions and advantages of NMN and NAD, offering insights that empower health-conscious individuals to make well-informed decisions for their well-being.
ByKomi: Comprehensive Guide to NMN and NAD Differences
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) are essential for sustaining cellular well-being, highlighting the differences in their functions in the discussion of NMN vs NAD. NMN acts as a precursor to NAD, converting into NAD upon ingestion. This distinction is crucial for individuals considering enhancements, particularly in the discussion of NMN vs NAD concerning aging and metabolic well-being.
Recent studies have highlighted NMN’s potential as a therapeutic strategy for combating age-related muscle decline, showcasing its significance in promoting vitality as we age. Clinical trials have demonstrated that NMN intake has a substantial clinical impact in preventing adult aging, reinforcing its role in health maintenance. As Made Yudha Asrithari Dewi noted, “In conclusion, NMN intake has a significant clinical impact in preventing adult aging.”
Furthermore, the recruitment process for NMN clinical trials has shown that targeted advertisements and strict inclusion criteria can lead to high compliance rates among participants, which is essential for the integrity of the results. This highlights the growing interest and dedication to understanding the advantages of NMN and NAD enhancement.
As research continues to evolve, the distinctions between NMN vs NAD become increasingly relevant. While the comparison of NMN vs NAD supplementation is associated with increased NAD levels, the specific advantages of each compound require thoughtful evaluation. Understanding these distinctions can empower wellness-focused individuals to make informed decisions regarding their well-being and lifestyle strategies.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): Essential Precursor to NAD+
In the discussion of NMN vs NAD, Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide, playing a crucial role in the biosynthesis of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD). This coenzyme is essential for numerous cellular functions, including:
- Energy metabolism
- DNA repair
- Cell signaling
By increasing NMN intake through additional sources, individuals may elevate their NAD levels, which can support cellular wellness and promote longevity, making the comparison of NMN vs NAD consumption particularly relevant in current studies highlighting their potential benefits. A systematic review of NAD enhancement revealed that while some studies reported low incidences of side effects and improvements in quality of life, others noted minimal clinically relevant effects and potential adverse outcomes, such as increased insulin resistance. This suggests that while NMN may enhance NAD levels, its effectiveness as a treatment for age-related issues remains uncertain in the context of NMN vs NAD.
In terms of energy metabolism, NMN supplementation has been linked to improved mitochondrial performance, which is vital for maintaining energy levels as we age. Furthermore, NMN’s involvement in DNA repair processes underscores its significance for cellular health, possibly mitigating age-related decline.
Expert opinions further affirm the importance of NMN in NAD+ biosynthesis. It has been suggested that sirtuins, a group of proteins that regulate cellular health, may influence the physiological improvements associated with NAD-boosting compounds. This connection emphasizes NMN’s potential to impact not just energy metabolism but also broader aspects of health and longevity.
As of 2025, ongoing research continues to explore the relationship between NMN and NAD levels in aging populations. Some trials indicate that while NMN intake may not lead to significant changes in body composition, it could still offer benefits for energy metabolism and overall vitality. Personal experiences, including my own with TMG (Trimethylglycine), demonstrate enhanced energy levels and improved metabolic function through NMN supplementation, highlighting its possible advantages in the discussion of NMN vs NAD. The synergistic relationship between NMN and TMG further amplifies its potential benefits, making it a noteworthy option for those aiming to enhance their well-being as they age. While research is ongoing, consulting with a healthcare provider can offer personalized insights into the use of NMN and TMG.
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD): Vital Role in Metabolism
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is a vital coenzyme found in all living cells, essential for redox reactions that transform food into energy. It participates in over 400 enzymatic processes, including DNA repair and the regulation of cellular metabolism. As individuals age, levels of NAD naturally decrease, significantly impacting metabolic health and lifespan, which brings attention to the comparison of NMN vs NAD in terms of their effects on cellular function.
Recent studies reveal that NAD concentrations differ among cellular compartments, with levels reaching approximately 109 μM in the cytosol, 106 μM in the nucleus, and 230 μM in the mitochondria of HeLa cells. This variability underscores the importance of maintaining optimal NAD levels for effective energy conversion and metabolic function.
Furthermore, research has highlighted the role of this coenzyme in metabolism, emphasizing its significance in energy production and redox reactions. NAD is crucial for converting nutrients into usable energy, facilitating the metabolic processes that sustain cellular function. Scholars suggest that increasing NAD concentrations, particularly in later years, may enhance well-being and lifespan.
A case study examining fluctuations in these levels illustrates how age-related variations in human blood metabolites can inform individualized wellness strategies, especially when considering NMN vs NAD to enhance metabolic health as individuals age. As the landscape of anti-aging therapies evolves, the focus on NMN vs NAD continues to grow, emphasizing their essential roles in fostering vitality and well-being.
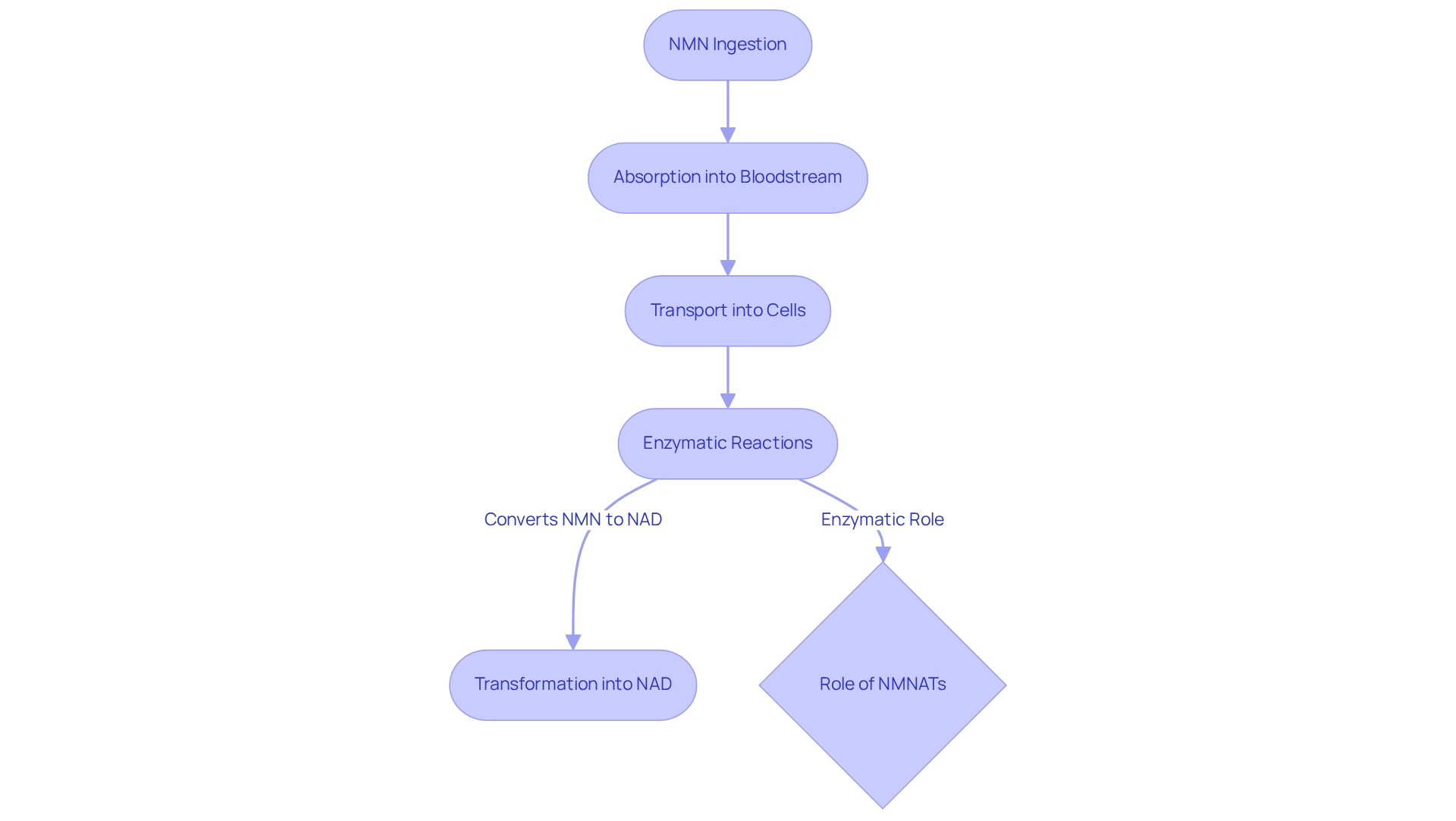
Conversion Process: How NMN Transforms into NAD
Upon ingestion, the comparison of NMN vs NAD shows that NMN is absorbed into the bloodstream and transported into cells, where it is transformed into NAD through a series of enzymatic reactions. The main enzymes enabling this transformation are NMN adenylyltransferases (NMNATs), which play a crucial role in the discussion of NMN vs NAD, specifically in converting NMN to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. This transformation is essential for restoring NAD levels in the body, particularly as these levels naturally decrease with age, emphasizing the relevance of NMN vs NAD supplements.
During my consultation, he stressed that sustaining ideal levels of NAD+ is vital for metabolic well-being and longevity, especially in the context of NMN vs NAD. Recent studies indicate that the administration of NMN vs NAD is safe and well-tolerated in healthy individuals, underscoring its potential as a beneficial supplement. Furthermore, ongoing research continues to examine the complete range of NMN vs NAD’s impacts on aging, emphasizing its significance in biomedicine and medical care.
Real-life examples illustrate that effective NMN absorption can greatly aid in replenishing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which is an important factor in the discussion of NMN vs NAD as a promising path for those looking to combat the aging process. As noted by Jinjun Guo and Li Rong, who directed and proofread the review, the ongoing exploration of NMN’s benefits is crucial for understanding its role in health and longevity.
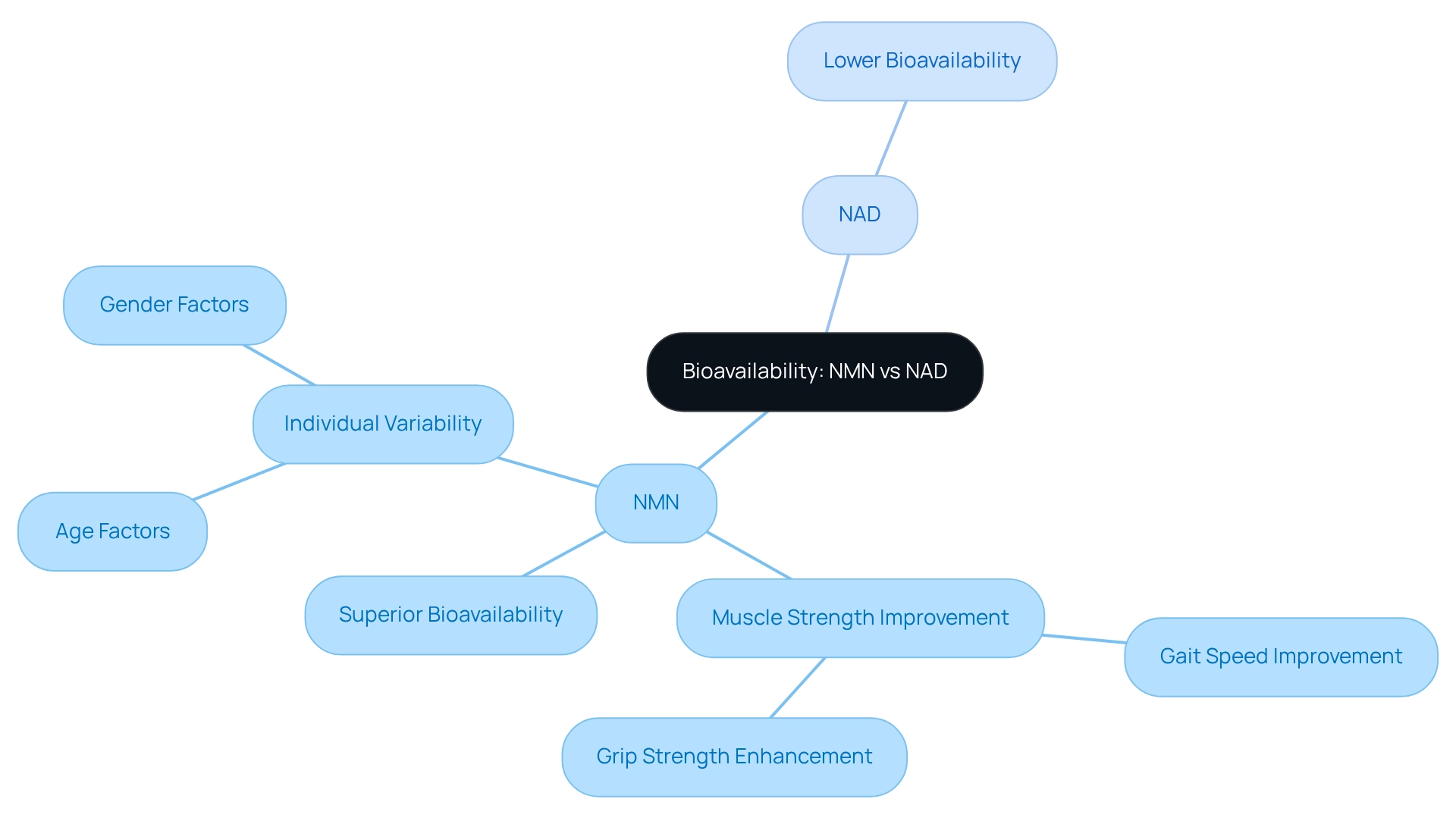
Bioavailability: NMN vs NAD Supplement Effectiveness
Bioavailability plays a crucial role in determining how effectively a substance can enter circulation and exert its effects in the body. In the debate of NMN vs NAD, NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is recognized for its superior bioavailability compared to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. Studies indicate that NMN can be absorbed more effectively through the intestinal barrier, leading to a quicker increase in NAD levels within the bloodstream. This enhanced absorption makes NMN an attractive option for individuals looking to elevate their NAD+ levels through supplementary sources, highlighting the importance of understanding NMN vs NAD.
Recent research has demonstrated that NMN intake can significantly improve muscle strength and performance in older adults, as evidenced by assessments of gait speed and grip strength. These findings underscore NMN’s potential to support overall muscle health, although further investigation is needed to fully understand its effects across various demographics.
Furthermore, recent insights into NMN absorption suggest that its bioavailability may differ based on individual factors such as age and gender. This variation emphasizes the need for personalized approaches to supplementation. ByKomi stresses the importance of tailoring supplement choices to individual wellness needs, ensuring optimal benefits. As research advances, our understanding of NMN’s role in wellness and aging will expand, paving the way for more targeted and effective anti-aging strategies. For those considering additional nutrients, consulting with a medical professional can help identify the most suitable options based on personal wellness goals.
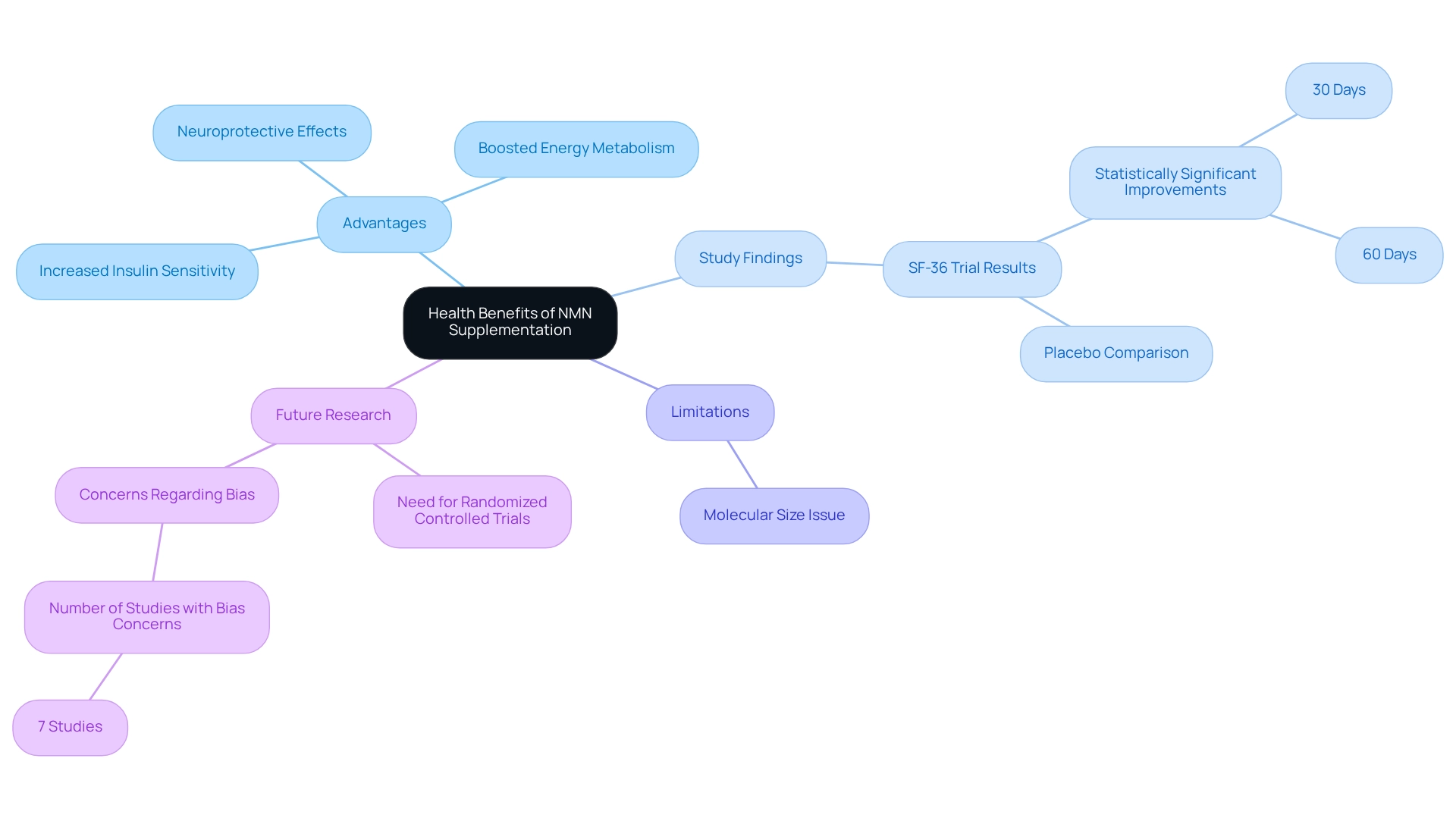
Health Benefits of NMN Supplementation Compared to NAD
Studies suggest that NMN intake provides various advantages, particularly increased insulin sensitivity, boosted energy metabolism, and possible neuroprotective effects. In a recent trial utilizing the 36-Item Short Form Survey Instrument (SF-36), participants receiving NMN showed statistically significant improvements in perceived health status compared to those on a placebo, particularly at 30 and 60 days. This highlights NMN’s beneficial effect on overall health.
Furthermore, although its enhancement offers possible benefits, its greater molecular size may obstruct its capacity to efficiently penetrate cell membranes. This limitation indicates that when considering NMN vs NAD, NMN might act as a more effective precursor for enhancing NAD levels within cells, thereby aiding various physiological functions. As research continues to develop, the necessity for upcoming randomized controlled trials with stringent designs becomes clear to further elucidate the effects of NMN supplementation, particularly since seven studies have highlighted concerns regarding bias.
In summary, NMN supplementation not only promotes metabolic well-being but also shows potential in enhancing subjective well-being. This makes it an attractive option for individuals looking to optimize their condition as they age.
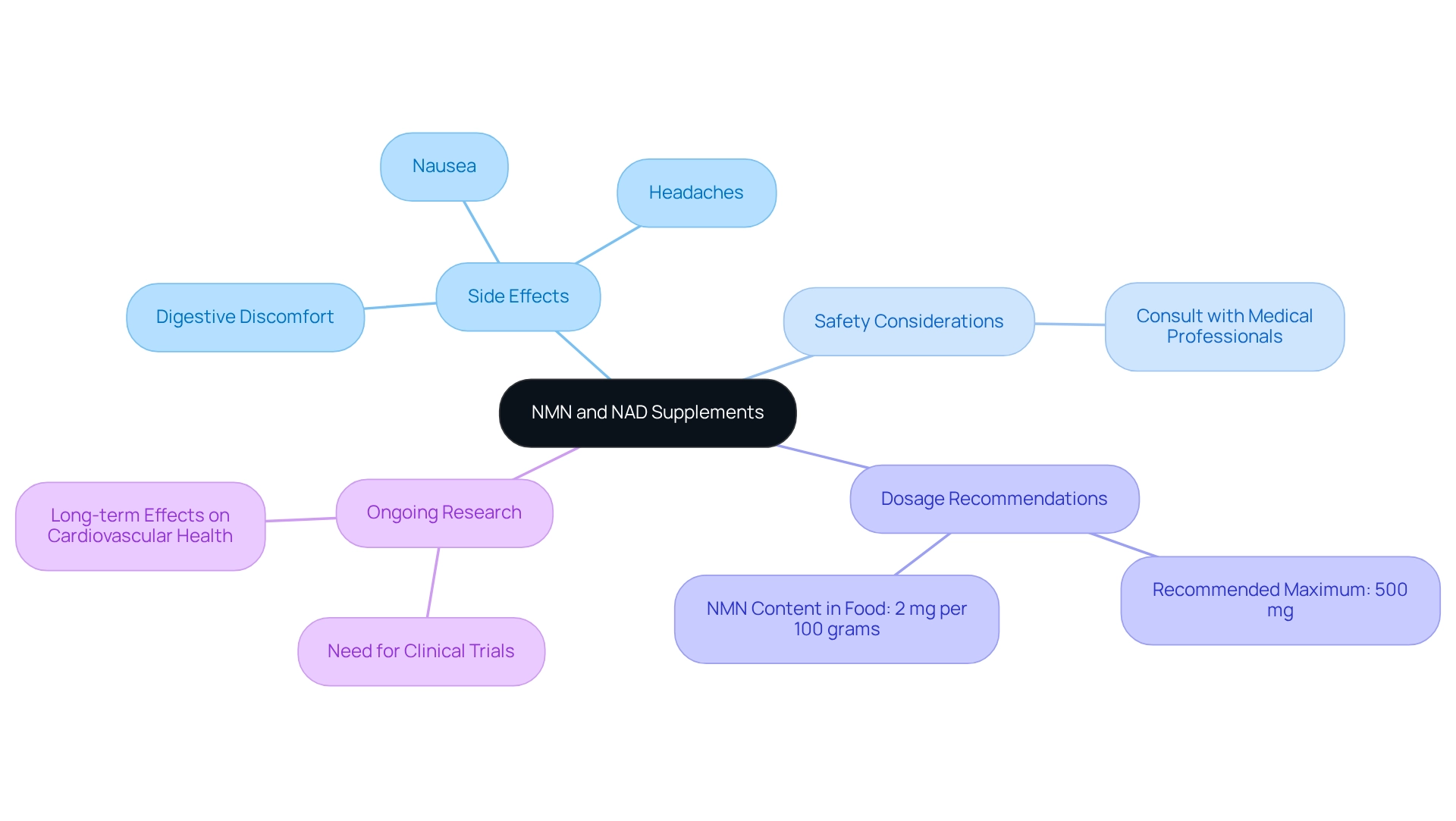
Side Effects and Limitations of NMN and NAD Supplements
While the comparison of NMN vs NAD+ supplements shows they are generally considered safe, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as digestive discomfort, headaches, or nausea. It is essential for users to consult with medical experts before beginning any new supplement routine, particularly if they have underlying medical issues or are using other medications.
A recent analysis indicates that while NMN content in food is approximately 2 milligrams per 100 grams, the safety of higher doses remains a topic of ongoing research. Experts, including Taylor C. Wallace, Ph.D., suggest that there isn’t much reason to supplement with more than 500 milligrams of NMN or NR. Furthermore, a study named ‘Long-term NMN Use Insights’ emphasized the necessity for additional clinical trials to fully comprehend the long-term impacts of NMN use on cardiovascular well-being, especially regarding arterial stiffness. As of 2025, the long-term effects of high-dose supplementation are still being studied in the context of NMN vs NAD, highlighting the significance of informed decision-making in supplement usage.
Are you considering NMN supplementation? It’s crucial to stay informed and consult with healthcare professionals to navigate this evolving landscape.
Aging and Its Impact on NAD+ Levels
As people age, there is a notable decrease in specific cellular compounds, significantly impacting overall well-being. Research indicates that levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) decline by approximately 50% between the ages of 20 and 80. This reduction contributes to various age-related medical issues, such as:
- Decreased energy production
- Impaired DNA repair mechanisms
- Heightened oxidative stress
Moreover, this decline is associated with several age-related diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic syndromes. Therefore, it is crucial to explore effective strategies for maintaining or enhancing NAD levels through dietary choices and supplements, particularly in the context of NMN vs NAD. By addressing these factors, individuals may be able to alleviate some adverse effects of aging and support healthier aging processes.
What dietary options or supplements have you considered to boost your NAD levels? Exploring these avenues could lead to significant improvements in your overall health.
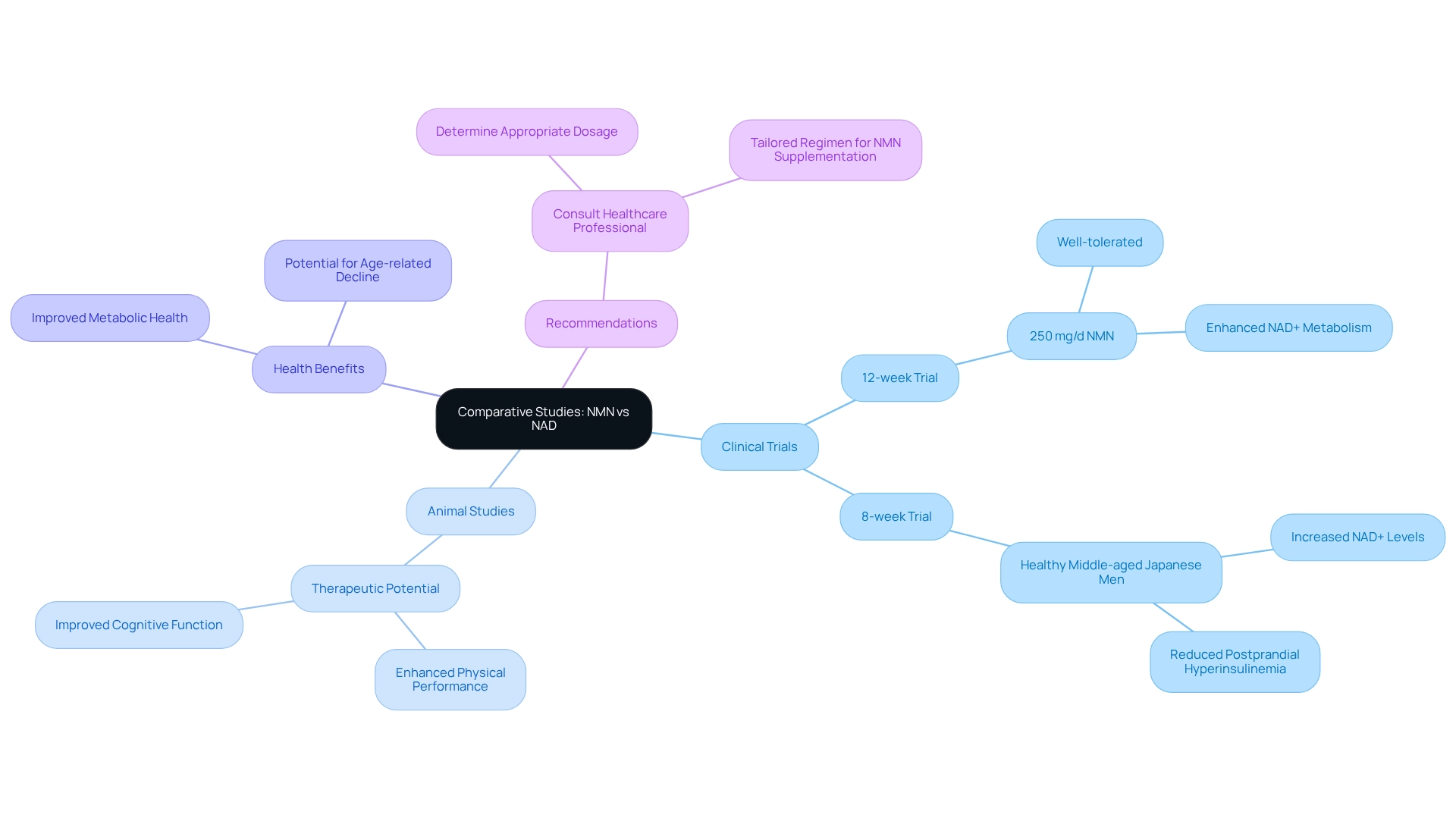
Comparative Studies: NMN vs NAD in Research
Recent studies have extensively compared the health results of NMN vs NAD enhancement, revealing that NMN is generally more effective in raising NAD levels within tissues and improving metabolic health indicators. A significant 12-week clinical trial demonstrated that a daily dose of 250 mg of NMN was well-tolerated and greatly enhanced the metabolism of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in healthy middle-aged adults. Furthermore, an 8-week clinical study involving healthy middle-aged Japanese men confirmed that NMN intake not only raised NAD levels but also showed potential in reducing postprandial hyperinsulinemia, a recognized risk factor for coronary artery disease.
Animal research further supports the therapeutic potential of NMN, indicating enhancements in physical performance and cognitive function, which are essential as individuals grow older. These findings suggest that in the comparison of NMN vs NAD+, NMN may serve as a more effective intervention for age-related decline than NAD+ addition alone. Overall, the evidence points to NMN’s exceptional capacity to improve well-being outcomes, making it an appealing option for individuals seeking to enhance their wellness through additional support.
To maximize the benefits of NMN, consider consulting with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and regimen tailored specifically to NMN supplementation.
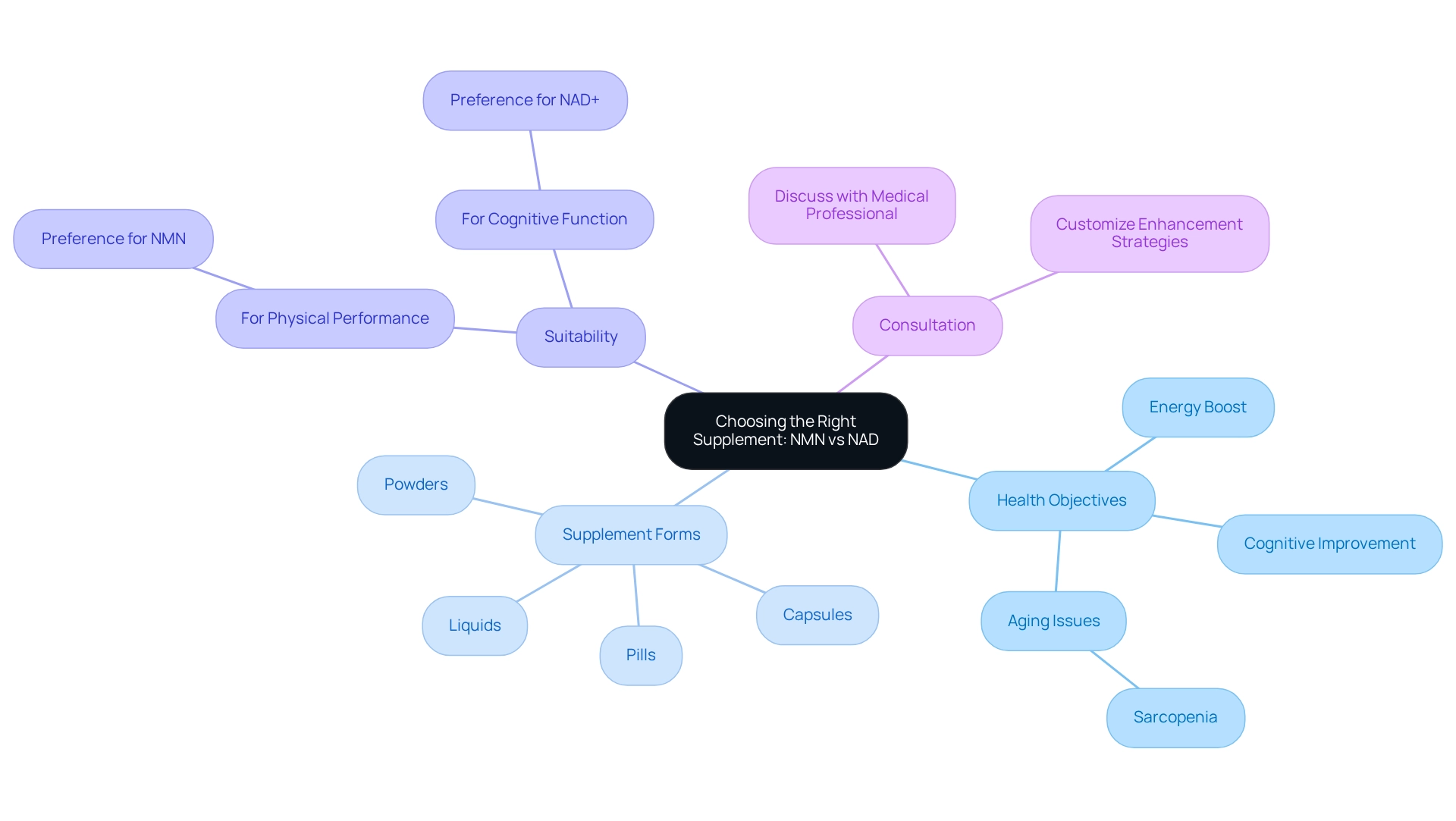
Choosing the Right Supplement: NMN or NAD?
Choosing between NMN vs NAD and other supplements requires a thorough evaluation of individual wellness objectives. NMN is often preferred by those looking to boost energy levels and enhance metabolic function, as it has shown potential in efficiently elevating essential coenzyme levels. In contrast, NADH enhancement may be more suitable for individuals pursuing targeted therapies, such as cognitive improvement or addressing aging-related issues like sarcopenia.
Dietary aids, including NMN and NADH, are available in various forms such as pills, capsules, powders, and liquids. They are designed to complement a healthy diet by filling potential nutrient gaps or addressing specific nutritional needs. Recent studies suggest that NMN could serve as a therapeutic strategy for various aging-related conditions, highlighting its potential benefits. However, rigorous clinical trials are essential to validate these findings across diverse populations.
Discussing with a medical professional is crucial to customize enhancement strategies to personal wellness requirements, ensuring both effectiveness and safety, as real-life examples illustrate how wellness objectives can influence the choice between NMN vs NAD. For instance, individuals focused on enhancing physical performance may lean towards NMN, while those prioritizing cognitive function might opt for NAD+.
As trends in supplementation evolve, staying informed about the latest research and professional insights can assist in making effective choices in the pursuit of optimal wellness. To make the best choice, consider your specific health goals and consult with a healthcare professional to determine which supplement aligns best with your needs.
Conclusion
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) are pivotal compounds in health and wellness, especially concerning aging and metabolic health. NMN acts as a crucial precursor to NAD, facilitating its production and supporting essential cellular functions. Increasing research highlights NMN’s potential in combating age-related decline, improving energy metabolism, and enhancing overall vitality. The benefits of NMN supplementation—ranging from improved muscle strength to enhanced insulin sensitivity—underscore its significance in health strategies for aging individuals.
Furthermore, understanding the differences in bioavailability between NMN and NAD is vital for informed supplementation choices. NMN’s superior absorption ability positions it as a more efficient option for elevating NAD levels within the body. This distinction is particularly important as individuals navigate their health journeys, seeking to optimize their well-being through targeted supplementation.
As the scientific community continues to explore the potential of NMN and NAD, it is clear that both compounds offer unique benefits that warrant consideration. While NMN shows promise in enhancing metabolic health and energy levels, NAD supplementation may cater to specific therapeutic needs. Ultimately, consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized insights, helping individuals select the most suitable approach based on their health goals. Embracing these compounds as part of a holistic health strategy could pave the way for improved longevity and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are NMN and NAD, and how are they related?
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide that serves as a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD). NMN converts into NAD upon ingestion, playing a crucial role in sustaining cellular well-being.
What functions does NAD serve in the body?
NAD is essential for numerous cellular functions, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cell signaling. It participates in over 400 enzymatic processes that transform food into energy.
How does NMN supplementation affect aging and metabolic health?
Recent studies suggest that NMN supplementation may combat age-related muscle decline and promote vitality as we age. Clinical trials have shown that NMN intake can have a significant clinical impact in preventing adult aging.
What are the potential benefits of increasing NMN intake?
Increasing NMN intake can elevate NAD levels, which supports cellular wellness and promotes longevity. It has been linked to improved mitochondrial performance and may mitigate age-related decline.
Are there any side effects associated with NMN or NAD supplementation?
A systematic review indicated low incidences of side effects and some improvements in quality of life from NAD enhancement. However, there are also reports of minimal clinically relevant effects and potential adverse outcomes, such as increased insulin resistance.
What is the importance of NAD levels in aging individuals?
NAD levels naturally decrease with age, significantly impacting metabolic health and lifespan. Maintaining optimal NAD levels is crucial for effective energy conversion and metabolic function.
How do NMN and NAD supplementation relate to individual wellness strategies?
Understanding the distinctions between NMN and NAD can empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their well-being and lifestyle strategies, particularly as research continues to evolve in this area.
What ongoing research is being conducted on NMN and NAD?
Ongoing research is exploring the relationship between NMN and NAD levels in aging populations, with some trials indicating that NMN may offer benefits for energy metabolism and overall vitality, despite not leading to significant changes in body composition.






