10 Spermidine Rich Foods to Boost Your Health Today
Overview
Spermidine-rich foods, including aged cheese, mushrooms, and whole grains, play a crucial role in enhancing health by promoting cellular regeneration and potentially increasing longevity. Research supports this claim, linking higher dietary intake of spermidine to reduced mortality rates and improved cardiovascular health. Therefore, it is essential to incorporate these foods into a balanced diet for overall well-being. By doing so, individuals can take proactive steps towards healthier living.
Introduction
In the quest for optimal health and longevity, attention is increasingly directed toward spermidine, a naturally occurring polyamine found in various foods. This remarkable compound is associated with numerous health benefits, including enhanced cellular regeneration and a decreased risk of chronic diseases. As individuals seek effective strategies to improve their diets, a pertinent question emerges: which spermidine-rich foods can be easily incorporated into daily meals to unlock these health advantages?
Exploring this topic unveils a delightful array of options that not only tantalize the taste buds but also promote a vibrant, health-focused lifestyle.
ByKomi: Nutritional Recipes Featuring Spermidine-Rich Ingredients
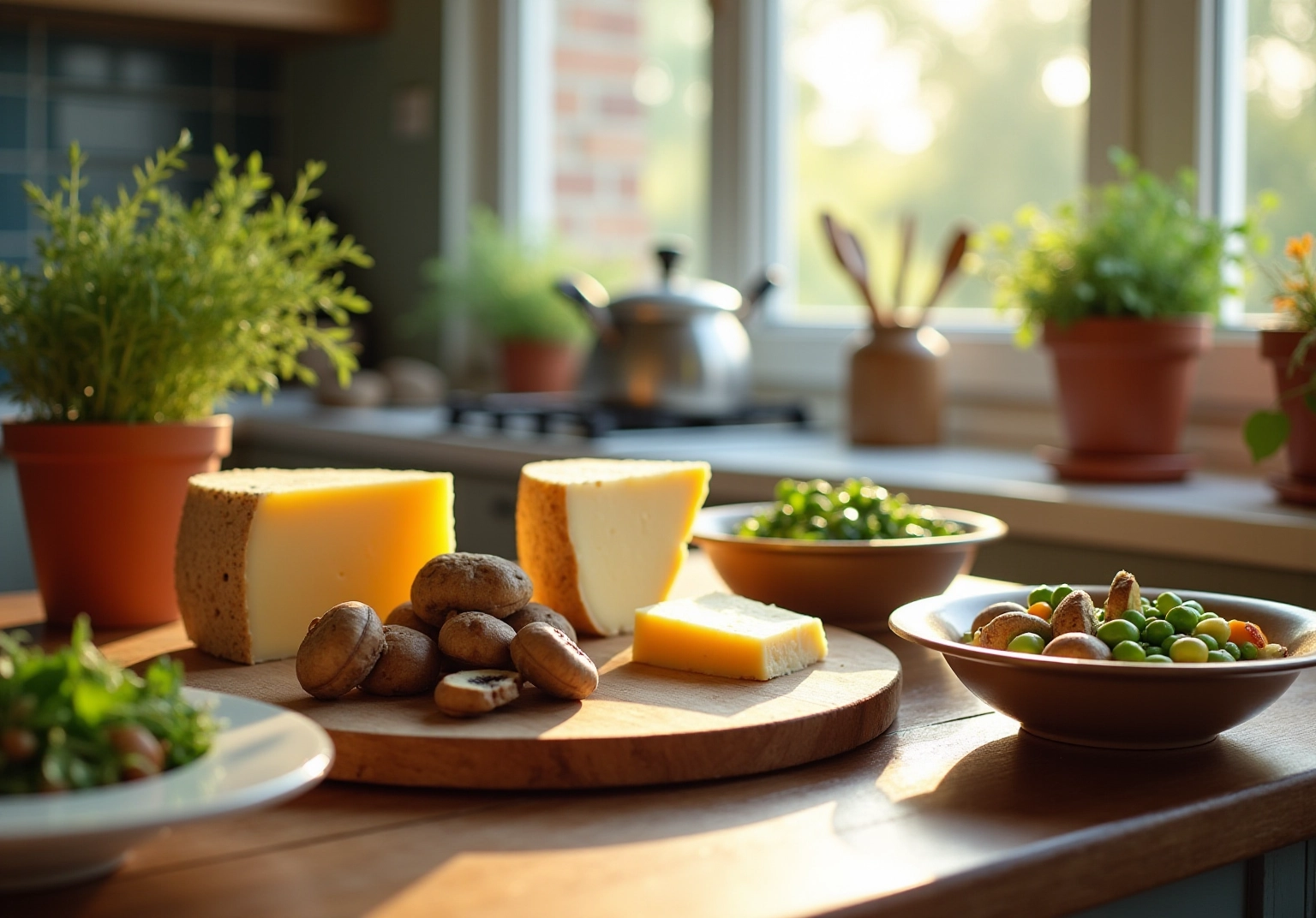
At ByKomi, we emphasize the essential role of including foods that are rich in spermidine in your nutrition. Spermidine rich foods, which contain this naturally occurring polyamine, are associated with numerous health benefits, including enhanced cellular regeneration and increased longevity. Recent studies have indicated that increased dietary intake of this specific polyamine is linked to a notable decrease in overall mortality and cardiovascular disease risk. Notably, individuals in the highest quartile of consumption exhibit a hazard ratio of 0.70 for all-cause mortality, underscoring its significance in a health-focused diet.
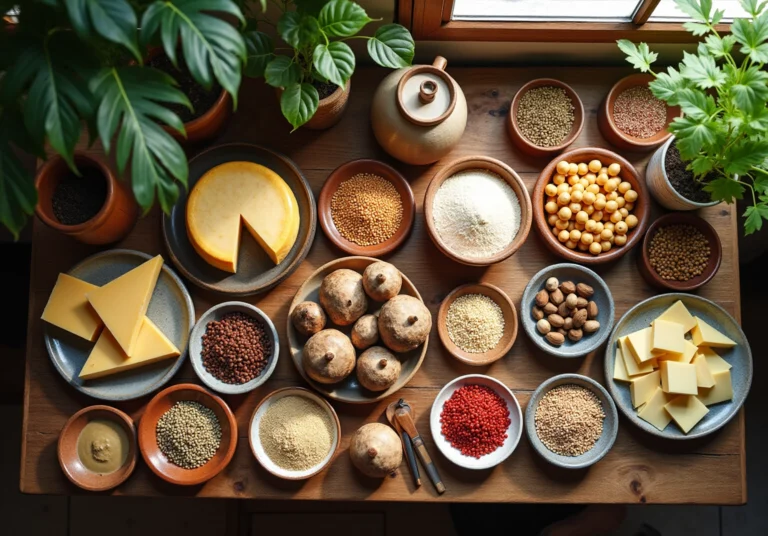
Our nutritional recipes include spermidine rich foods such as:
- Aged cheese
- Mushrooms
- Wheat germ
These allow you to enjoy tasty meals while improving your well-being. For instance, a portion of aged cheese can provide between 1.5 to 3 mg of spermidine per 100g, making it a flavorful addition to your meals. Furthermore, incorporating mushrooms not only enhances taste but also boosts your intake of beneficial compounds.
Explore our collection of recipes, including:
- A savory mushroom risotto
- A cheese platter featuring aged cheese
These dishes not only taste great but also support your journey towards healthy aging. By making informed dietary choices, you can enjoy the advantages of spermidine rich foods while indulging in flavorful, nutrient-rich meals.
Aged Cheese: A Delicious Source of Spermidine
Aged cheeses, such as cheddar and parmesan, are renowned not only for their rich flavors but also for their notable content of a specific polyamine, with cheddar containing roughly 200 mg/kg of this compound. The aging process significantly boosts the concentration of this beneficial compound, which makes these cheeses one of the spermidine rich foods that are a delightful addition to a health-conscious diet.
Research suggests that people consuming greater amounts of aged cheese may enjoy increased longevity and better cardiovascular condition. A study revealed that high intake of certain compounds among Italians was linked to a 40% reduced risk of heart failure. Clare Collins, a nutrition expert, notes that ‘aged cheese could help you age well,’ highlighting its potential role in promoting overall wellness.
Incorporating spermidine rich foods, such as aged cheeses, into your meals in moderation can provide both enjoyment and health benefits, supporting your journey toward healthy aging. It’s important to note that while some compounds are heat-sensitive, light cooking is acceptable; however, overcooking may reduce their levels.
Mushrooms: Versatile and Nutrient-Dense Spermidine Source
Mushrooms, particularly shiitake and maitake varieties, are considered spermidine rich foods and can be easily added to various dishes. Whether sautéed, grilled, or incorporated into soups, mushrooms enhance flavor while delivering essential nutrients that support well-being and longevity. With just 15 calories per cup of whole cremini mushrooms, their low-calorie profile, along with high levels of antioxidants and fiber, makes them an excellent choice for those aiming to sustain vitality as they age.
Furthermore, a study involving individuals aged 60 and older revealed that those consuming more than two servings of mushrooms weekly experienced a significantly lower risk of developing mild cognitive impairment. This finding highlights their potential contribution to brain health. Chefs frequently recommend mushrooms as a meat substitute in recipes, as they offer a satisfying umami flavor while helping to reduce sodium intake.
In addition, incorporating mushrooms into your diet is straightforward. You can add them to salads, stir-fries, or pasta dishes. For a delightful variation, consider replacing half of the meat in your favorite ground beef recipe with mushrooms. This adjustment not only maintains flavor but also enhances nutritional value.
Soy Products: Fermented Options for Enhanced Spermidine Intake
Fermented soy products, such as miso and tempeh, are considered spermidine rich foods that serve as excellent sources of a specific polyamine. The fermentation process not only boosts the polyamine content but also enhances the digestibility of nutrients. By including spermidine rich foods in your meals, you can promote digestive well-being while also benefiting from a rich supply of this advantageous compound.
Have you considered how these foods could fit into your diet? Exploring options like miso soup or tempeh stir-fries could be a delicious way to start!
Whole Grains: Essential for a Spermidine-Rich Diet
Whole grains, such as wheat germ, oats, and brown rice, are not only rich in essential nutrients but also serve as vital sources of a compound associated with longevity and wellness benefits. Research indicates that higher consumption of this compound correlates with lower mortality rates, underscoring the importance of these grains in your diet.
Including whole grains in your meals can significantly boost your intake of spermidine rich foods, which promotes cellular health and reduces age-related decline. For example, starting your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with fresh fruits or adding cooked brown rice to salads can enhance both flavor and nutritional value.
By opting for whole grain choices, such as those highlighted in the Bruneck and SAPHIR studies, you maximize health benefits, supporting your journey toward healthy aging and vitality. Aim to incorporate a variety of spermidine rich foods into your meals to fully enjoy the advantages of this essential compound.
Legumes: Nutrient-Dense Foods Packed with Spermidine
Legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, are excellent sources of protein and are classified as spermidine rich foods. For instance, spermidine rich foods such as lentils contain approximately 5 mg of spermidine per cup, while chickpeas offer around 6 mg per cup. Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into your diet can be straightforward; they can be easily added to salads, soups, and stews, enhancing both flavor and nutrition.
A cup of lentils provides around 18 grams of protein and is filled with vital vitamins and minerals, making it a powerhouse for overall wellness. Nutrition experts emphasize that regular consumption of legumes can significantly contribute to longevity, as they are associated with lower blood pressure and reduced cardiovascular risks. As nutritionist Paul M. Insel states, ‘Legumes offer a variety of nutrients that promote cardiovascular well-being and longevity.’
Practical examples include Mediterranean diets, which frequently highlight legumes as staples, showcasing their versatility and nutritional advantages. To boost your intake, consider adding chickpeas to your salads or preparing lentil-based soups, ensuring a delicious and healthful addition to your meals. However, it’s important to consume spermidine rich foods in moderation, as high-spermidine foods can cause digestive discomfort in some individuals. By embracing legumes, you can support your wellness journey while enjoying a variety of tasty dishes.
Corn: A Versatile Food Rich in Spermidine
Corn, particularly in its whole state, serves as a remarkable source of a compound recognized for its role in enhancing autophagy and lowering inflammation—essential elements in healthy aging. This versatile ingredient can be enjoyed in various ways, such as:
- Fresh corn on the cob
- Vibrant salads
- Ground into cornmeal for baking
Including corn in your meals not only improves flavor and texture but also aids in raising levels of beneficial compounds, promoting overall health and longevity.
For instance, consider adding grilled corn to a summer salad or using cornmeal to create nutritious pancakes. These straightforward modifications can greatly enhance your dietary consumption of this essential nutrient while savoring the delightful advantages of this staple. Furthermore, the Mediterranean diet, known for its abundance of certain nutrients, emphasizes the significance of incorporating such foods for a health-focused lifestyle.
With the compound found in corn contributing to potential lifespan increases, these dietary choices can be both enjoyable and advantageous.
Nuts and Seeds: Healthy Snacks with Spermidine Benefits
Nuts and seeds, including almonds, walnuts, and pumpkin seeds, are not only rich in healthy fats but also serve as excellent sources of polyamines. For instance, spermidine rich foods like almonds contain approximately 2.1 mg of spermidine per 100 grams, while walnuts provide around 5.5 mg per 100 grams. These nutrient-dense foods can easily be integrated into your meals, whether as snacks or mixed into salads and smoothies for an extra wellness boost.
Research indicates that consistent intake of nuts and seeds is linked to improved cardiovascular health, as they can lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart-related conditions. Almonds offer about 12 grams of healthy fats per ounce, and walnuts are particularly rich in omega-3 fatty acids, essential for heart function. Nutritionists highlight the significance of including nuts in a balanced diet, noting their contribution to overall wellness.
A recent analysis underscores that walnuts, in particular, are among spermidine rich foods that may support cellular health and longevity. Furthermore, incorporating these foods into your daily meals enhances your intake of vital nutrients, such as fiber, protein, and various vitamins and minerals.
Real-world examples reveal the benefits of consuming nuts and seeds; individuals who regularly include these foods report increased energy levels and improved overall well-being. For aging populations, the antioxidant properties of nuts and seeds can help combat oxidative stress, a critical factor in the aging process. By adding a variety of nuts and seeds to your diet, you can enjoy their delightful flavors while reaping the numerous benefits they offer, making them a wise choice for anyone looking to enhance their well-being.
Fermented Foods: Boost Your Spermidine and Gut Health
Incorporating a variety of fermented products, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, can significantly enhance your intake of beneficial compounds and support a healthy gut microbiome. These foods are rich in probiotics, which not only aid digestion but also improve overall well-being by enhancing nutrient absorption and immune function. The presence of microorganisms during fermentation increases polyamine levels, which makes spermidine rich foods particularly beneficial for enhancing spermidine levels. For example, yogurt can serve as a breakfast staple or a snack, while kefir can be blended into smoothies for an added nutritional boost. Sauerkraut, with its tangy flavor, can complement salads or act as a side dish, making it easy to incorporate into meals.
Recent studies underscore the importance of spermidine rich foods, particularly fermented foods, for gut health, showing that regular consumption can lead to improved metabolic functions and higher polyamine levels. Research indicates that a well-rounded diet rich in these foods is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders. Furthermore, this compound has been shown to enhance cognitive function and reduce neurodegeneration in animal models, highlighting its role in anti-aging. By integrating fermented foods into your daily diet, you can harness their benefits for health and support your journey toward longevity and vitality.
Green Peas: A Hidden Gem for Spermidine Intake
Green peas are an outstanding source of a beneficial compound, making them a valuable addition to any diet. Their naturally sweet flavor and vibrant color enhance a variety of dishes, from soups and salads to stir-fries and side dishes. Including spermidine rich foods such as green peas in your meals not only enhances your spermidine consumption but also benefits your overall well-being.
Nutritionally, green peas are rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as fiber and protein, making them a powerhouse of nutrients. Nutritionists suggest incorporating green peas into meals for their wellness advantages, including enhanced cardiovascular well-being and assistance for digestive function. For example, Dr. Dainyal Siddiqui, an internal medicine expert, mentions, “Beneficial dietary sources consist of wheat germ, soybeans, aged cheese, mushrooms, green peas, broccoli, cauliflower, and fermented items like natto.”
You can toss them into a fresh salad, blend them into a creamy soup, or sauté them with garlic and olive oil as a delicious side. By integrating green peas into your daily meals, you can enjoy their health benefits while enhancing your culinary repertoire. Additionally, studies have shown that incorporating spermidine rich foods, such as green peas, may help reduce mortality rates, particularly from cardiovascular and cancer-related causes. To maximize your intake of spermidine rich foods, consider adding green peas to your breakfast smoothies or incorporating them into a vibrant vegetable stir-fry.
Conclusion
Incorporating spermidine-rich foods into daily nutrition not only enhances culinary experiences but also significantly contributes to overall health and longevity. By focusing on foods like aged cheese, mushrooms, legumes, and whole grains, individuals can tap into the powerful benefits of this naturally occurring polyamine, which has been linked to improved cellular regeneration and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Various spermidine-rich options have been highlighted, showcasing the versatility and nutritional value of these ingredients. From the savory richness of aged cheese to the nutrient density of legumes and the antioxidant properties of mushrooms, each food offers unique advantages that can support a health-conscious lifestyle. Furthermore, the inclusion of fermented foods and whole grains emphasizes the importance of a diverse diet in promoting well-being and longevity.
Embracing a diet rich in spermidine not only enhances flavor and satisfaction in meals but also serves as a proactive approach to health. As research continues to unveil the myriad benefits associated with spermidine, individuals are encouraged to explore and integrate these foods into their daily routines. By doing so, one can enjoy delicious meals while supporting a healthier, longer life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is spermidine and why is it important in nutrition?
Spermidine is a naturally occurring polyamine found in certain foods that is associated with health benefits such as enhanced cellular regeneration and increased longevity. It is linked to a decrease in overall mortality and cardiovascular disease risk.
What foods are rich in spermidine?
Foods rich in spermidine include aged cheese, mushrooms, and wheat germ.
How much spermidine is found in aged cheese?
Aged cheese, such as cheddar, contains roughly 200 mg/kg of spermidine, with a portion providing between 1.5 to 3 mg of spermidine per 100g.
What are the health benefits of consuming aged cheese?
Consuming aged cheese may lead to increased longevity and better cardiovascular health. Studies suggest that high intake of certain compounds in aged cheese is linked to a reduced risk of heart failure.
How can mushrooms contribute to a healthy diet?
Mushrooms, particularly shiitake and maitake, are low in calories and high in antioxidants and fiber, making them a nutrient-dense choice. They may also lower the risk of mild cognitive impairment in older adults when consumed regularly.
How can I incorporate mushrooms into my meals?
Mushrooms can be added to salads, stir-fries, pasta dishes, or used as a meat substitute in recipes, enhancing flavor while boosting nutritional value.
What types of recipes featuring spermidine-rich ingredients are available?
Recipes include savory mushroom risotto and cheese platters featuring aged cheese, allowing for enjoyable meals that promote healthy aging.






