Is NMN Safe? Understanding Risks and Benefits for Health
Overview
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is widely regarded as safe for health, particularly in its role in enhancing NAD+ levels and potentially alleviating age-related health concerns. Recent clinical studies support this, showing no significant negative outcomes from supplementation. While mild side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, may occur, the overall evidence indicates that NMN is well-tolerated, especially among older adults. This positions NMN as a promising candidate for anti-aging therapies when used responsibly.
Furthermore, understanding the implications of NMN supplementation can empower individuals to make informed health choices. With its ability to support cellular health and combat age-related decline, NMN presents an intriguing option for those seeking to enhance their well-being. As a result, exploring NMN further could lead to valuable insights into its benefits and applications.
Introduction
As the quest for longevity and enhanced health continues to capture public interest, nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a potential game-changer in the realm of anti-aging supplements. This intriguing compound, a precursor to the vital coenzyme NAD+, promises to restore cellular function and combat age-related decline. However, with rising enthusiasm comes the pressing question: is NMN truly safe for human consumption?
By delving into the latest clinical studies and safety evaluations, this article will explore the benefits and risks associated with NMN supplementation, providing insights for those considering it as part of their health regimen. What should individuals know before embarking on this journey towards improved metabolic health and vitality?
Furthermore, understanding both the advantages and potential concerns surrounding NMN is crucial for making informed decisions about its use. As a result, this exploration aims to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the evolving landscape of health supplements.
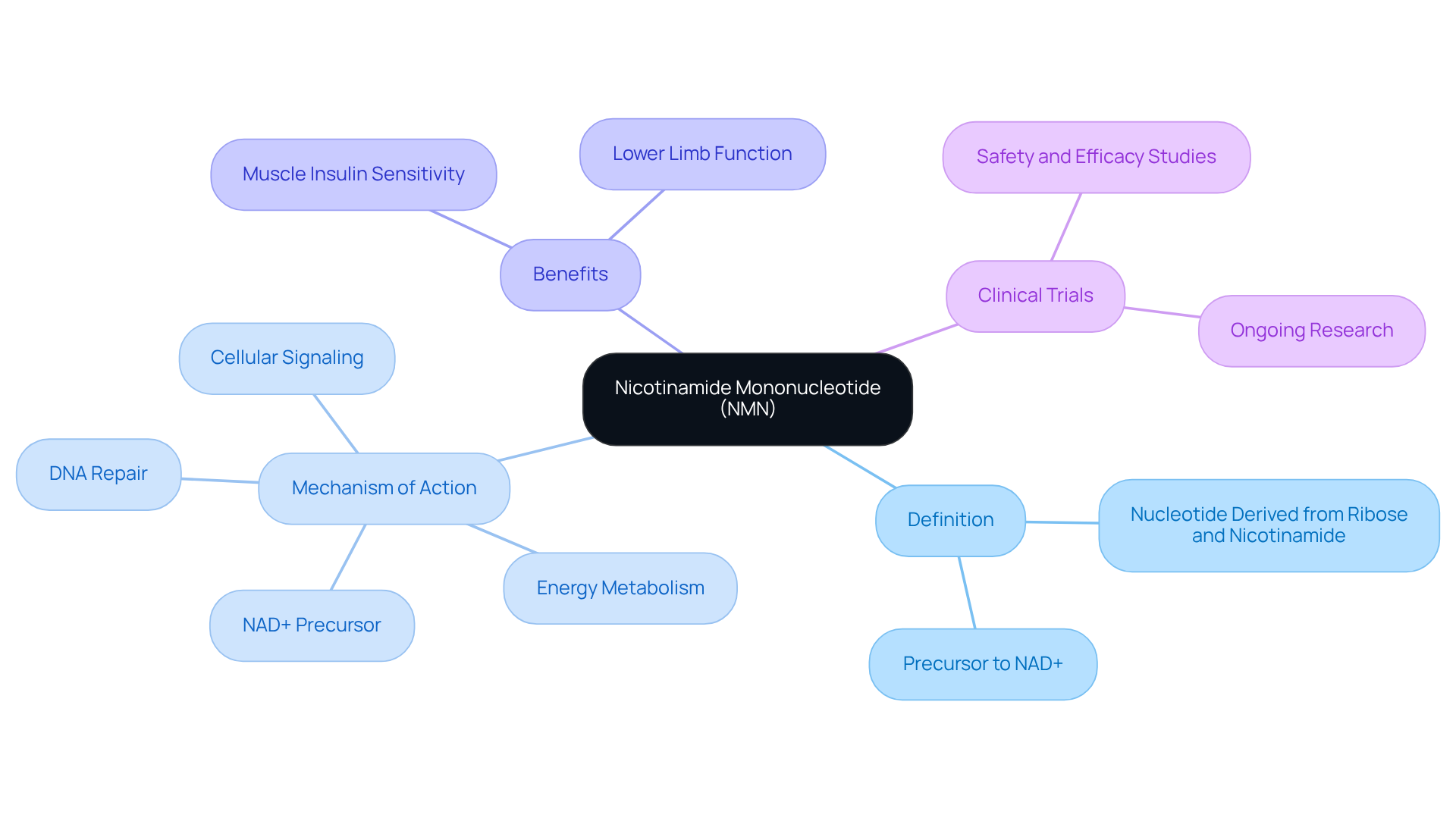
Understand NMN: Definition and Mechanism of Action
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide, serving as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). This essential coenzyme is crucial for numerous biological processes, including:
- Energy metabolism
- DNA repair
- Cellular signaling
As individuals age, NAD+ levels naturally decline, which can lead to various age-related health issues. Therefore, the inquiry into whether NMN is safe focuses on its potential to restore these NAD+ levels, potentially mitigating the effects of aging.
How does this work? NMN is absorbed into cells, where it is converted into NAD+, enhancing cellular functions and supporting overall well-being. Recent studies raise the question of whether NMN is safe, as they indicate that NMN supplementation can significantly boost NAD+ levels in the body. Clinical trials have shown improvements in:
- Muscle insulin sensitivity
- Lower limb function
This highlights NMN’s potential as a therapeutic strategy for addressing age-related decline and enhancing metabolic health.
In conclusion, considering NMN as part of a health regimen could be a proactive approach to combat aging and improve metabolic function. For those interested in exploring further, research continues to uncover the full benefits of NMN supplementation.
Examine Clinical Evidence: Safety Studies and Findings
Recent clinical studies indicate that the question of whether NMN is safe for human consumption has been positively addressed. A crucial study released in 2022 demonstrated that daily doses of up to 900 mg did not lead to significant negative outcomes, which supports the conclusion that NMN is safe. Furthermore, a trial involving older adults confirmed that NMN effectively elevated NAD+ levels, leading to the question of whether NMN is safe without inducing toxicity. This aligns with findings from Keio University, which investigated whether NMN is safe and reported no safety concerns. Notably, a significant dose-dependent increase in NAD concentration was observed following NMN intake, with clinical efficacy peaking at a dose of 600 mg daily. Mild gastrointestinal symptoms were the only negative outcomes reported, underscoring the importance of monitoring individual responses. Collectively, these studies suggest that NMN is well-tolerated, which leads to the inquiry of whether NMN is safe as a promising candidate for anti-aging therapies.
Moreover, current studies are examining the ideal dosages and long-term impacts of NMN, while also addressing the question of whether NMN is safe, with specialist viewpoints supporting individualized intake plans to enhance advantages. In the broader context of anti-aging research, rapamycin has emerged as a significant compound, functioning as an inhibitor of the mTOR pathway, which regulates cellular growth and aging. Integrating insights from both NMN and rapamycin could provide a more comprehensive understanding of dietary supplements in the quest for longevity.
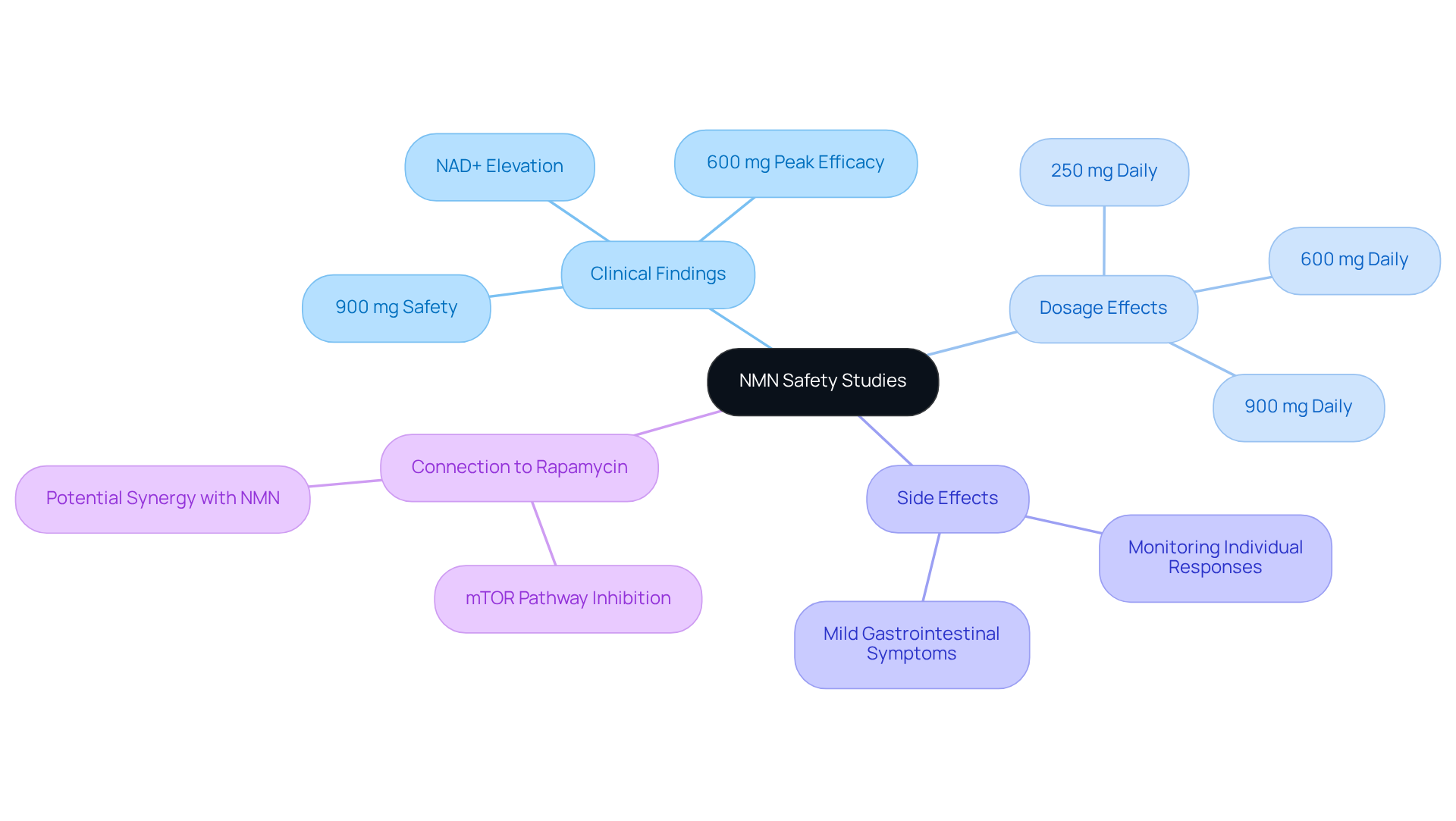
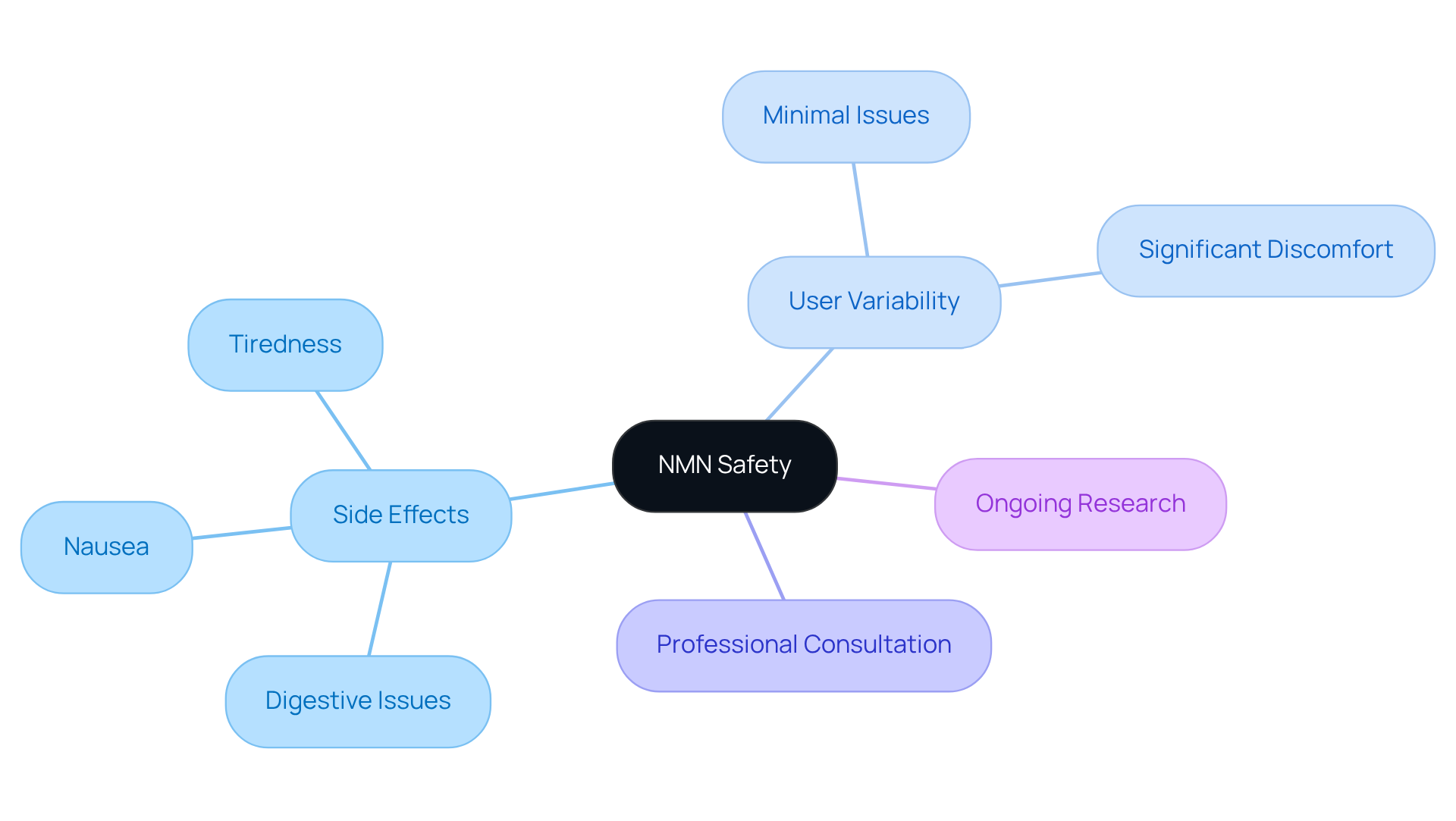
Assess Risks: Side Effects and Safety Concerns
Many people wonder, is NMN safe for most users? However, some individuals have reported mild reactions, particularly digestive issues, nausea, and tiredness, especially during the initial stages of use. Studies indicate that these effects are usually temporary, often diminishing as the body adapts to the supplement. A 2023 review highlighted the question of whether NMN is safe, noting that NMN-boosting compounds are well-accepted among healthy middle-aged and older adults. Yet, individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those on medications should consult healthcare professionals before starting NMN use.
Real-world accounts suggest that the occurrence of digestive discomfort varies among users. Some experience minimal issues, while others report more significant discomfort. Ongoing research is essential for monitoring the long-term effects of NMN, ensuring that any potential risks are identified and effectively managed. As a result, staying informed and seeking professional guidance can help maximize the benefits of NMN while minimizing any adverse reactions.
Consider Population-Specific Safety: Who Can Benefit from NMN?
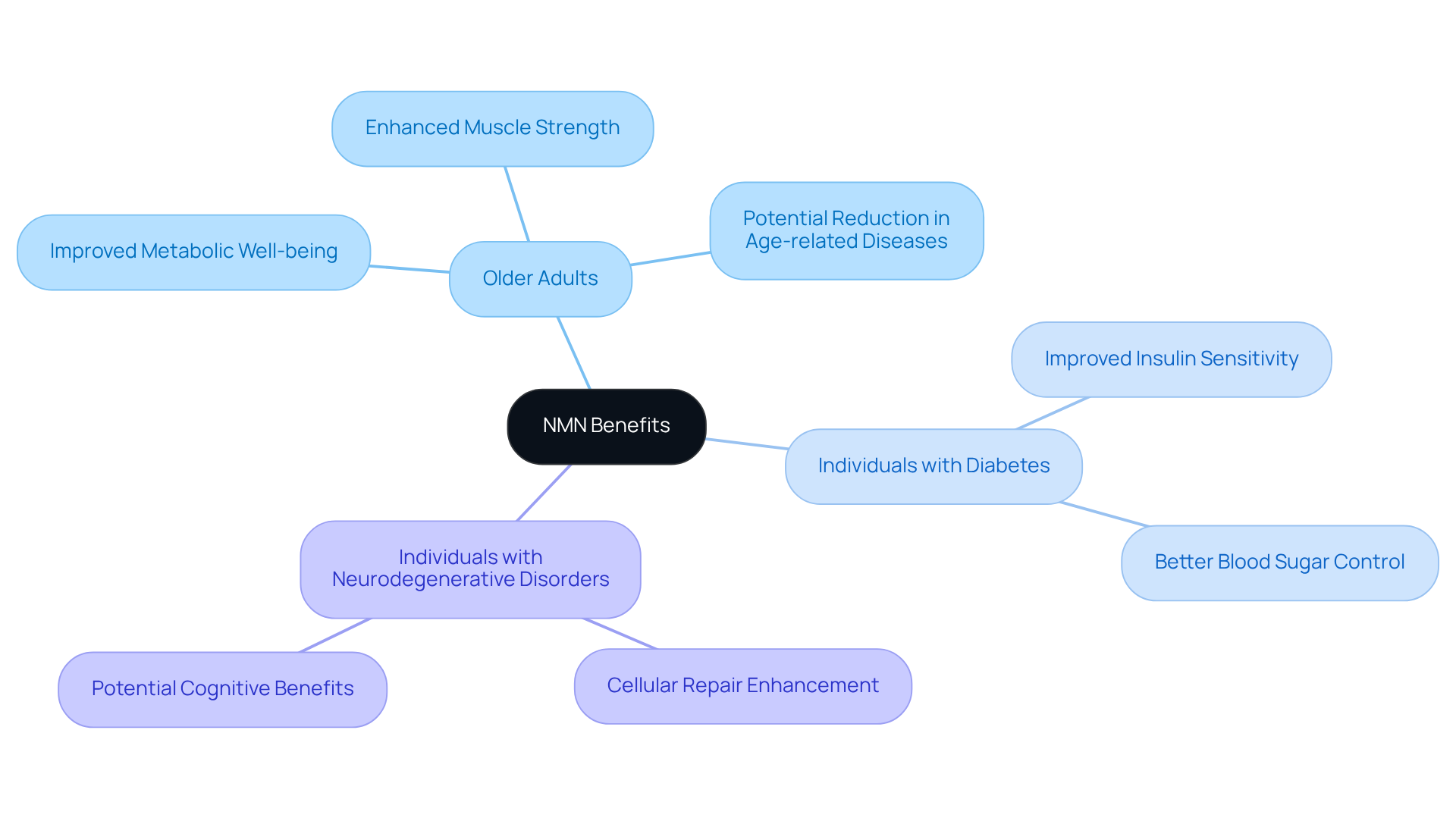
NMN intake holds particular promise for older adults, who often experience a natural decline in NAD+ levels. Research shows that older populations can use NMN to enhance metabolic well-being, improve physical performance, and potentially reduce the risk of age-related diseases, leading to the question of whether NMN is safe. For instance, a study involving healthy older men demonstrated that NMN supplementation improved muscle strength and performance without significant adverse effects.
Furthermore, individuals with specific medical conditions, such as diabetes or neurodegenerative disorders, may gain advantages from NMN due to its role in cellular repair and energy metabolism. In one study, NMN was shown to improve insulin sensitivity by 25% in postmenopausal women with prediabetes, indicating its potential in managing metabolic wellness.
However, it is essential for these individuals to consult healthcare professionals to customize supplementation according to their unique health profiles, ensuring that is NMN safe and effective. By doing so, they can maximize the benefits of NMN while minimizing any risks associated with its use.
Conclusion
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) stands out as a promising supplement in the pursuit of better health and longevity, particularly due to its role as a precursor to the essential coenzyme NAD+. As we age, NAD+ levels naturally decline, and NMN supplementation presents a potential avenue for restoring these levels, thereby enhancing energy metabolism and cellular functions. Investigating NMN’s safety is crucial, especially as research indicates its ability to significantly elevate NAD+ levels without substantial adverse effects.
This article explores various studies affirming NMN’s safety profile, highlighting clinical trials where daily doses of up to 900 mg resulted in no serious negative outcomes. While mild gastrointestinal issues were reported, these effects were generally transient. The potential benefits for older adults, who may face age-related health challenges, are emphasized, with evidence suggesting improvements in metabolic health and physical performance. Moreover, individuals with specific health conditions could also find NMN advantageous, provided they seek professional guidance to tailor supplementation to their needs.
Given the growing body of evidence supporting NMN’s safety and efficacy, it is essential to approach supplementation thoughtfully. Staying informed about ongoing research and consulting healthcare professionals can empower individuals to make educated decisions regarding NMN use. Embracing NMN as part of a holistic health strategy may not only mitigate the effects of aging but also enhance overall well-being, positioning it as a valuable ally in the pursuit of a healthier, more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is NMN and what role does it play in the body?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide, serving as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which is crucial for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular signaling.
Why is NMN important as we age?
As individuals age, NAD+ levels naturally decline, which can lead to various age-related health issues. NMN has the potential to restore NAD+ levels, potentially mitigating the effects of aging.
How does NMN work in the body?
NMN is absorbed into cells and converted into NAD+, which enhances cellular functions and supports overall well-being.
What benefits have been observed from NMN supplementation?
Clinical trials have shown that NMN supplementation can significantly boost NAD+ levels and improve muscle insulin sensitivity and lower limb function.
Can NMN be considered safe for supplementation?
Recent studies indicate that NMN supplementation can boost NAD+ levels significantly, suggesting it may be safe, but ongoing research is needed to fully understand its benefits and safety.
How might NMN supplementation impact metabolic health?
NMN supplementation has the potential to enhance metabolic health by restoring NAD+ levels, which may help address age-related decline in various biological functions.