Do Vitamin Infusions Work? Comparing Benefits and Risks to Supplements
Overview
Vitamin infusions offer immediate benefits and higher bioavailability compared to traditional supplements. This makes them particularly advantageous for individuals facing specific deficiencies or those who require rapid nutrient replenishment. However, it is essential to exercise caution. The article highlights that vitamin infusions carry inherent risks and have limited scientific support for their purported benefits. Therefore, a thorough consultation with healthcare professionals is crucial before deciding between these options.
Introduction
In the quest for optimal health, individuals increasingly face the choice between vitamin infusions and traditional supplements. Vitamin infusions promise rapid nutrient delivery directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. In contrast, traditional supplements rely on a more conventional approach, which may be influenced by various factors such as diet and digestive health.
This article delves into the mechanisms, benefits, and risks associated with both methods, shedding light on their effectiveness in enhancing nutrient intake. With a growing interest in alternative therapies, understanding the nuances of these options becomes essential for making informed health decisions.
Understanding Vitamin Infusions and Traditional Supplements
Nutrient solutions administered through veins deliver concentrated amounts of essential compounds and minerals directly into the bloodstream, promoting instant absorption and utilization by the body. This method effectively bypasses the digestive system, which can often impede nutrient uptake. In contrast, traditional supplements—available in pills, capsules, or powders—must navigate the digestive tract, where absorption can be influenced by factors such as food intake and gastrointestinal health.
Research indicates that nutrient infusions can achieve significantly higher bioavailability rates compared to oral supplements. For instance, while oral B12 may have a bioavailability of around 50%, intravenous administration can result in nearly 100% absorption. This difference is crucial for individuals with specific deficiencies or those seeking rapid nutrient replenishment. In practical terms, individuals lacking B12 may request a B12 supplement during hydration treatment to meet their needs effectively.
A case study on the cardiovascular health advantages of IV administration illustrates how certain amino acids and minerals in IV infusions can assist in blood pressure regulation, promoting better cardiovascular health through enhanced nutrient delivery and relaxation of blood vessels. This analysis reinforces the benefits of IV treatment, demonstrating its potential efficacy compared to conventional alternatives, while also addressing the question of do vitamin infusions work in relation to traditional methods. As Benjamin Franklin wisely noted, ‘The best doctor gives the least medicine,’ suggesting that a thoughtful approach to supplementation is essential. Specialists, including Dr. Bauer, recommend discussing possible risks, advantages, and options with a healthcare team prior to proceeding with IV therapy, emphasizing the significance of expert advice in making health choices, particularly to understand do vitamin infusions work in comparison to conventional dietary aids. Therefore, it is vital for individuals to consider their specific health needs and consult with professionals when choosing between these options.
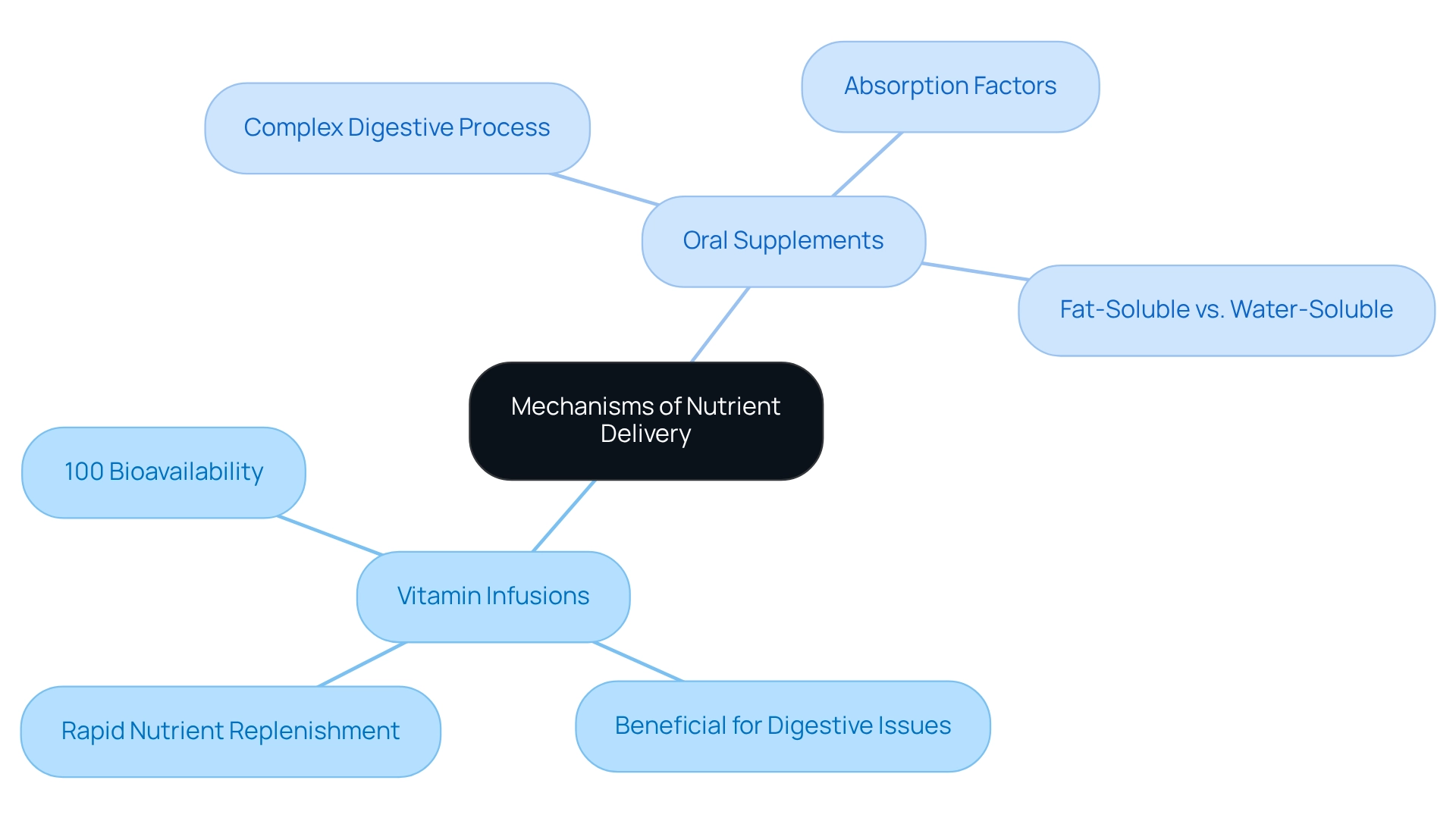
Mechanisms of Nutrient Delivery: Infusions vs. Supplements
To understand how effective they are, many people ask, do vitamin infusions work in delivering nutrients directly into the bloodstream, ensuring nearly 100% bioavailability? This method is particularly beneficial for individuals with digestive issues or for those who want to know if do vitamin infusions work for rapid nutrient replenishment. In contrast, conventional products undergo a complex digestive process, where only a fraction of the nutrients may be absorbed. Factors such as digestive health, the presence of other foods, and the form of the product all play a role in this absorption.
For instance, fat-soluble vitamins require dietary fats for optimal absorption, while water-soluble vitamins may be lost through urine if taken in excess. Thus, the efficiency of nutrient delivery raises the question of how well do vitamin infusions work compared to oral supplements. Furthermore, understanding these differences can empower individuals to make informed choices about their nutritional needs.
Are you considering the best way to enhance your nutrient intake? Exploring intravenous options might be a beneficial step for your health journey.
Evaluating Health Benefits: Infusions Compared to Supplements
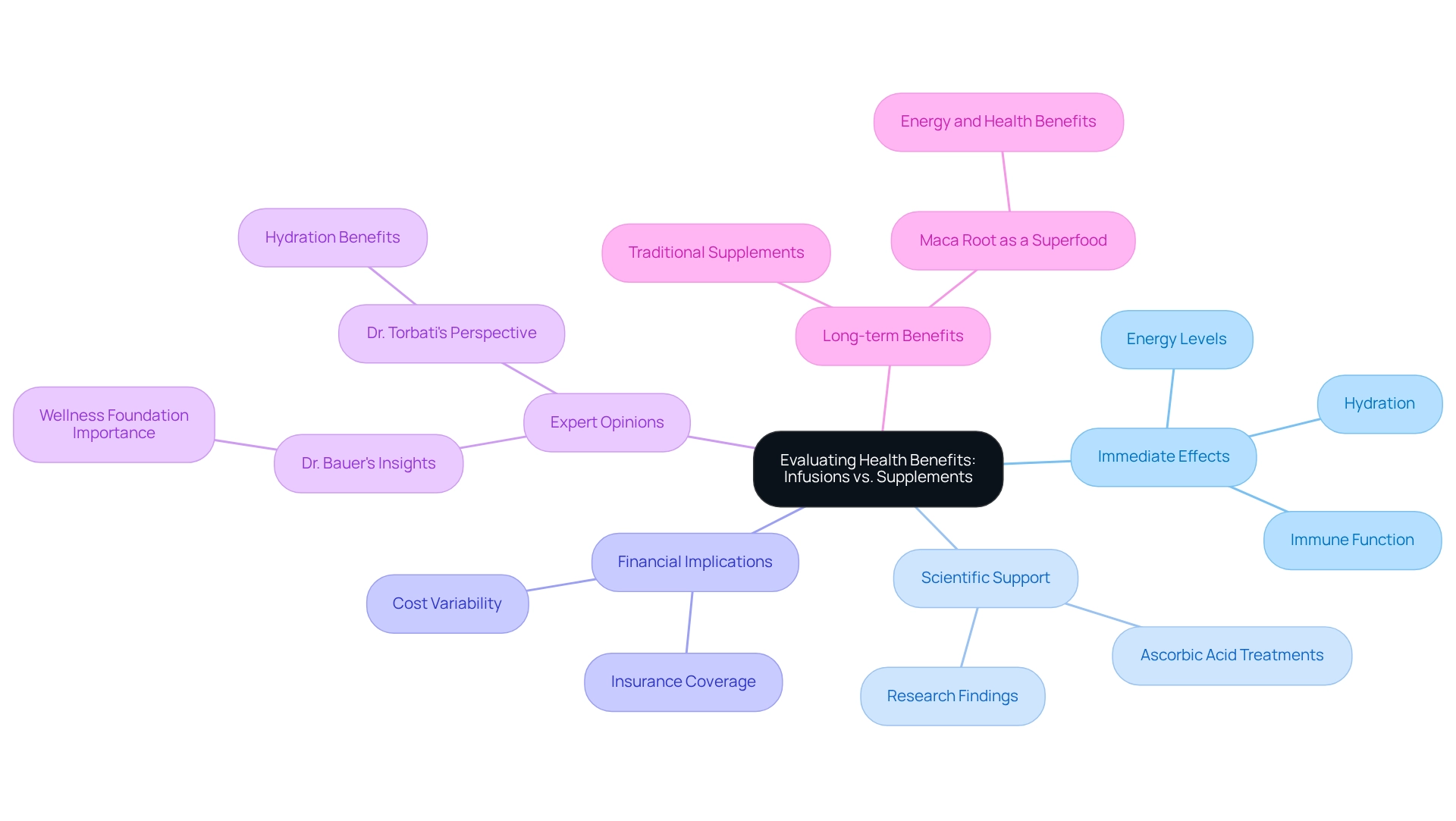
Many people wonder, do vitamin infusions work for their immediate effects, such as increased energy levels, enhanced immune function, and improved hydration? Infusions abundant in vitamin C, for example, are frequently employed to enhance immunity and reduce fatigue. However, the scientific support for these claims about whether do vitamin infusions work is often limited, especially for individuals who already maintain a balanced diet. In contrast, traditional products, while usually slower to produce noticeable results, can provide lasting advantages over time, particularly for individuals with specific deficiencies. For instance, vitamin D supplements are essential for individuals with restricted sun exposure, as they serve an important function in enhancing bone health and aiding immune function.
Recent research suggests that the question of whether do vitamin infusions work can lead to considerable enhancements in energy levels and immune response. One study emphasized that participants receiving ascorbic acid treatments reported a significant decrease in fatigue levels, which leads to the inquiry of do vitamin infusions work in addressing energy deficits. Furthermore, the effectiveness of ascorbic acid treatments, along with the question of do vitamin infusions work, has been backed by scientific studies, indicating that they can improve immune function, especially in individuals facing acute stress or illness.
However, it’s important to consider the financial implications of selecting nutrient therapies over conventional supplements. IV therapy costs can vary significantly based on location and mixture, and most insurance companies do not cover it. This raises questions about the accessibility and practicality of such treatments for the average consumer.
Dr. Bauer, Research Chair for Mayo Clinic Integrative Medicine and Health, highlights the significance of establishing a solid wellness foundation before contemplating vitamin treatments. He states, “On the one hand, it’s great to see so many people taking an active interest in their health. But when it comes to improving your health, I always encourage starting by building a very strong wellness foundation.”
Dr. Torbati notes that the primary benefit of IV treatments is hydration, which could also be achieved through sports drinks. This viewpoint clarifies that while treatments may provide a quick boost, traditional supplements can offer a more gradual and sustained approach to health improvement. Ultimately, the decision between the two should be informed by personal health needs and the advice of healthcare professionals. Additionally, the rising popularity of superfoods, such as maca root, illustrates the broader context of health-conscious individuals seeking various methods to enhance their well-being.
Safety and Risks: Analyzing Infusions and Supplements
Vitamin drips are increasingly recognized for their ability to deliver nutrients rapidly. However, they also carry considerable risks. Complications can arise, including infections, allergic reactions, and electrolyte imbalances, particularly when infusions are not administered correctly. The FDA has raised concerns about the safety of unregulated IV nutrient therapy, emphasizing the need for professional oversight in these treatments.
In contrast, conventional aids are generally regarded as safe, yet they are not without their own risks. For instance, excessive consumption of nutrient A can lead to toxicity, and some additional products may interact negatively with medications. Furthermore, IV nutrient treatments typically range from $150 to $200 per session, which is a significant consideration for individuals contemplating this option.
Given these factors, it is essential for individuals to consult healthcare professionals before starting any new nutrient regimen, whether through infusions or traditional supplements. As interest in whether do vitamin infusions work continues to grow, ongoing studies are anticipated to shed light on its possible advantages and dangers. Present studies are limited, as highlighted in the case analysis titled ‘Future Research Directions for IV Nutrient Administration,’ which stresses the necessity for further research to determine if do vitamin infusions work for chronic illnesses. Bauer observes that ‘regarding the other assertions about IV treatment — including enhanced immunity, stress relief, and effective management of various illnesses — there are very few studies that have scientifically examined these claims, which raises the important question of do vitamin infusions work, as many studies that do exist suffer from poor design.’ This skepticism within the medical community underscores the importance of viewing IV vitamin therapy as a complementary approach rather than a primary treatment.
Conclusion
The comparison between vitamin infusions and traditional supplements underscores significant differences in nutrient delivery and absorption.
Vitamin infusions offer nearly 100% bioavailability by bypassing the digestive system, making them especially beneficial for individuals with specific deficiencies or those needing immediate nutrient replenishment. Conversely, traditional supplements must navigate complex digestive processes, resulting in variable absorption rates influenced by dietary factors and individual health.
While vitamin infusions are often linked to rapid benefits like increased energy and improved immune response, these claims warrant careful examination. Studies indicate potential advantages, yet scientific support is frequently limited, particularly for well-nourished individuals. Traditional supplements, though slower to yield results, provide sustained health benefits over time for those with specific nutrient deficiencies. Additionally, the financial implications of vitamin infusions deserve attention, as their costs can be substantial and are generally not covered by insurance.
Safety remains a critical consideration when selecting between these options. Vitamin infusions carry risks such as infections and allergic reactions, highlighting the importance of professional oversight. Traditional supplements, while typically safe, can also pose risks if consumed in excess or without appropriate guidance. Ultimately, the choice between vitamin infusions and traditional supplements should be guided by individual health needs and professional advice.
In summary, both vitamin infusions and traditional supplements present unique benefits and limitations. Grasping the nuances of each method is vital for making informed health decisions. As interest in alternative therapies continues to grow, individuals are encouraged to consult healthcare professionals to identify the most suitable approach for enhancing their nutrient intake and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are nutrient solutions administered through veins?
Nutrient solutions administered through veins deliver concentrated amounts of essential compounds and minerals directly into the bloodstream, promoting instant absorption and utilization by the body.
How do intravenous nutrient solutions differ from traditional supplements?
Intravenous nutrient solutions bypass the digestive system, allowing for direct absorption into the bloodstream, while traditional supplements in pills, capsules, or powders must navigate the digestive tract, where absorption can be affected by food intake and gastrointestinal health.
What is the bioavailability difference between oral supplements and intravenous administration?
Research indicates that intravenous administration can achieve nearly 100% absorption, while oral supplements, such as B12, have a bioavailability of around 50%.
Who might benefit from intravenous nutrient infusions?
Individuals with specific deficiencies or those seeking rapid nutrient replenishment may benefit from intravenous nutrient infusions, such as those lacking B12 who may request a supplement during hydration treatment.
How can IV administration impact cardiovascular health?
Certain amino acids and minerals in IV infusions can assist in blood pressure regulation and promote better cardiovascular health through enhanced nutrient delivery and relaxation of blood vessels.
What should individuals consider before proceeding with IV therapy?
Individuals should discuss possible risks, advantages, and options with a healthcare team prior to proceeding with IV therapy, emphasizing the importance of expert advice in making health choices.
What is the significance of consulting professionals regarding nutrient solutions?
It is vital for individuals to consider their specific health needs and consult with professionals when choosing between intravenous nutrient infusions and traditional dietary aids.