Understanding Senolytic Drugs: Definition, Benefits, and Mechanisms
Overview
Senolytic drugs represent a new frontier in therapeutics, specifically designed to selectively eliminate senescent cells. These cells, which accumulate with age, significantly contribute to age-related diseases and inflammation. The ultimate goal of these drugs is to enhance longevity and improve overall health.
Furthermore, the mechanisms of action for senolytic drugs are quite compelling. They work by inducing apoptosis in dysfunctional cells, thereby improving immune response. Evidence from various studies indicates their potential in enhancing both physical and cognitive functions in aging populations. This presents a promising avenue for addressing the challenges of aging and promoting a healthier, more vibrant life as we age.
Introduction
As the quest for longevity and healthier aging intensifies, a new class of therapeutics known as senolytic drugs emerges at the forefront of medical research. These innovative agents are designed to selectively target and eliminate senescent cells—those dysfunctional remnants of cellular aging that accumulate in tissues over time, contributing to a host of age-related diseases and chronic inflammation. By harnessing the potential of senolytic drugs, researchers aim to enhance physical and cognitive functions, extend lifespan, and improve the overall quality of life for aging populations.
Furthermore, with promising findings from recent studies and ongoing clinical trials, the journey of senolytic drug development is both exciting and complex. This raises important questions about their efficacy, safety, and the future of aging therapies. As we delve deeper into this field, it becomes essential to explore the implications of these therapies and their potential impact on our health as we age.
Defining Senolytic Drugs: What They Are and Their Purpose
Senolytic drugs represent a specialized category of therapeutics designed to selectively eliminate senescent cells—those that have lost their ability to divide and function effectively. As individuals age, these malfunctioning cells accumulate in various tissues, contributing to age-related illnesses and chronic inflammation. By targeting and removing these aging cells, senolytic drugs aim to restore tissue function and promote healthier aging. The primary objective of senolytic drugs is to enhance lifespan and overall well-being by addressing the detrimental effects associated with cellular aging. Recent studies have validated the age-related cell-clearing capabilities of compounds such as D+Q, fisetin, and navitoclax, underscoring their potential for therapeutic applications. However, translating these findings from animal models to human contexts poses significant challenges, necessitating rigorous clinical trials to confirm safety and efficacy.
Furthermore, structure-activity relationship (SAR) investigations may enhance the therapeutic window of these agents. Yet, without robust evidence from double-blind placebo trials, the clinical application of such therapies remains uncertain, highlighting the importance of caution in their prescription. In summary, senolytic drugs show promise as a treatment strategy for addressing various age-related conditions by effectively removing aging cells.
The Evolution of Senolytic Drugs: Historical Context and Development
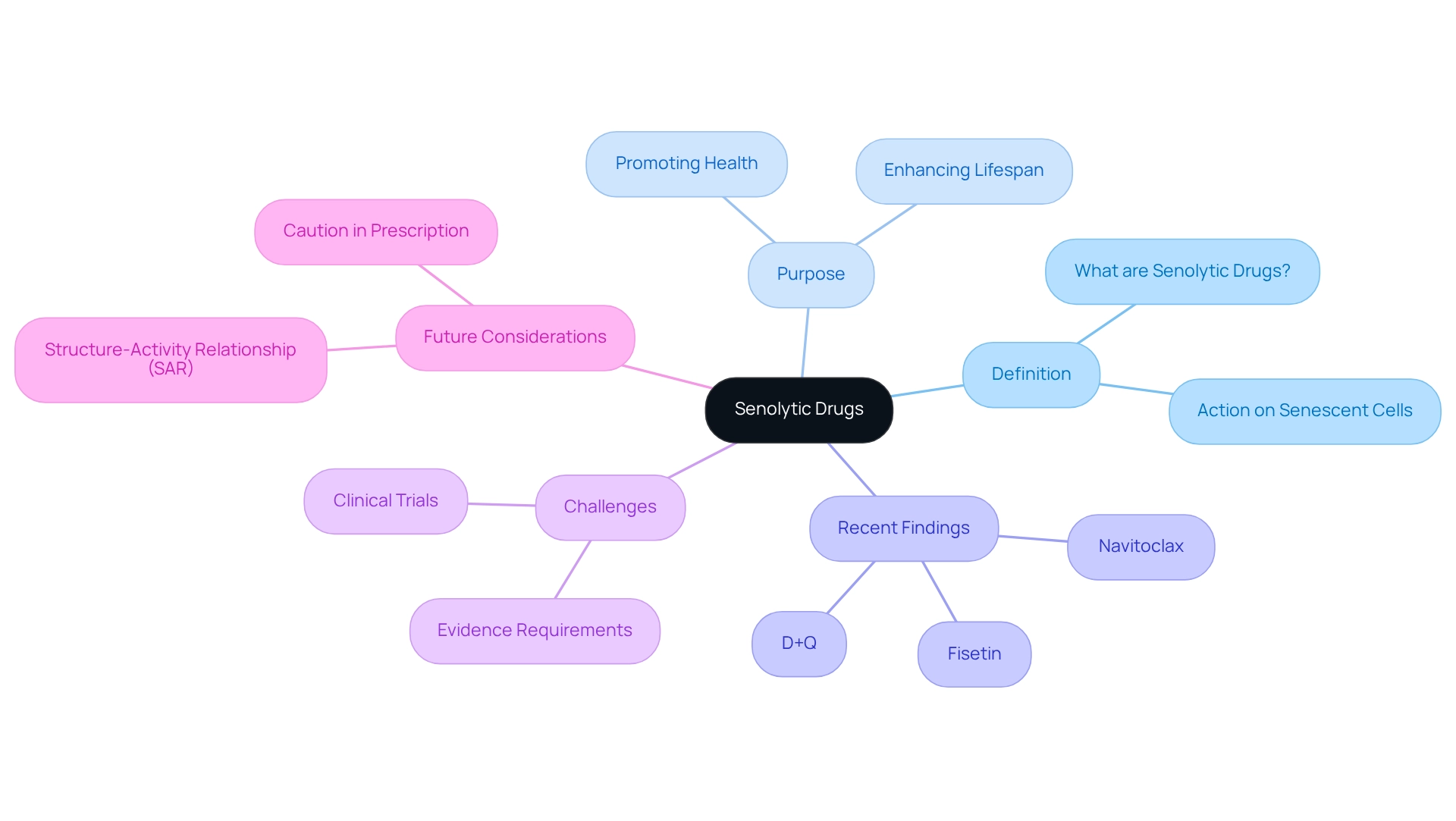
The concept of senolytic drugs originates from research into cellular senescence, which was first identified in the 1960s. Over the decades, researchers have delved into the role of senescent structures in aging and age-related diseases. The term ‘senolytic drugs’ emerged in 2015, marking a pivotal moment when scientists recognized specific compounds that can selectively target and eliminate these cells.
Early investigations centered on natural compounds like quercetin and dasatinib, which demonstrated potential in preclinical models. Notably, Helga, a self-experimenter, observed that the decrease in senescent cells might be attributed to quercetin alone, possibly through the reduction of PGE2.
As research progressed, the development of more refined and potent agents, specifically senolytic drugs, gained traction, leading to clinical trials to assess their effectiveness in humans. The ubiquitous nature of cellular aging across eukaryotes underscores the significance of these drugs, suggesting that the mechanisms of aging have evolved for various purposes throughout history.
However, persistent challenges in senolytic drugs research underscore the need for a cohesive theory of senescence mechanisms to improve the design and efficacy of these therapies. The interplay between scientific advancements and public perception will be crucial for the future of therapies aimed at the elderly.
Mechanisms of Action: How Senolytic Drugs Combat Aging
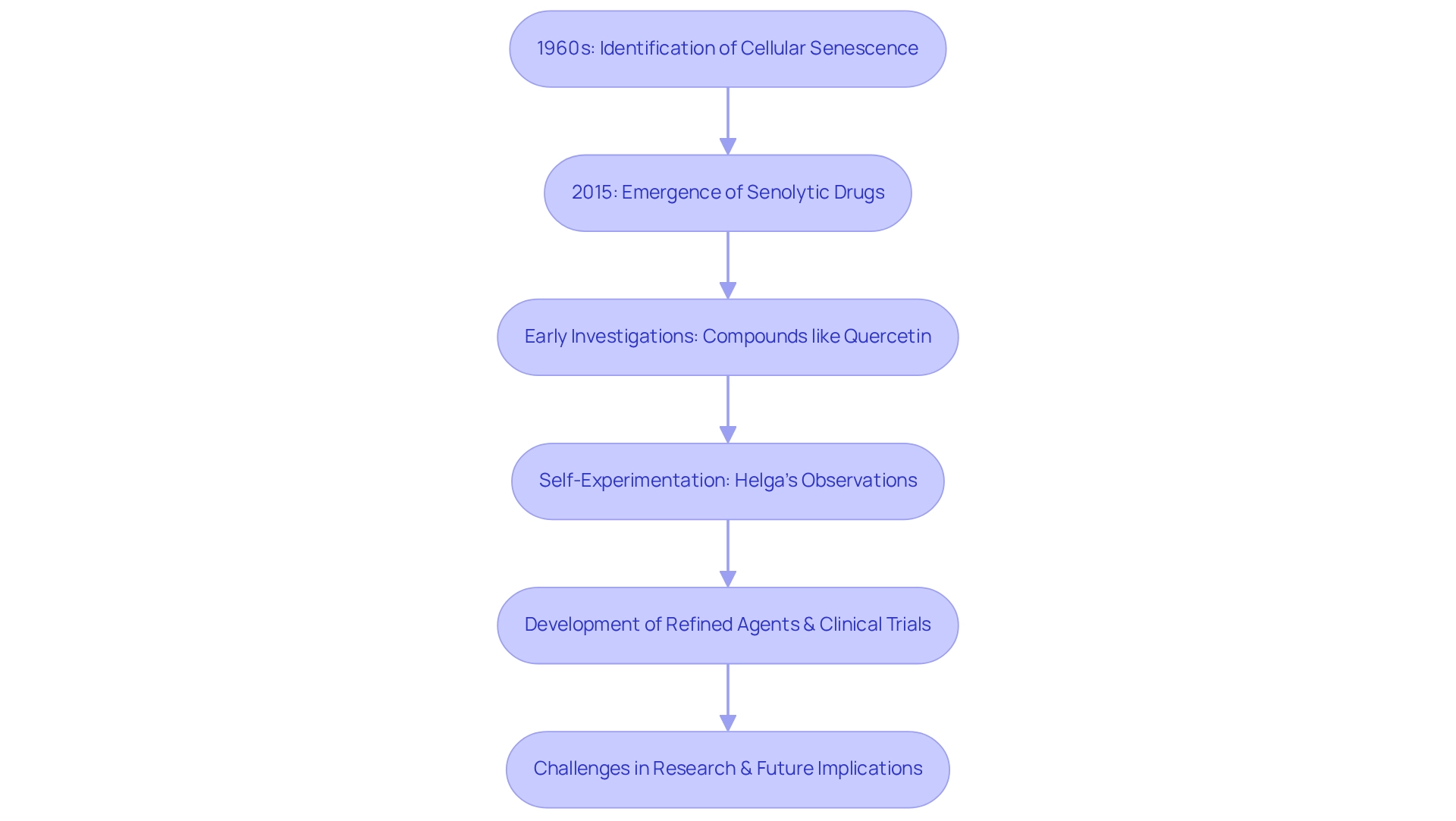
Senolytic drugs use various methods to effectively eliminate senescent entities, which are known for their contribution to aging and age-related illnesses. A primary mechanism involves the induction of apoptosis, or programmed death, of these dysfunctional entities. By disrupting the survival mechanisms that aging structures depend on, agents that promote selective elimination facilitate their targeted demise. Furthermore, these medications can enhance the immune system’s capacity to identify and remove senescent entities, thereby improving overall cellular health.
Reducing the burden of senescent entities is crucial, as it can significantly diminish chronic inflammation—a common concern among older adults. This reduction not only fosters tissue regeneration but also leads to better health outcomes. For example, recent trials have investigated the use of fisetin, a senolytic drug, in preventing disease progression in elderly patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, underscoring its potential role in managing viral infections in vulnerable populations. Research suggests that senolytic drugs can lower morbidity and mortality associated with infections in individuals burdened with high levels of senescent cells.
The neuroprotective benefits of Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) further illustrate the connection between brain health and therapies for older adults. LDN has demonstrated promise in managing neurodegenerative diseases by reducing microglial activation, a prevalent feature in such conditions, and has been effective in treating multiple sclerosis and chronic pain disorders like fibromyalgia. As our understanding of these drugs advances, their applications in clinical settings are expected to broaden. However, their use should remain within the confines of carefully monitored, placebo-controlled trials to ensure safety and efficacy.
The ongoing exploration of senolytic drugs emphasizes their potential in combating the aging process and enhancing longevity. Additionally, personal experiences, such as consultations with specialists like Dr. Alan Green, who advocates for therapies like Rapamycin for anti-aging, highlight the evolving landscape of treatments aimed at improving health outcomes in older populations.
Potential Benefits of Senolytic Drugs: Enhancing Longevity and Health
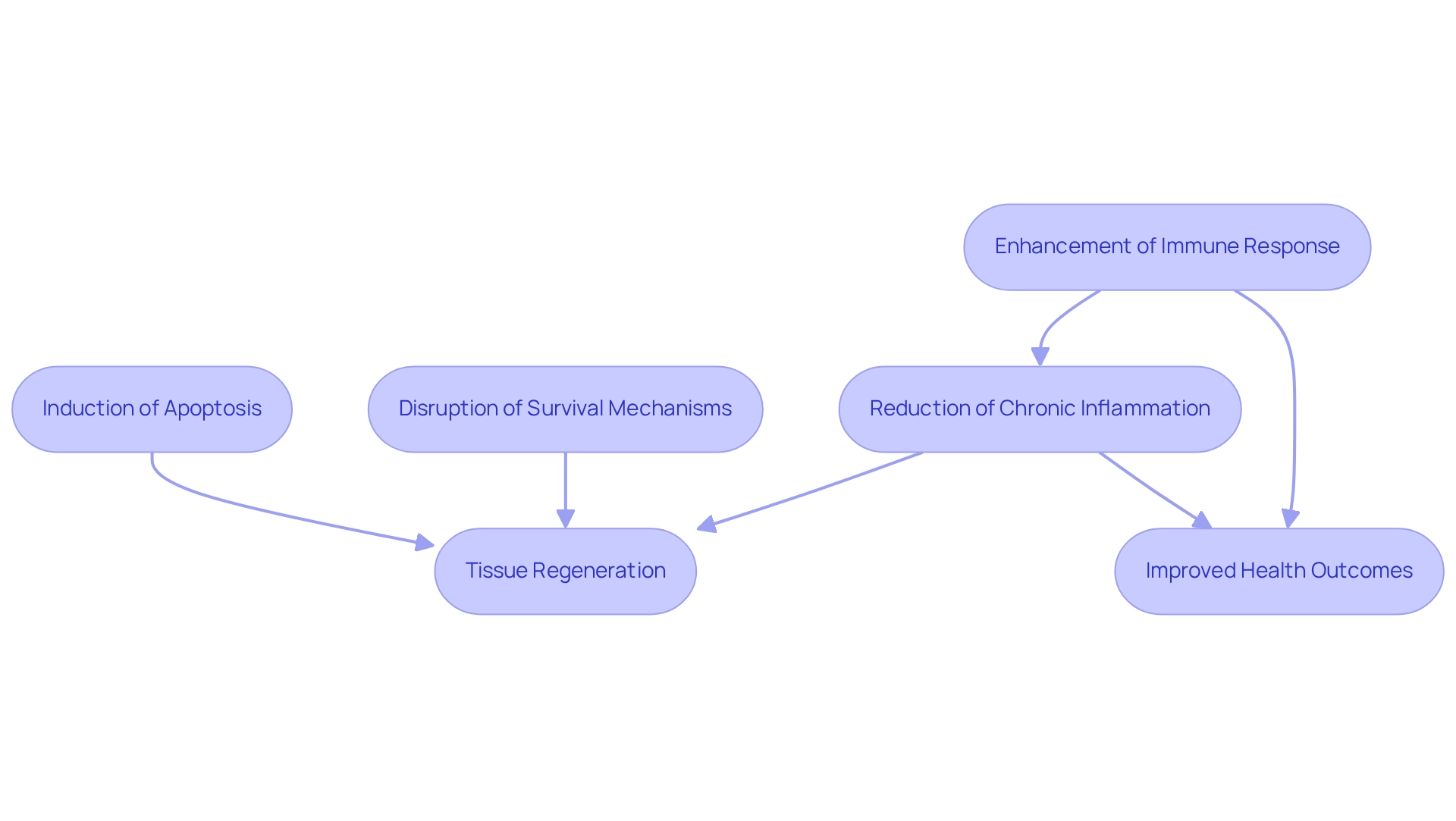
Senolytic drugs offer significant potential advantages, particularly in addressing aging and age-related illnesses. Research indicates that senolytic drugs can significantly enhance physical function and cognitive abilities, while also reducing the prevalence of conditions such as cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis. Furthermore, studies utilizing animal models have demonstrated that these therapies can prolong lifespan and improve healthspan—the duration of life spent in good health.
For example, a study investigating inflammation caused by senescent cells revealed that targeting these cells could diminish inflammation and enhance physical function. This underscores the importance of senolytic drugs as therapies aimed at eliminating these cells to improve health outcomes for older adults.
As clinical trials advance, there is growing optimism that senolytic drugs will emerge as a viable therapeutic approach to promote longevity and elevate the quality of life for individuals in their senior years.
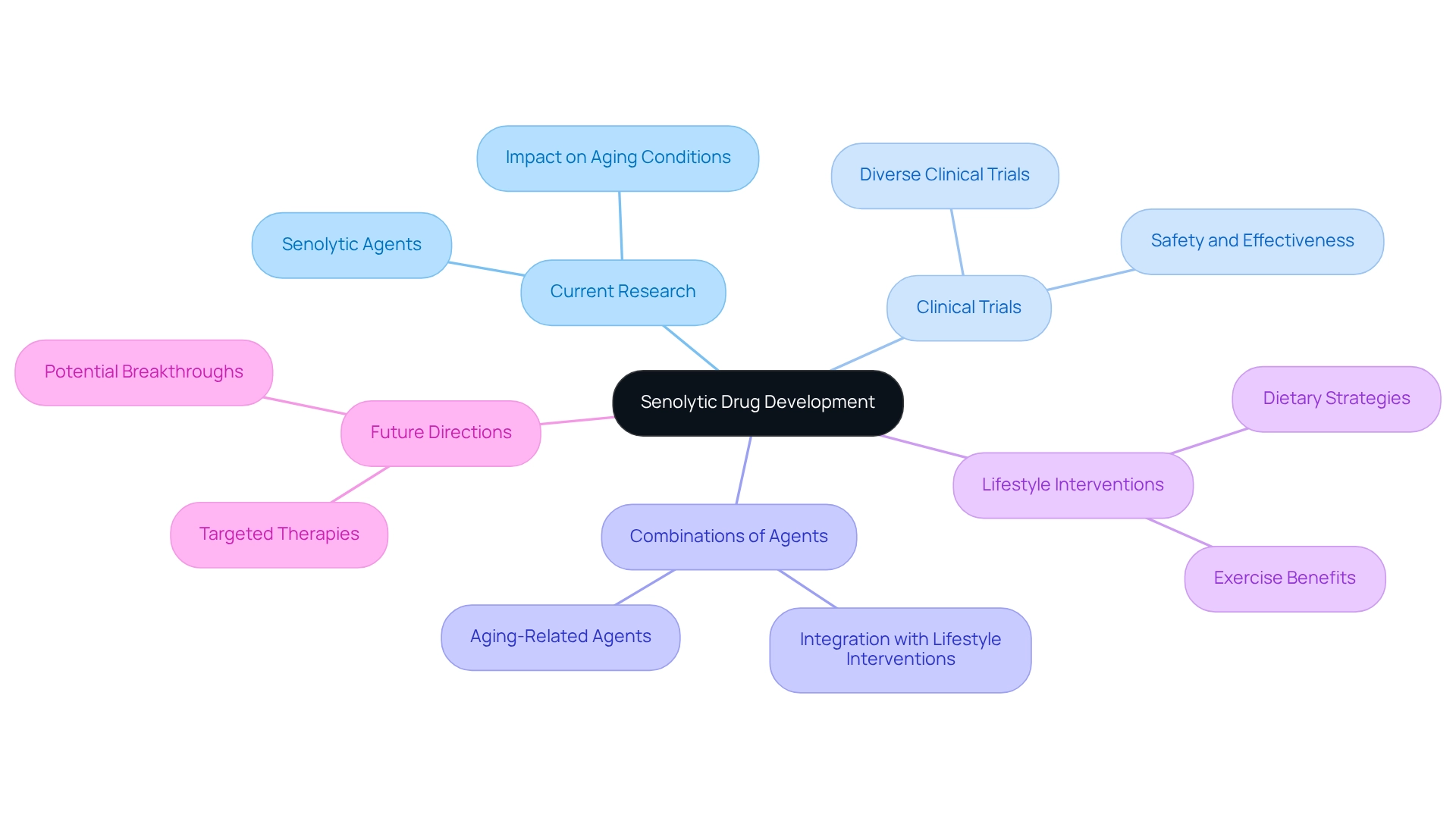
Current Research and Future Directions in Senolytic Drug Development
Recent studies on age-related therapies are advancing rapidly, with numerous clinical trials underway to evaluate their safety and effectiveness in humans. Researchers are exploring various combinations of aging-related agents and their impacts on different age-related conditions. Future directions may involve the development of more targeted therapies that minimize side effects while maximizing benefits. Furthermore, the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions, such as diet and exercise, could be enhanced by the integration of senolytic drugs.
Quality nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting the body’s natural defenses against aging. As James L. Kirkland from the Mayo Clinic noted, D + Q significantly reduced (p = 0.001) abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue p16 cells, underscoring the potential of senolytic drugs in combating age-related decline. Additionally, the case study titled ‘Future Directions in Senolytic Research‘ emphasizes the necessity for varied clinical trials to investigate different senolytic drugs and their applications.
As the field progresses, the potential of senolytic drugs to revolutionize aging therapies continues to represent a promising frontier in health and wellness, particularly when integrated with effective dietary strategies. Are you ready to explore the future of age-related therapies? The journey toward innovative solutions is just beginning.
Conclusion
The exploration of senolytic drugs marks a significant advancement in our quest for healthier aging and longevity. These innovative therapeutics specifically target and eliminate senescent cells, which are known contributors to chronic inflammation and age-related diseases. As research continues to affirm the efficacy of compounds like fisetin and dasatinib in preclinical models, the potential for these drugs to enhance physical and cognitive functions—and extend healthspan—becomes increasingly evident.
The historical context of senolytic drug development reveals a fascinating journey, punctuated by significant milestones since the term was coined in 2015. This evolution underscores the necessity for ongoing research to tackle the challenges of translating findings from animal models to human applications. The mechanisms by which senolytic drugs induce apoptosis and bolster immune responses further illustrate their promise in combating the aging process.
As clinical trials progress, the potential benefits of senolytic drugs in improving health outcomes for aging populations are becoming clearer. With the ability to mitigate conditions such as cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis, these drugs could play a transformative role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals as they age. The future of senolytic research holds exciting possibilities, especially when combined with lifestyle interventions that support overall health.
In conclusion, the journey of senolytic drugs represents a promising frontier in the field of aging therapies. With rigorous research and clinical trials paving the way, these therapeutics could revolutionize our approach to aging, offering hope for improved healthspan and longevity. As this field evolves, the implications for individual health and wellness are profound, emphasizing the importance of continued exploration and understanding of these groundbreaking treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are senolytic drugs?
Senolytic drugs are therapeutics designed to selectively eliminate senescent cells, which are cells that have lost their ability to divide and function effectively. These drugs aim to restore tissue function and promote healthier aging.
Why are senescent cells a concern as individuals age?
As individuals age, senescent cells accumulate in various tissues, contributing to age-related illnesses and chronic inflammation. Their presence can negatively impact overall health and well-being.
What is the primary goal of senolytic drugs?
The primary goal of senolytic drugs is to enhance lifespan and overall well-being by addressing the detrimental effects associated with cellular aging.
Which compounds have shown potential as senolytic drugs?
Recent studies have validated the age-related cell-clearing capabilities of compounds such as D+Q, fisetin, and navitoclax, indicating their potential for therapeutic applications.
What challenges exist in translating research findings from animal models to humans?
Significant challenges include the need for rigorous clinical trials to confirm the safety and efficacy of senolytic drugs in humans, as findings from animal models may not directly apply to human contexts.
What is the importance of double-blind placebo trials in senolytic drug research?
Double-blind placebo trials are crucial for providing robust evidence of the safety and efficacy of senolytic drugs. Without such evidence, the clinical application of these therapies remains uncertain.
What historical context led to the development of senolytic drugs?
The concept of senolytic drugs originated from research into cellular senescence, first identified in the 1960s. The term ‘senolytic drugs’ emerged in 2015, marking the recognition of specific compounds that can target and eliminate senescent cells.
What early compounds were investigated for their senolytic properties?
Early investigations focused on natural compounds like quercetin and dasatinib, which showed potential in preclinical models for reducing senescent cells.
What ongoing challenges exist in the research of senolytic drugs?
Persistent challenges include the need for a cohesive theory of senescence mechanisms to improve the design and efficacy of these therapies, as well as the interplay between scientific advancements and public perception.
Why is the research on senolytic drugs significant?
The research on senolytic drugs is significant because cellular aging is a universal phenomenon across eukaryotes, and understanding these mechanisms can lead to effective treatments for age-related conditions.






