Understanding the Benefits of Amino Acid for Health and Wellness
Overview
The benefits of amino acids for health and wellness are substantial, as they play critical roles in muscle repair, hormone production, and overall bodily functions essential for maintaining health. Did you know that both essential and non-essential amino acids significantly contribute to physical performance, recovery, and even mental health? Research has shown a strong link between adequate amino acid intake and improved wellness outcomes, as well as longevity. Therefore, ensuring you consume a balanced array of amino acids can be a vital step toward enhancing your overall well-being.
Introduction
Amino acids, often referred to as the building blocks of life, play an indispensable role in maintaining the structure and function of living organisms. With 20 standard amino acids categorized into essential and non-essential types, these organic compounds are vital for a myriad of biological processes, from protein synthesis to neurotransmitter production. As research continues to unveil their significance, the health benefits of amino acids extend beyond muscle recovery and immune function to encompass mood enhancement and overall well-being.
Understanding the dietary sources that provide these essential nutrients is crucial for optimizing health, particularly in today’s fast-paced world where nutrition often takes a backseat. This exploration delves into the critical roles of amino acids, their health benefits, and how to effectively incorporate them into daily diets for a healthier lifestyle.
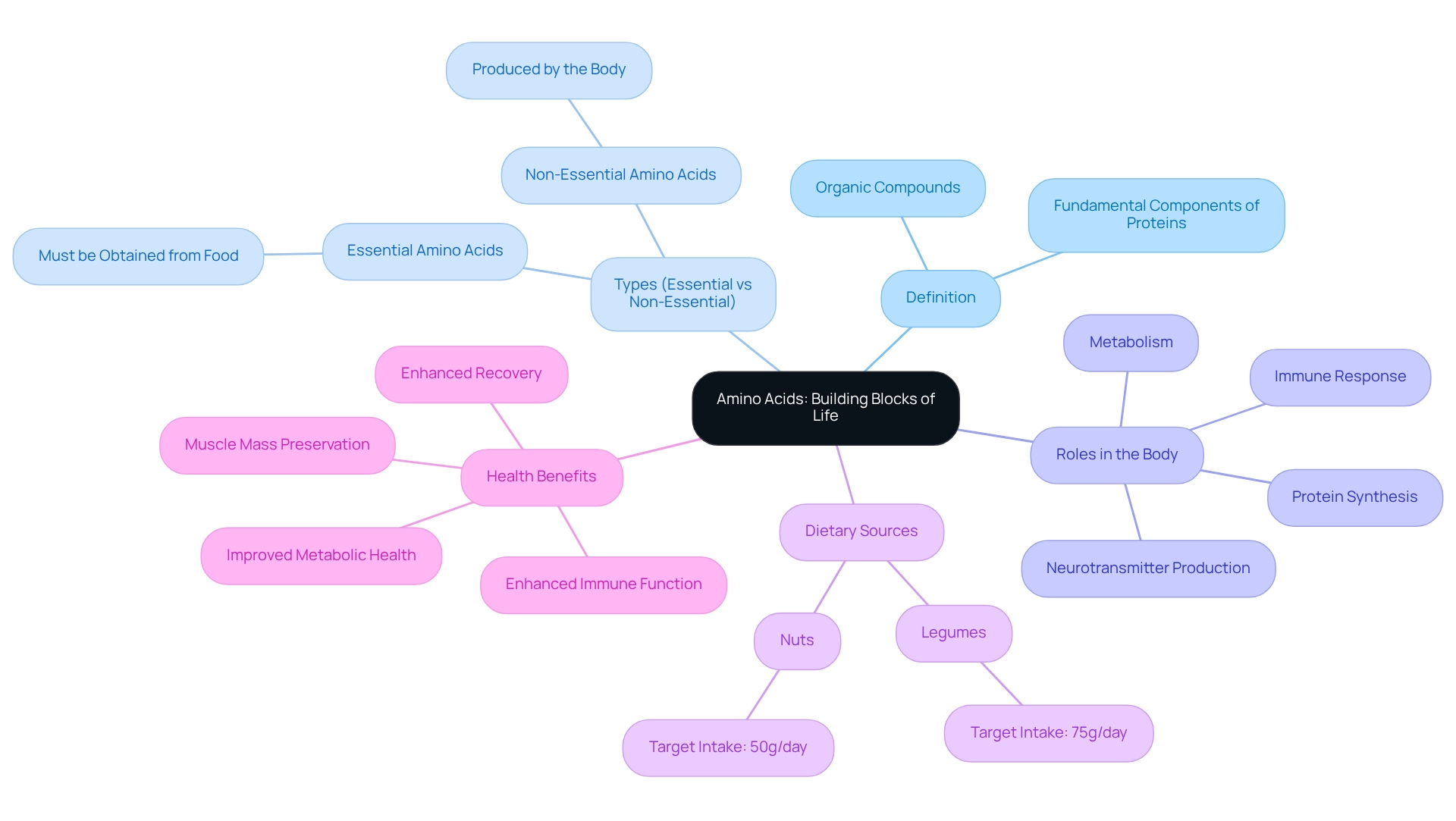
Define Amino Acids: Building Blocks of Life
Amino substances are organic compounds that serve as the fundamental components of proteins, crucial for the structure and operation of all living cells. Each protein building block contains a fundamental amine group (-NH2), a sour carboxyl group (-COOH), and a unique side chain (R group) that determines its specific characteristics. The 20 standard building blocks of proteins, classified into essential and non-essential types, each play crucial roles in various biological processes such as metabolism, immune response, and neurotransmitter production, illustrating the benefits of amino acid in protein creation, which is vital for growth, repair, and overall health. Recent studies emphasize the benefits of amino acid, which are essential building blocks of protein that must be acquired through food, as especially important for preserving muscle mass and aiding recovery following physical activity. For instance, research shows that sufficient consumption of these building blocks can boost muscle protein creation, thus enhancing physical performance and recovery durations.
In the Hunza Valley, the challenging farming methods and landscape require consistent physical work, ensuring that the Hunza population maintains a high degree of physical fitness throughout their lives. Daily walking and manual labor serve as natural forms of exercise that strengthen the body, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance metabolic efficiency. This vigorous lifestyle, combined with a nutrition plan rich in essential building blocks from legumes and nuts, showcases the benefits of amino acid for their lifespan and general well-being. Data indicates that these building blocks are integral to cellular function; they participate in the creation of hormones and enzymes, managing various physiological processes. According to the EAT Lancet planetary diet, the target consumption for legumes is 75g daily and for nuts is 50g daily, highlighting the significance of these dietary sources in supplying essential proteins. The distinction between essential and non-essential proteins is significant, as the former must be obtained from food sources, whereas the latter can be produced by the body. Understanding the benefits of amino acid is essential for individuals striving to enhance their nutrition for well-being and longevity, and practical examples of protein compounds in action, such as leucine, highlight the benefits of amino acid in promoting muscle protein synthesis during athletic recovery. Additionally, case studies, such as ‘The Role of Amino Substances in Nutrition,’ illustrate the benefits of amino acid intake for achieving improved wellness outcomes, including enhanced immune function and better metabolic health. As highlighted by researcher A.A.F., ‘The significance of organic compounds as fundamental elements of life cannot be overstated, as they contribute greatly to our overall wellness and vitality.’ In summary, the benefits of amino acids are essential for life, as they serve as the building blocks of proteins that support numerous bodily functions. Their significance in nutrition is profound due to the benefits of amino acid, as they are vital for sustaining health, vitality, and overall well-being, especially when paired with an active lifestyle like that of the Hunza Valley inhabitants.
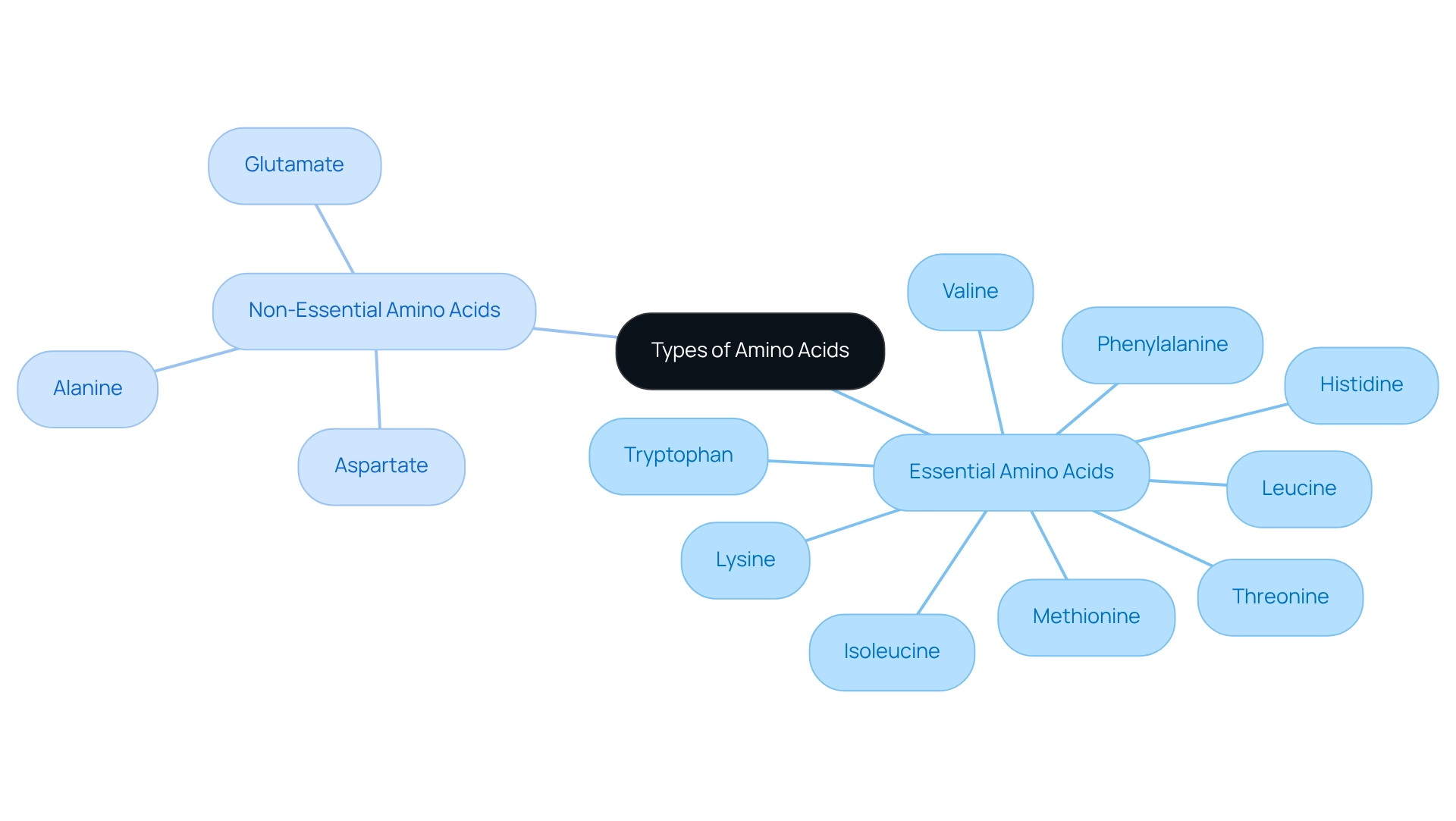
Differentiate Types of Amino Acids: Essential vs. Non-Essential
Amino compounds are classified into two main categories: vital and non-vital. Vital building blocks cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained from food consumption. There are nine vital building blocks of protein: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. The benefits of amino acid are essential, as these organic compounds play a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, including muscle repair, hormone production, and immune response.
In contrast, non-essential building blocks of protein can be synthesized by the body, which means they do not necessarily need to be obtained through diet. Instances of non-essential building blocks include alanine, aspartate, and glutamate. While both types are important, the distinction is vital for individuals aiming to optimize their nutrition.
Current dietary recommendations highlight the benefits of amino acid by emphasizing the significance of incorporating sufficient sources of vital building blocks in one’s diet. Foods abundant in these building blocks include high-quality animal products such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy, along with specific plant-based sources like quinoa and soy. Notably, whole chicken meat with skin contains approximately 141 milligrams of cholesterol per 3.5 oz. serving, emphasizing the nutritional richness of animal-derived foods and their contribution to supplying essential proteins.
Research suggests that the benefits of amino acid composition in dietary protein should be a central aspect in nutritional studies, particularly concerning health results. For example, a study investigating the connection between diabetes and non-essential nutrient intake discovered that diabetic individuals with reduced non-essential nutrient consumption encountered higher mortality risks. This underscores the necessity for tailored dietary strategies, especially for vulnerable populations. Furthermore, the relationship between smoking status and BCAAs consumption has been demonstrated to affect overall mortality, indicating that nutrient intake may have different consequences depending on lifestyle factors.
Despite the recognized advantages, understanding of vital versus non-vital building blocks remains restricted among the general public. Statistics indicate that a considerable proportion of people are not completely aware of the distinctions and dietary sources of these building blocks. As Jared Meacham, PhD, RD, CSCS, states, “These vital compounds are found in many animal- and plant-based foods, so most people can meet their daily needs by eating a healthy, balanced diet.” Specialist views indicate that a balanced nutrition, abundant in both vital and non-vital building blocks of proteins, is vital for preserving peak wellness, showcasing the benefits of amino acid. As research continues to advance, comprehending the functions of these crucial substances will be important for encouraging improved wellness results, and additional investigations are required to elucidate the connections between protein intake and wellness results across various groups.
Explore Health Benefits of Amino Acids: From Muscle Recovery to Mood Enhancement
Amino compounds play a crucial role in overall wellness, providing the benefits of amino acid that significantly impact both physical performance and mental health. Among these, branched-chain protein compounds (BCAAs) are particularly noteworthy for their effectiveness in muscle recovery and growth. Research shows that BCAAs can reduce muscle soreness and enhance exercise performance, with plasma creatine kinase (CK) levels demonstrating notable reductions after supplementation. For instance, a study revealed that plasma CK levels at 48 hours post-exercise for the PLCB group averaged 1422.9 ± 630.8 IU/L. This suggests that prolonged supplementation—extending beyond seven days—may yield even greater benefits in lowering CK levels. Such findings deepen our understanding of the role of BCAAs in recovery from muscle-damaging exercise.
Furthermore, organic compounds are essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, which affects mood and cognitive abilities. Tryptophan, for example, serves as a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter vital for mood regulation and sleep quality. When free tryptophan levels rise in the bloodstream, this compound can effectively cross the blood–brain barrier. Other organic compounds, like glycine and glutamine, also support digestive well-being and immune functionality, further enhancing overall wellness.
The benefits of amino acid components extend into various areas, including mood improvement. Real-life examples illustrate how these organic compounds can enhance cognitive ability and emotional balance, making them a valuable addition to a health-focused diet. Experts emphasize the importance of organic compounds in exercise performance, highlighting their role in improving recovery strategies for athletes. Future research directions, as noted in the case study titled “Future Directions for BCAA Research,” suggest exploring different dosages and timing of consumption, as well as the synergistic effects of BCAAs with other proteins or performance-enhancing substances.
Incorporating sufficient protein components into your diet can lead to the benefits of amino acid, which include improved physical performance, better mood management, and enhanced recovery from exercise, establishing them as a foundational aspect of wellness strategies. While BCAA supplements are generally considered safe when taken as directed, it is important to consult a doctor if serious side effects occur.
Identify Dietary Sources: How to Incorporate Amino Acids into Your Diet
To guarantee sufficient consumption of the building blocks of protein, it is essential to eat a variety of foods rich in protein. Animal-derived sources, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products, are complete proteins that provide all vital building blocks necessary for optimal health. For instance, beef, particularly nutritious ribeye steaks and liver patties made from quality ingredients, stands out as an excellent source of superior protein, delivering a robust profile of essential nutrients that supports muscle maintenance and overall well-being.
Current dietary trends reveal an increasing preference for animal-derived proteins among health-conscious individuals, many of whom recognize their superior protein content compared to plant-derived options. A study conducted between September 2021 and January 2023 indicated that individuals prioritizing protein intake often achieve better health outcomes. While plant sources like quinoa, soy products, lentils, and beans can contribute to protein intake, they frequently lack one or more essential building blocks. However, by combining various plant proteins—such as rice and beans—one can create a complete profile of essential nutrients, making them a viable option for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Incorporating a diverse range of foods into daily meals is crucial for optimal amino acid intake to fully experience the benefits of amino acid. Meal plans that emphasize animal-based proteins can feature dishes like savory beef liver patties, which are nutrient-dense and customizable, grilled chicken with vegetables, or a hearty omelet with cheese. Expert cooking techniques, such as achieving the perfect egg wash finish on patties, can enhance the flavor and presentation of these meals. Nutritionists recommend focusing on high-quality animal proteins to effectively meet dietary needs, particularly for those committed to a carnivore-based diet, due to the benefits of amino acid.
Claire Berryman, an author, notes, “In addition, it is important to keep in mind that consuming any macronutrient—protein, carbohydrate, or fat—in excess of calorie needs will lead to weight gain.” It is also vital to be cautious with processed meats, as they should be avoided due to their associated risks and preparation methods. Furthermore, a case study on ultraprocessed food intake among vegans highlighted the broader implications of such diets, emphasizing the necessity for thoughtful dietary choices. Statistics indicate that individuals prioritizing protein intake often achieve better health outcomes, underscoring the importance of making informed dietary decisions.
Conclusion
Amino acids are undeniably essential to sustaining life and promoting overall health. Functioning as the building blocks of proteins, they play critical roles in numerous biological processes, including metabolism, immune function, and neurotransmitter synthesis. Understanding the distinction between essential and non-essential amino acids is pivotal for individuals striving to optimize their nutrition. Essential amino acids must be sourced from the diet, while non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body, highlighting the importance of a balanced intake.
The health benefits of amino acids extend well beyond muscle recovery; they significantly influence mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being. Research demonstrates that branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) not only enhance physical performance but also aid in recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage. Additionally, amino acids like tryptophan play a crucial role in neurotransmitter production, affecting mood regulation and sleep quality.
Incorporating a variety of protein-rich foods into daily diets is vital for ensuring adequate amino acid intake. While animal-based sources provide complete proteins, plant-based options can also contribute significantly when combined thoughtfully. By prioritizing high-quality protein sources, individuals can enhance their health outcomes and support their physical and mental performance.
In conclusion, understanding the vital role of amino acids and incorporating them into a balanced diet can lead to improved health and vitality. As research continues to reveal their significance, embracing a diet that includes a diverse array of amino acid sources will empower individuals to optimize their well-being and enhance their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are amino substances and their role in living cells?
Amino substances are organic compounds that are the fundamental components of proteins, essential for the structure and function of all living cells.
What is the structure of a protein building block?
Each protein building block contains an amine group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a unique side chain (R group) that determines its specific characteristics.
How many standard building blocks of proteins are there, and how are they classified?
There are 20 standard building blocks of proteins, classified into essential and non-essential types.
What biological processes do amino acids play a role in?
Amino acids play crucial roles in various biological processes such as metabolism, immune response, and neurotransmitter production.
Why are amino acids important for physical activity and recovery?
Amino acids are essential for preserving muscle mass and aiding recovery after physical activity, with sufficient consumption boosting muscle protein creation and enhancing physical performance.
What lifestyle factors contribute to the health of the Hunza population?
The Hunza population maintains high physical fitness through consistent physical work, daily walking, and manual labor, combined with a nutrition plan rich in essential amino acids from legumes and nuts.
What are the recommended daily consumption targets for legumes and nuts according to the EAT Lancet planetary diet?
The target consumption for legumes is 75g daily and for nuts is 50g daily.
What is the difference between essential and non-essential proteins?
Essential proteins must be obtained from food sources, while non-essential proteins can be produced by the body.
How do amino acids contribute to overall wellness and vitality?
Amino acids are vital for sustaining health, supporting numerous bodily functions, and enhancing well-being, especially when paired with an active lifestyle.
What are some specific benefits of amino acids highlighted in research?
Research indicates that amino acids can improve immune function, metabolic health, and promote muscle protein synthesis during athletic recovery.






