Understanding Spermidine Side Effects for Health Enthusiasts
Overview
This article delves into the side effects of spermidine, a compound known for its potential health benefits, including cellular repair and longevity. However, it is crucial to note that high doses of spermidine can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort and other associated risks. Therefore, understanding these aspects is essential for anyone considering supplementation.
Consulting healthcare professionals before starting spermidine supplementation is highly recommended. Tailoring dosages can help mitigate potential interactions with medications, ensuring safe usage for health enthusiasts. By seeking professional advice, individuals can navigate their health journeys more effectively and safely.
In summary, while spermidine offers promising health benefits, awareness of its side effects and the importance of professional guidance cannot be overstated. This proactive approach will help individuals make informed decisions regarding their health and wellness.
Introduction
Spermidine, a vital polyamine present in all living cells, plays a crucial role in cellular health, growth, and longevity. As health enthusiasts increasingly explore the benefits of spermidine supplementation—from enhanced autophagy to potential reductions in age-related illnesses—understanding its advantages alongside possible side effects is essential.
What occurs when the pursuit of longevity through spermidine meets potential risks? This article examines the intricate balance between the promising health benefits of spermidine and the caution necessary to navigate its side effects effectively.
Define Spermidine and Its Role in Health
Spermidine, a naturally occurring polyamine found in all living cells, is essential for cellular growth, repair, and longevity. It significantly contributes to various biological processes, particularly autophagy, which is the body’s mechanism for eliminating damaged cells and regenerating new ones. Recent studies suggest that spermidine supplementation can enhance cellular health, reduce inflammation, and improve mitochondrial function, making it a vital component in the aging process.
Notably, research indicates that higher consumption of spermidine is linked to lower mortality rates and a reduced risk of age-related illnesses. For instance, the Bruneck study highlighted that increased intake of this compound was associated with a marked decrease in all-cause mortality. This suggests that incorporating spermidine into one’s diet could be an effective strategy for promoting longevity.
Furthermore, spermidine’s ability to upregulate genes involved in polyamine metabolism, along with its antioxidative properties, emphasizes its potential in health and longevity strategies. This makes spermidine a focal point for individuals seeking to enhance their well-being as they age.
Explore Potential Side Effects of Spermidine
Spermidine is generally considered safe for most individuals, but it is important to be aware of potential side effects, especially at high doses. Commonly reported side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating, nausea, and upset stomach. In studies, approximately 7% of participants experienced mild gastrointestinal symptoms during the initial weeks of supplementation, particularly at doses exceeding 5 mg per day, which may be associated with spermidine side effects.
Furthermore, treatments involving human growth hormone (GH) can pose risks, including:
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Insulin resistance
- An increased likelihood of diabetes
Prolonged use of GH therapy may also be linked to a higher risk of certain cancers. Less frequently, concerns about electrolyte imbalances and, in rare cases, an elevated chance of stroke associated with very high levels of supplementation have been noted.
As a result, it is essential for individuals to consult medical experts before starting any new supplement regimen, particularly if they have existing medical conditions or are undergoing other treatments. Monitoring dosage and being attuned to one’s body response can help mitigate these risks, ensuring safe practices in anti-aging strategies.
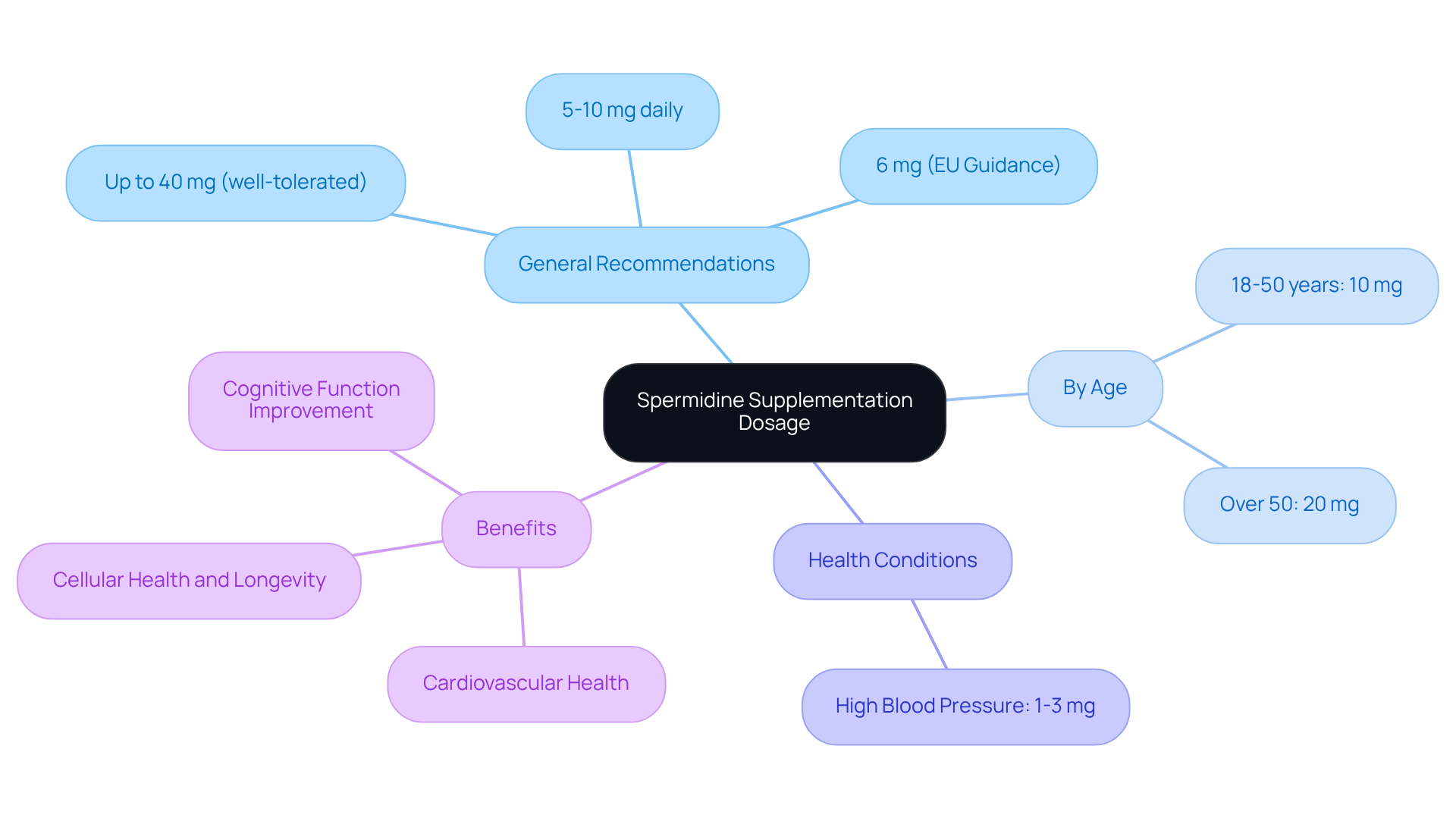
Recommended Dosage for Spermidine Supplementation
The suggested amount of the compound varies based on personal wellness goals and the specific supplement formulation. For most adults, a daily intake of 5 to 10 mg is considered safe and effective, with the European Union recommending a daily intake of 6 mg from supplements. Research indicates that higher doses, up to 40 mg per day, can be well-tolerated by healthy individuals, with minimal spermidine side effects reported. It is advisable to start with a lower dose, such as 1 mg, and gradually increase it while closely monitoring for any adverse reactions, including mild gastrointestinal side effects and spermidine side effects like nausea or bloating.
Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to tailor the dosage to personal health conditions and goals, especially for individuals with high blood pressure, who are advised to take 1 to 3 mg daily. For adults aged 18 to 50, a daily intake of 10 mg is recommended, while those over 50 may benefit from a higher dosage of 20 mg, taken in two capsules daily—one in the morning and one at night. Nutritionists emphasize the importance of adhering to these guidelines to optimize the benefits of this compound while minimizing potential risks, such as spermidine side effects.
Real-world examples illustrate that participants in studies who followed these dosage recommendations experienced significant improvements in cognitive function. Notably, the high-dose group showed an increase in cognitive scores, reinforcing the value of proper supplementation.
Sources of Spermidine in Diet
Spermidine is abundant in a variety of foods, particularly those rich in protein and select plant-based sources. Have you ever considered the dietary sources of this beneficial compound? Significant sources include:
- Aged cheeses, which can contain between 39 to 200 mg of spermidine per kg.
- Mushrooms, offering approximately 8.8 mg per 100 g.
- Soy products, such as natto, stand out with 65-340 mg per kg, making them an excellent choice for those looking to enhance their intake.
- Legumes and whole grains also contribute significantly, with whole grains providing 10-30 mg per kg.
Furthermore, specific fruits and vegetables, like grapefruit and cruciferous options such as broccoli, hold spermidine, albeit in lesser quantities (approximately 2.5 mg per 100 g for broccoli). For individuals following a carnivore-based diet, organ meats, particularly liver, are outstanding sources, with chicken liver offering around 4.8 mg per 100 g. By incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into a balanced diet, wellness enthusiasts can naturally boost their levels of spermidine, promoting overall well-being and longevity. Are you ready to explore these options and enhance your dietary choices?
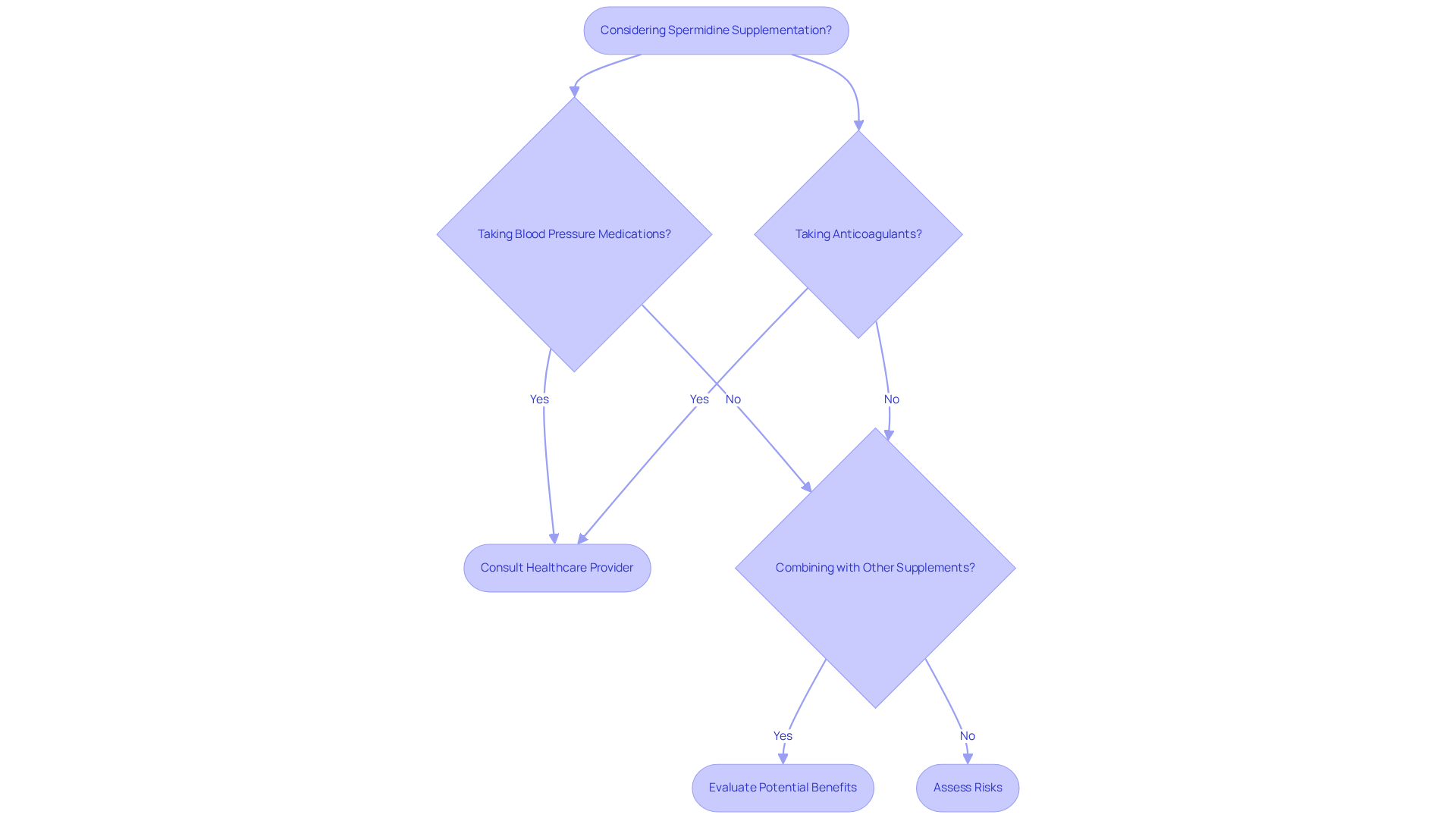
Interactions with Other Supplements and Medications
Spermidine side effects may occur as a result of interactions with specific medications and supplements, especially those that influence blood pressure or blood clotting. Individuals taking anticoagulants or antihypertensive medications should consult their healthcare provider before incorporating this compound into their regimen, as spermidine side effects could amplify the effects of these drugs. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is responsible for approximately one third of all global deaths, underscoring the critical need for effective blood pressure management.
Furthermore, reports indicate that combining spermidine with other supplements that enhance autophagy or cellular health can yield synergistic benefits. However, this approach should be taken with caution. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of any new supplement routine, especially when considering the spermidine side effects and potential interactions with blood pressure medications and anticoagulants.
User testimonials have highlighted increased energy levels and improved cellular metabolism when spermidine is paired with other health-promoting compounds. This further emphasizes the importance of personalized advice in navigating supplementation effectively.
Conclusion
Spermidine emerges as a significant player in cellular health, longevity, and overall well-being. Its role in enhancing autophagy and potentially reducing age-related illnesses underscores its importance for health enthusiasts seeking to optimize their wellness strategies. However, it is crucial to remain vigilant about the potential side effects associated with its supplementation, particularly at higher doses.
The article highlights key insights into spermidine’s health benefits, including:
- Its antioxidative properties
- Its ability to support mitochondrial function
Furthermore, it discusses the importance of adhering to recommended dosages to mitigate side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort. It emphasizes the need for consultation with healthcare professionals before starting any new supplement regimen. Understanding the dietary sources of spermidine and its interactions with other medications further enriches the narrative around safe and effective supplementation.
In light of the growing interest in spermidine for health and longevity, individuals are encouraged to take a proactive approach. This includes:
- Integrating spermidine-rich foods into their diets
- Engaging with healthcare providers to tailor supplementation to their personal health needs
By balancing the promise of spermidine with informed decision-making, health enthusiasts can harness its potential while prioritizing their safety and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is spermidine and what role does it play in health?
Spermidine is a naturally occurring polyamine found in all living cells, essential for cellular growth, repair, and longevity. It contributes to biological processes like autophagy, helping eliminate damaged cells and regenerate new ones.
How does spermidine affect aging and longevity?
Research suggests that spermidine supplementation can enhance cellular health, reduce inflammation, and improve mitochondrial function. Higher consumption of spermidine is linked to lower mortality rates and a reduced risk of age-related illnesses, indicating its potential as a strategy for promoting longevity.
What are the potential benefits of spermidine supplementation?
Benefits of spermidine supplementation include improved cellular health, enhanced autophagy, reduced inflammation, and better mitochondrial function. It may also upregulate genes involved in polyamine metabolism and has antioxidative properties.
Are there any side effects associated with spermidine?
Spermidine is generally considered safe, but potential side effects at high doses can include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating, nausea, and upset stomach. About 7% of participants in studies reported mild gastrointestinal symptoms at doses exceeding 5 mg per day.
What risks are associated with human growth hormone (GH) treatments?
Risks of GH treatments can include joint pain, swelling, insulin resistance, an increased likelihood of diabetes, and potentially a higher risk of certain cancers with prolonged use.
What precautions should individuals take before starting spermidine supplementation?
Individuals should consult medical experts before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if they have existing medical conditions or are undergoing other treatments. Monitoring dosage and being aware of one’s body response can help mitigate risks.






