NAD+ Dosage: Guidelines for Safe and Effective Supplementation
Overview
The article outlines essential guidelines for safe and effective NAD+ supplementation. It recommends a daily dosage ranging from 250 mg to 1,000 mg for oral supplements, with 500 mg often proving effective for many individuals. This recommendation is backed by research demonstrating that such dosages can enhance metabolic function and support cellular repair.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals to customize dosages based on individual health conditions. This ensures that potential side effects are monitored effectively. By following these guidelines, individuals can optimize their NAD+ supplementation experience.
Introduction
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is essential for cellular health, serving as a vital coenzyme that powers energy metabolism and aids in DNA repair. Research indicates that NAD+ levels decline with age, leading to increased interest in supplementation as a means to enhance energy production and bolster cellular resilience.
However, with various supplementation methods available, how can individuals navigate the complexities of safe and effective dosing? Understanding the guidelines for NAD+ dosage not only reveals its therapeutic potential but also underscores the importance of personalized approaches to supplementation.
Explore the Role of NAD+ in Cellular Health
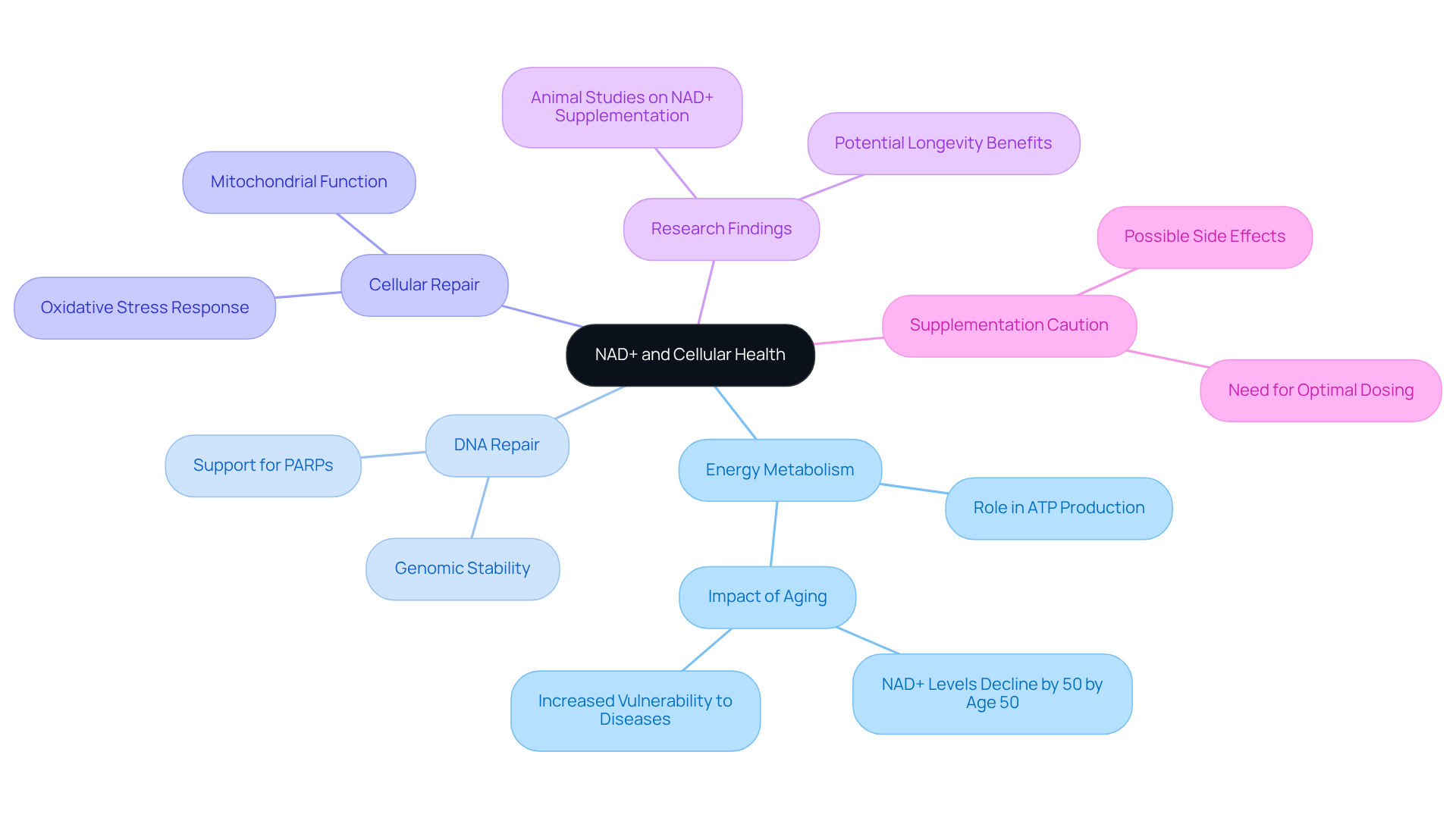
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is a vital coenzyme present in every cell, playing a crucial role in energy metabolism and cellular repair. It facilitates redox reactions essential for converting nutrients into usable energy. Furthermore, NAD+ is integral to DNA repair, supporting genomic stability and overall cellular health.
As we age, studies indicate that NAD+ dosage declines, leading to decreased energy production and increased vulnerability to age-related illnesses. This decline is linked to various medical issues, including metabolic disorders and neurodegeneration. Recent research suggests that NAD+ dosage can enhance energy metabolism, improve mitochondrial performance, and aid cellular repair processes, potentially reversing some signs of aging.
For instance, animal studies show that increasing NAD+ dosage can enhance exercise capacity and metabolic health, emphasizing its importance in promoting longevity and vitality. However, it is essential to approach supplementation with caution, as excessive doses may cause mild reactions. Understanding the dynamics of this coenzyme is crucial for exploring its therapeutic potential in combating the effects of aging and improving overall well-being.
Examine NAD+ Supplementation Methods and Forms
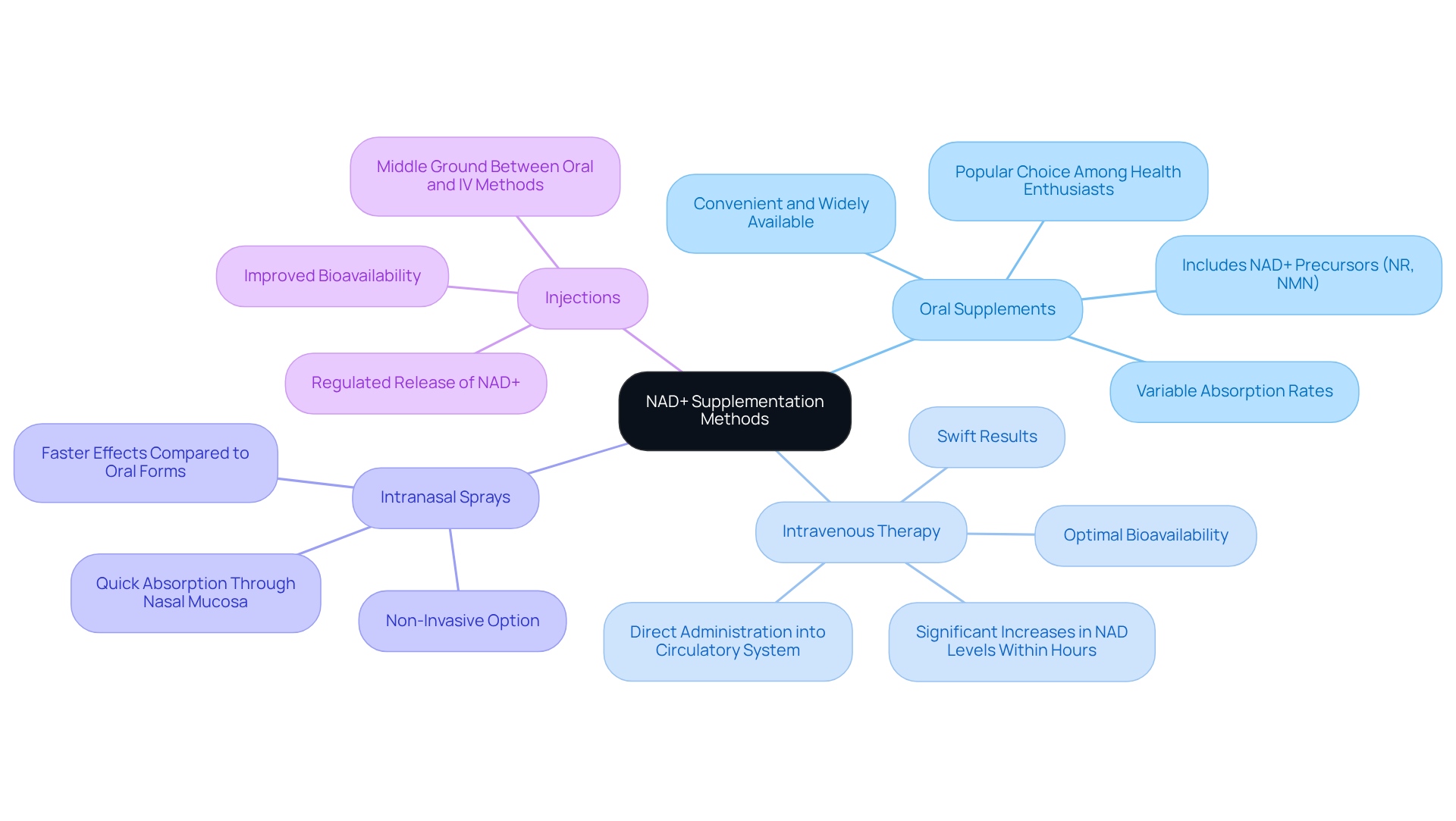
NAD+ can be supplemented in several forms, each offering distinct advantages:
- Oral Supplements: These include capsules and powders containing NAD+ precursors like Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN). They are convenient and widely available, making them a popular choice among health enthusiasts. However, absorption rates can vary significantly among individuals, which may affect their overall efficacy.
- Intravenous (IV) Therapy: This technique administers NAD directly into the circulatory system, ensuring optimal bioavailability and swift results. Clinical studies have shown that IV administration can lead to significant increases in NAD levels within hours, making it a preferred option for those seeking immediate results, particularly in clinical settings.
- Intranasal Sprays: These provide a non-invasive option that allows for quick absorption through the nasal mucosa. Research indicates that intranasal delivery may offer faster effects compared to oral forms, making it an appealing alternative for individuals who prefer not to take pills or undergo injections.
- Injections: Subcutaneous or intramuscular injections serve as a middle ground between oral and IV methods. They can offer a more regulated release of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide compared to oral supplements, potentially improving bioavailability while circumventing the intricacies of IV therapy.
Choosing the suitable approach for enhancing levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide should consider the NAD+ dosage based on personal wellness objectives, preferences, and expert advice. Recent studies emphasize the significance of taking into account both the bioavailability and the particular wellness outcomes sought when selecting among these forms of supplements.
Determine Safe and Effective NAD+ Dosage Guidelines
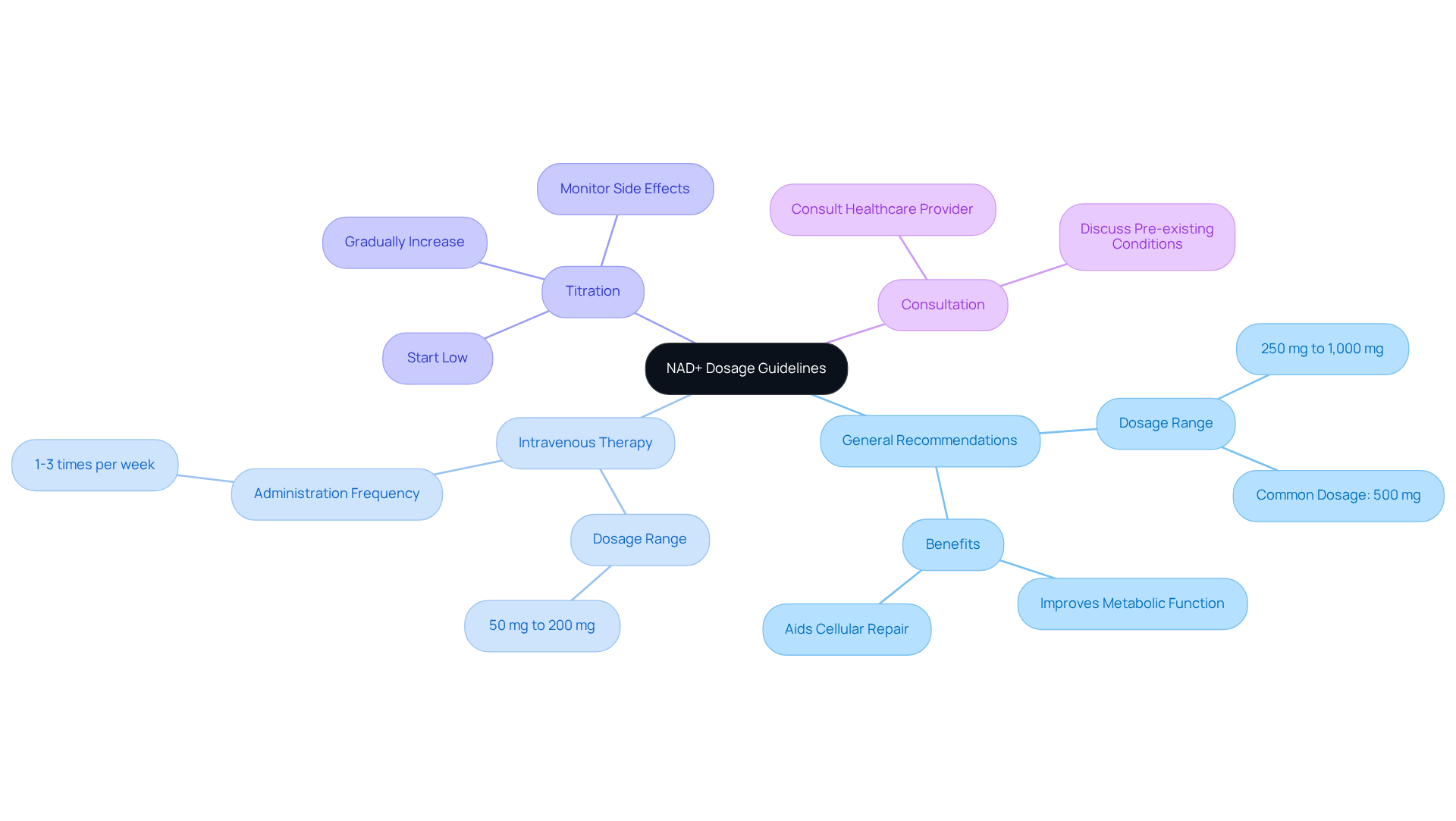
When considering NAD+ supplementation, adhering to established dosage guidelines is crucial for ensuring both safety and effectiveness.
General Recommendations: Research indicates that a daily NAD+ dosage of 250 mg to 1,000 mg is effective for oral supplements, with many individuals experiencing benefits at approximately 500 mg per day. Studies have shown that doses within this range can improve metabolic function and aid cellular repair. For instance, a 2021 study observed that a NAD+ dosage of 250 mg daily for 10 weeks enhanced insulin sensitivity in postmenopausal individuals with prediabetes.
For Intravenous Therapy, the NAD+ dosage typically ranges from 50 mg to 200 mg for initial intravenous doses, administered 1-3 times per week, tailored to individual health conditions and goals. This method provides rapid increases in NAD+ levels but requires professional administration.
Titration: It is advisable to begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it while closely monitoring for any side effects. This personalized method aids in maximizing the advantages of dietary additions while reducing possible negative effects. A case study highlights that merging accurate testing with focused additions results in customized protocols that improve cellular well-being and vitality.
Consultation: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new regimen involving supplements, especially for individuals with underlying health issues or those using other medications. Professional guidance is essential to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure safe use. As specialists emphasize, discussing pre-existing conditions or medications with a healthcare professional is crucial before beginning NAD therapy.
Understand Safety Considerations and Side Effects of NAD+
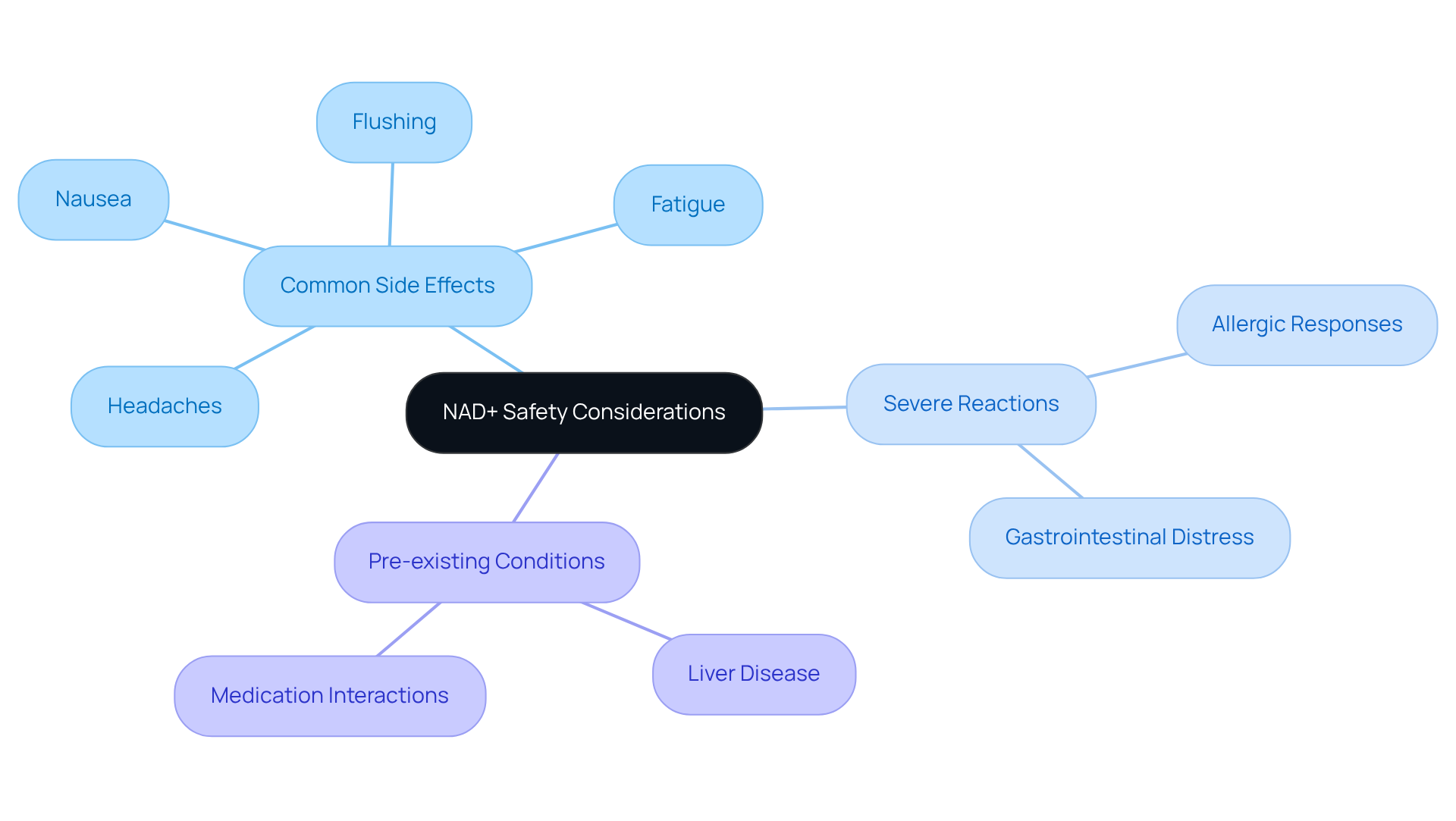
NAD+ supplementation is generally regarded as safe, yet being aware of potential side effects is crucial for optimizing the experience.
Common Side Effects: Users may encounter mild symptoms such as headaches, nausea, fatigue, and flushing. These reactions are typically manageable and often lessen with ongoing use. For example, a clinical trial demonstrated that the addition of 500 mg of nicotinamide (NAM) resulted in a marginally significant rise in NAD levels after 12 hours, with most participants reporting only mild discomfort.
Severe Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience more serious reactions, such as allergic responses or significant gastrointestinal distress. In these cases, it is essential to discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional immediately. Safety information from multiple studies indicates that while most adverse reactions are minor, attentiveness is vital, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with specific health issues, such as liver disease or those on certain medications, should exercise caution and consult a healthcare professional before starting this therapy. The FDA has established a tolerable upper intake level for nicotinamide at 900 mg/day, but personalized guidance from healthcare providers is recommended to ensure safety.
By understanding these considerations, individuals can make informed decisions regarding NAD+ dosage, balancing the potential benefits with the management of side effects.
Conclusion
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular health, particularly in energy metabolism and DNA repair. As levels of this essential coenzyme decrease with age, interest in NAD+ supplementation has surged, highlighting its potential to enhance energy production and improve overall cellular resilience. Understanding the proper dosage and methods of supplementation is crucial for maximizing benefits while ensuring safety.
The article has explored various supplementation methods, including:
- Oral supplements
- Intravenous therapy
- Intranasal sprays
- Injections
Each method comes with unique advantages and considerations. It has emphasized the importance of adhering to recommended dosage guidelines, which typically range from:
- 250 mg to 1,000 mg for oral supplements
- 50 mg to 200 mg for intravenous therapy
Furthermore, the significance of consulting healthcare professionals before starting supplementation has been underscored, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications.
In light of the growing body of research on NAD+ and its potential health benefits, individuals are encouraged to take a proactive approach to their well-being. By understanding the role of NAD+ in cellular function and adhering to safe supplementation practices, one can harness its therapeutic potential to promote longevity and vitality. Prioritizing informed choices in NAD+ supplementation not only enhances personal health but also contributes to a broader understanding of its significance in combating age-related decline.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is NAD+ and why is it important for cellular health?
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a vital coenzyme present in every cell, crucial for energy metabolism and cellular repair. It facilitates redox reactions that convert nutrients into usable energy and is integral to DNA repair, supporting genomic stability and overall cellular health.
How does NAD+ dosage change with age?
As we age, studies indicate that NAD+ dosage declines, which leads to decreased energy production and increased vulnerability to age-related illnesses.
What are the consequences of declining NAD+ levels?
The decline in NAD+ levels is linked to various medical issues, including metabolic disorders and neurodegeneration, which can affect overall health and increase the risk of age-related diseases.
Can increasing NAD+ levels have health benefits?
Yes, recent research suggests that increasing NAD+ dosage can enhance energy metabolism, improve mitochondrial performance, and aid in cellular repair processes, potentially reversing some signs of aging.
What evidence supports the benefits of NAD+ supplementation?
Animal studies have shown that increasing NAD+ dosage can enhance exercise capacity and metabolic health, highlighting its importance in promoting longevity and vitality.
Are there any risks associated with NAD+ supplementation?
While NAD+ supplementation may have benefits, it is essential to approach it with caution, as excessive doses may cause mild reactions.
Why is understanding NAD+ dynamics important?
Understanding the dynamics of NAD+ is crucial for exploring its therapeutic potential in combating the effects of aging and improving overall well-being.






