Can Oxidative Stress Be Reversed? Understanding Its Causes and Solutions
Overview
Oxidative stress can potentially be reversed through dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and supplementation aimed at enhancing the body’s antioxidant defenses. By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and utilizing specific supplements, individuals can mitigate cellular damage and promote overall health. This approach supports the possibility of reversing oxidative stress.
Furthermore, consider how these changes can positively impact your life. Are you ready to explore the benefits of a healthier lifestyle? Making informed dietary choices and staying active not only helps combat oxidative stress but also contributes to your overall well-being. Take action today by examining your current habits and identifying areas for improvement.
Introduction
Oxidative stress is a condition that arises from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species and the body’s capacity to neutralize them. This imbalance poses significant threats to health, contributing to various diseases and the aging process. Understanding how oxidative stress can be reversed opens a world of possibilities for enhancing well-being through lifestyle choices and dietary interventions.
However, can simple adjustments in nutrition and lifestyle truly mitigate the damaging effects of oxidative stress? Or is it a more complex issue that requires deeper exploration? These questions invite us to delve further into the relationship between our daily choices and our health.
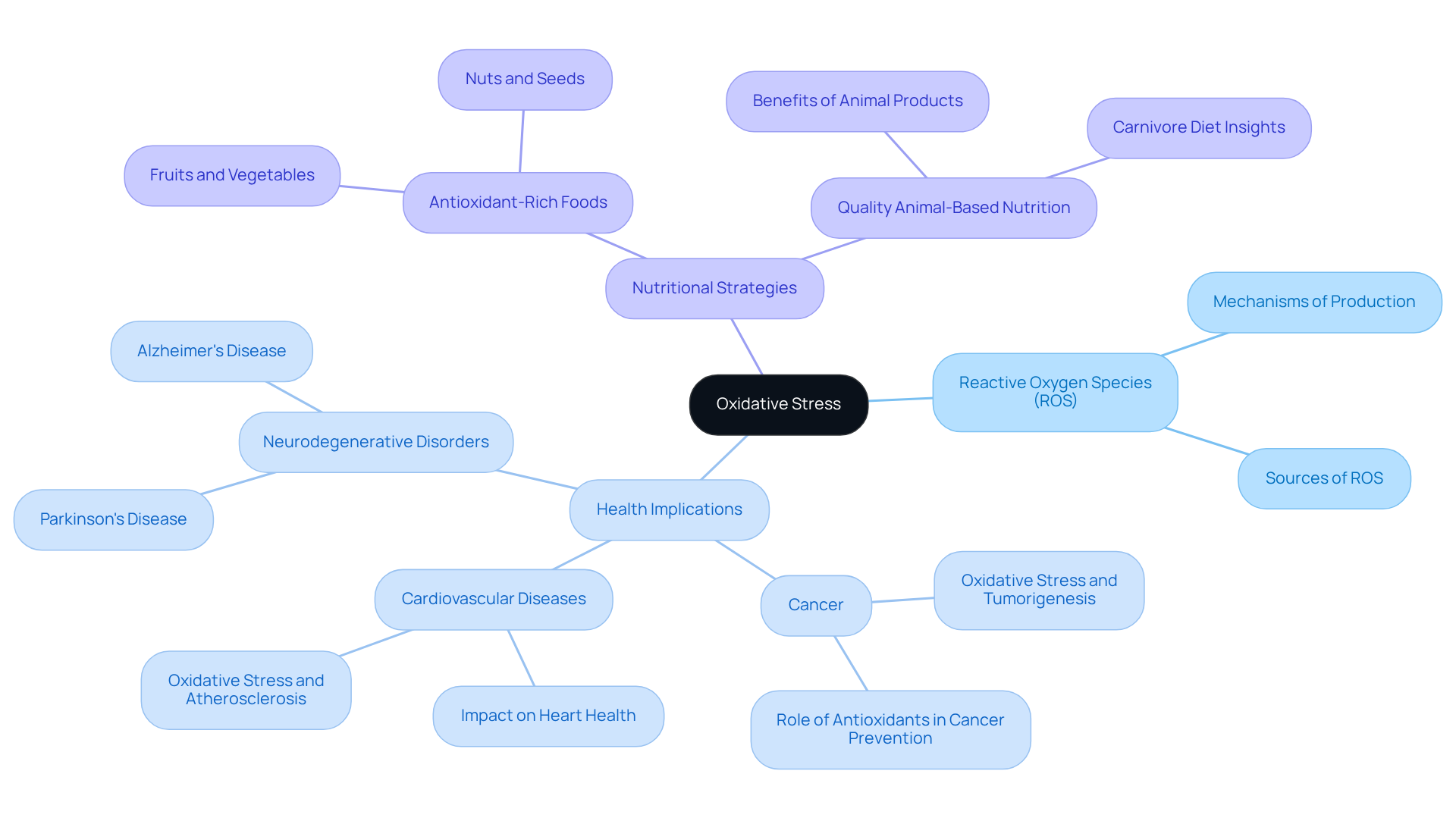
Define Oxidative Stress: Understanding Its Role in Health
Oxidative imbalance refers to the disparity between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to neutralize these substances or repair the resulting damage. This condition can lead to cellular damage and is associated with various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. The body naturally produces ROS during metabolic processes; however, when their levels exceed the protective mechanisms, an imbalance occurs.
Understanding the imbalance of reactive oxygen species is crucial for investigating whether oxidative stress can be reversed, as it significantly affects aging and the onset of chronic illnesses. This makes it a vital focus for wellness strategies. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods, such as those found in ByKomi.com’s carnivore recipes, can provide essential vitamins and minerals that bolster the body’s antioxidant defenses.
By prioritizing quality animal-based nutrition, individuals can enhance their overall health and explore whether oxidative stress can be reversed. This aligns with innovative therapies aimed at promoting longevity. Are you ready to explore how dietary choices can impact your health? Discover more about the benefits of antioxidant-rich foods today.
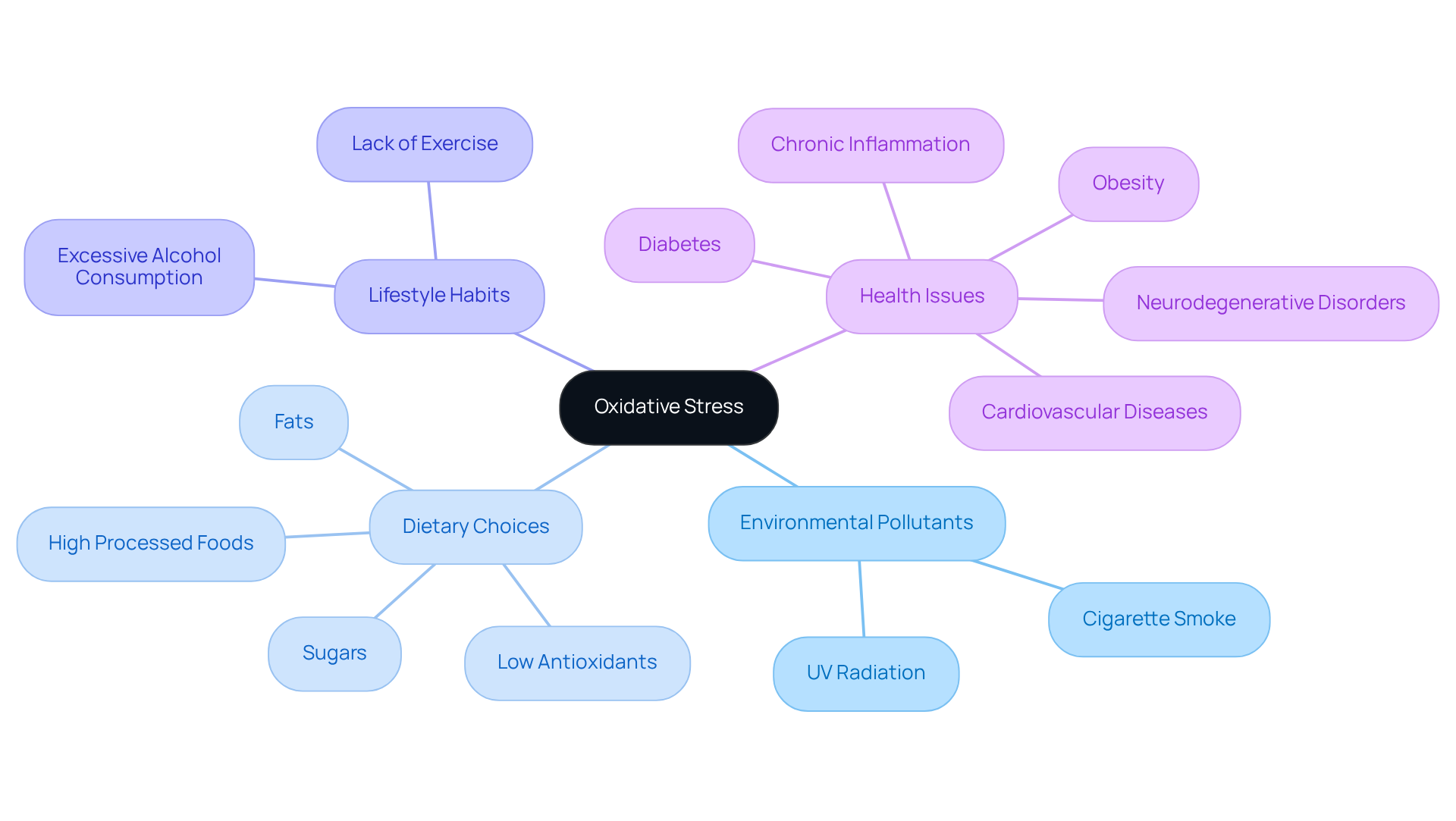
Identify Causes of Oxidative Stress: Triggers and Risk Factors
Oxidative pressure can be triggered by a multitude of factors, including environmental pollutants, dietary choices, and lifestyle habits. Key contributors encompass exposure to cigarette smoke, excessive alcohol consumption, and diets high in processed foods, fats, and sugars. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation also plays a significant role. Chronic inflammation and health issues like obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders further worsen reactive imbalance levels.
Significantly, recent studies, including findings from Dr. Dituri’s underwater journey, indicate that different environments may affect cellular damage and overall well-being. This pioneering study suggests that prolonged exposure to specific environmental conditions, such as increased pressure and oxygen levels, could stimulate cellular regeneration and potentially reverse aging processes.
Studies show that diets low in antioxidants and high in processed foods can result in heightened cellular damage. Conversely, a well-rounded diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which provide essential antioxidants such as vitamins A, C, and E, may assist in reducing these impacts. Moreover, consistent exercise has been demonstrated to lower harmful cellular effects, further highlighting the importance of physical activity in enhancing longevity, as observed in the active lifestyles of Hunza Valley inhabitants.
By identifying these risk elements and the possible effects of environmental conditions, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce exposure and decrease the likelihood of health problems linked to cellular damage, leading to the inquiry of whether oxidative stress can be reversed. Furthermore, the findings from Dr. Dituri’s research could pave the way for clinical trials to test the effectiveness of similar environmental interventions on aging, potentially leading to the development of new anti-aging treatments based on environmental exposure.
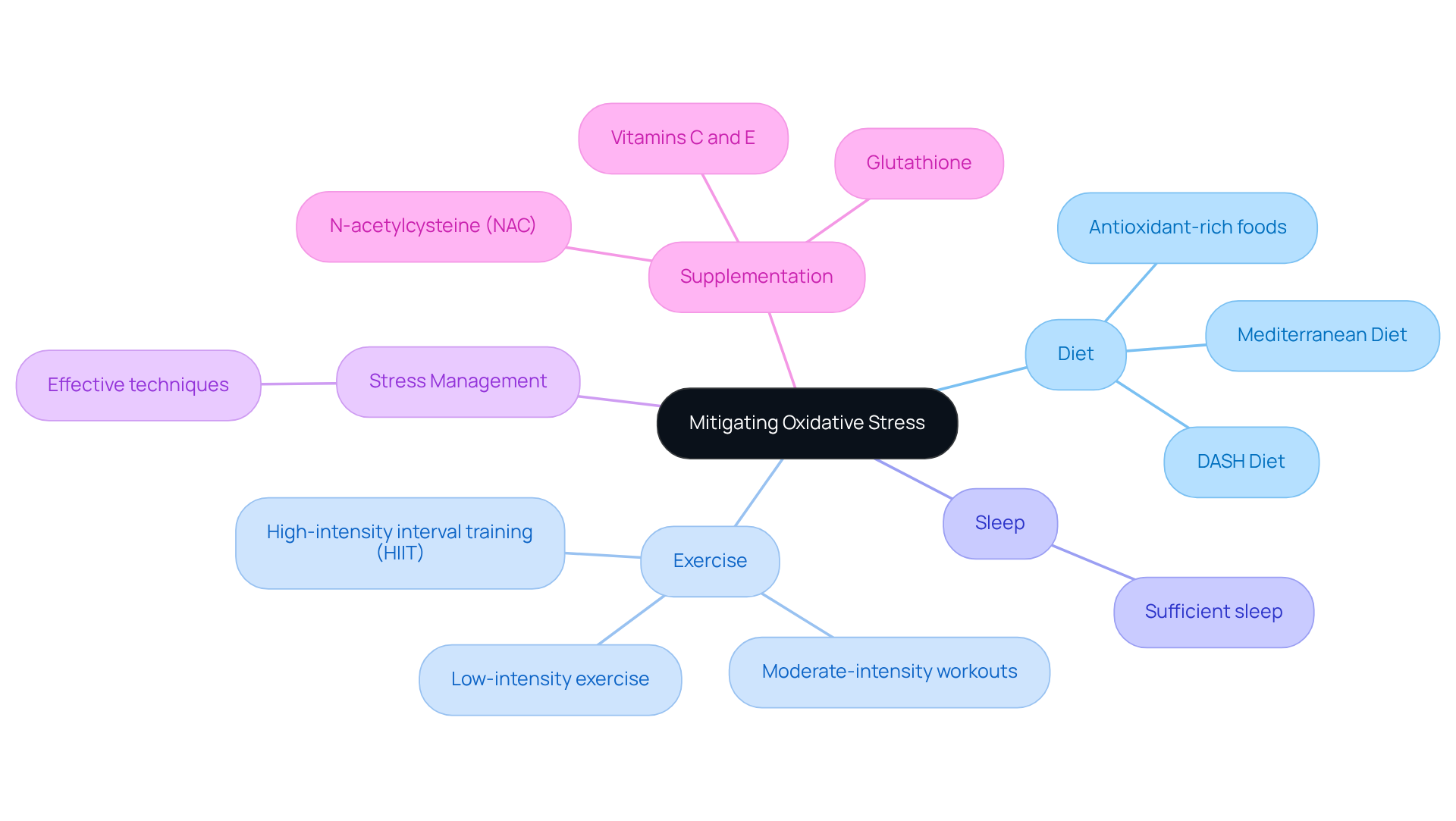
Explore Reversal Strategies: Can Oxidative Stress Be Mitigated?
Reducing cellular damage requires a multifaceted strategy that encompasses dietary adjustments, lifestyle alterations, and supplementation. Including foods high in antioxidants—such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains—is crucial for neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing damage from oxidation. Studies show that following eating plans like the Mediterranean and DASH diets can significantly decrease cellular damage and inflammation, enhancing overall health.
Consistent physical activity, particularly moderate-intensity workouts, has been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity and decrease inflammatory markers. This further aids in reducing harmful cellular reactions. Furthermore, sufficient sleep and effective stress management techniques are essential for maintaining a healthy balance of oxidation.
Certain dietary supplements, especially those well-researched in the anti-aging field, can play a significant role in enhancing the body’s antioxidant defenses. Vitamins C and E, along with compounds like N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and glutathione, have shown potential in this regard. For instance, NAC can enhance intracellular glutathione levels, which are vital for cellular redox balance and combating free radical damage.
My personal experience with these supplements has yielded encouraging outcomes in boosting vitality and overall well-being. However, it is crucial to approach supplementation with caution, as excessive intake may lead to adverse effects. By adopting these strategies—focusing on nutrient-rich foods, engaging in regular exercise, and considering appropriate supplementation—individuals can investigate if oxidative stress can be reversed to significantly reduce their levels of cellular damage and promote improved wellness outcomes. This empowers their journey towards anti-aging through informed nutritional choices.
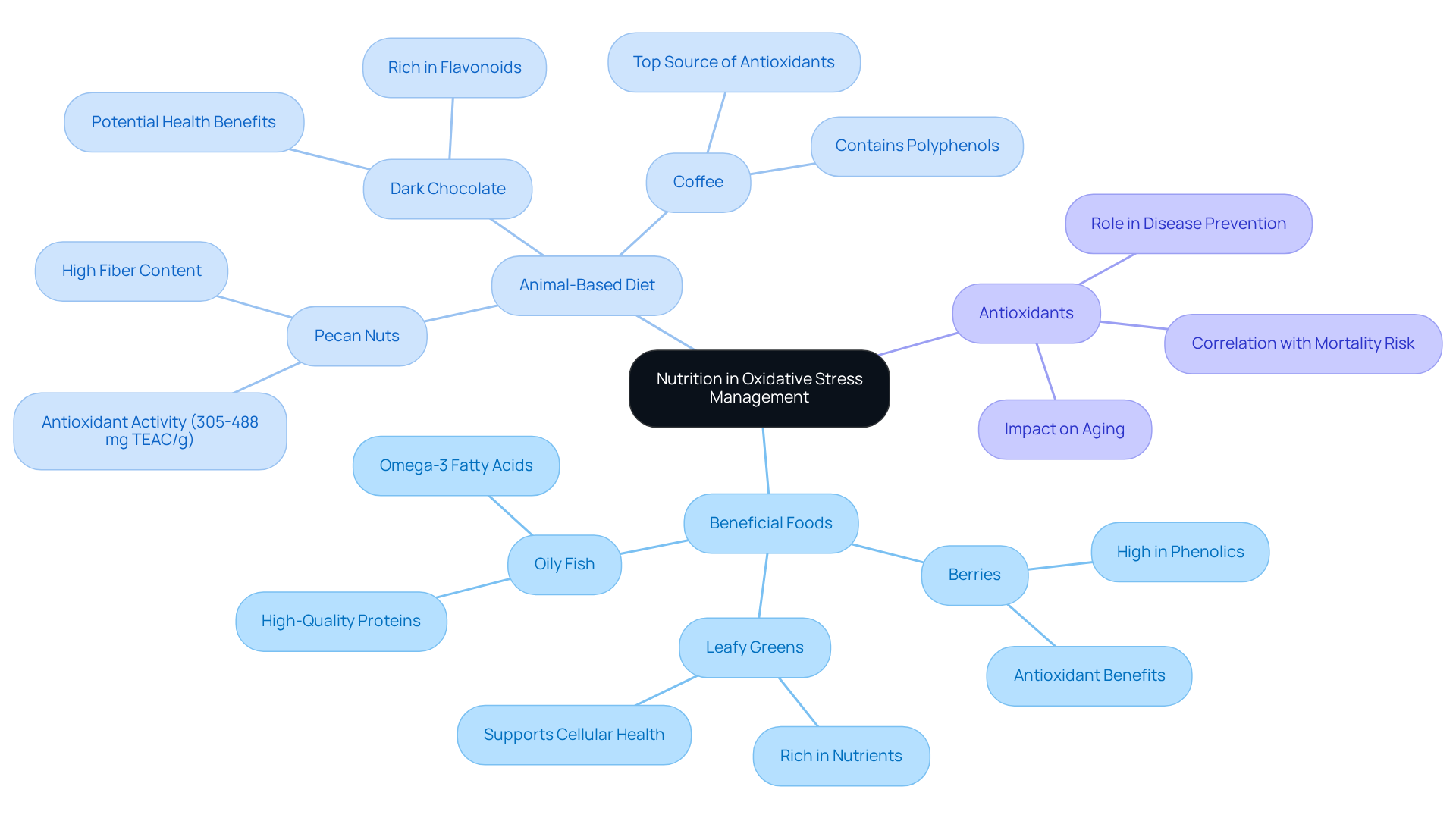
The Role of Nutrition in Oxidative Stress Management
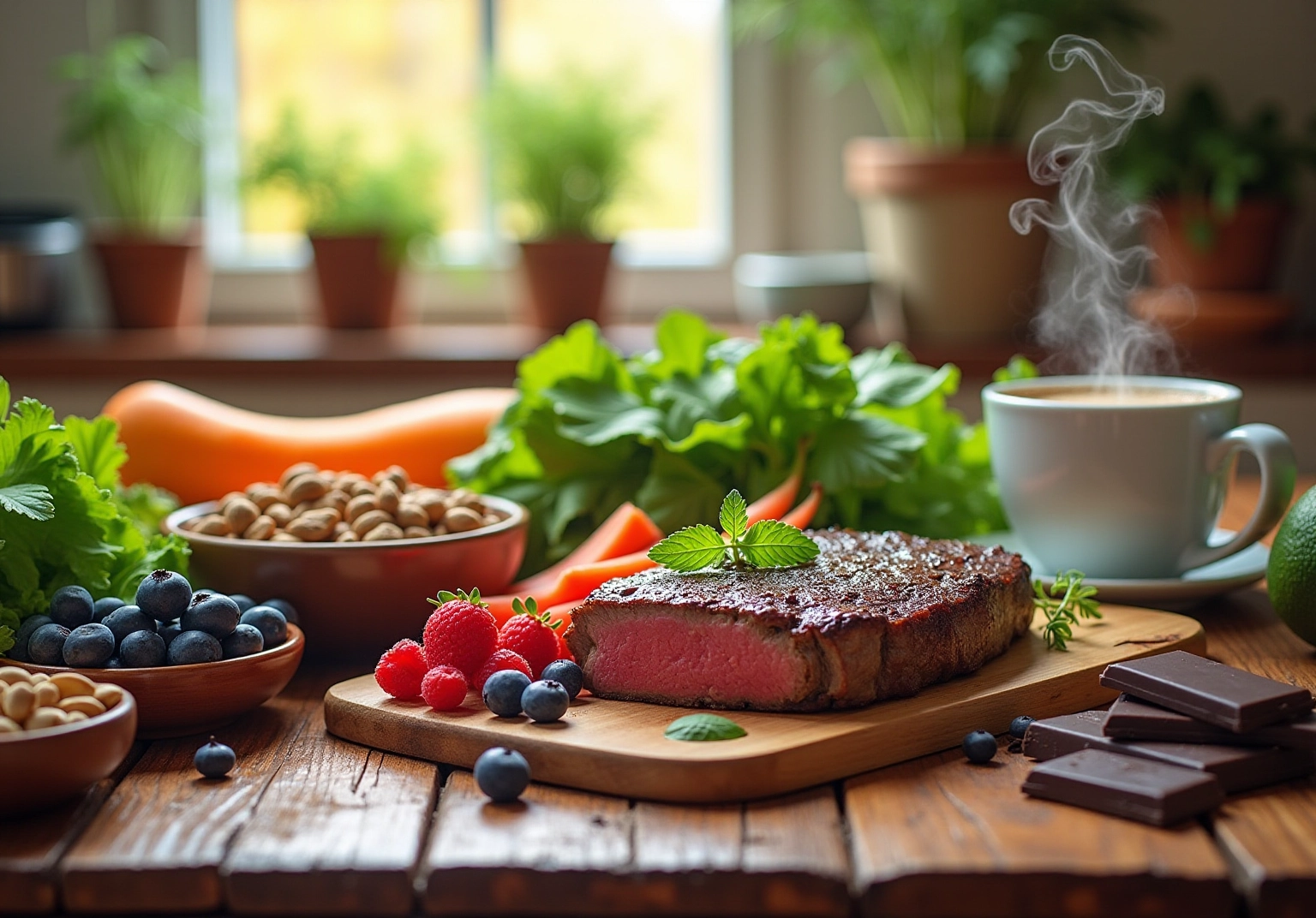
Nutrition plays a crucial role in understanding how can oxidative stress be reversed. Diets rich in beneficial compounds significantly counteract oxidative damage and enhance overall well-being. Berries, leafy greens, and oily fish are well-known for their high levels of protective compounds, supplying essential nutrients that promote cellular health. Furthermore, ByKomi.com underscores the advantages of animal-based diets, which deliver high-quality proteins and nutrients that bolster the body’s defense mechanisms.
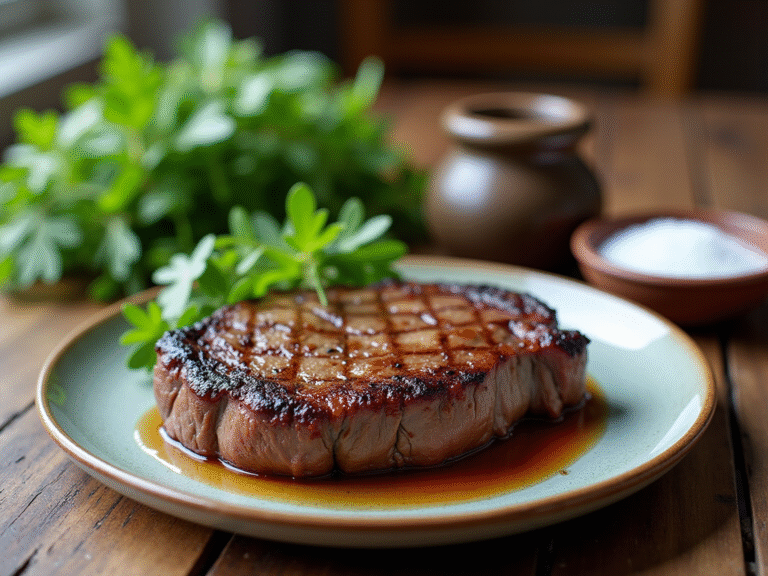
For instance, pecan nuts exhibit protective activity ranging from 305 to 488 mg TEAC/g, while dark chocolate is packed with flavonoids that enhance its protective properties. In addition, coffee stands out as a primary source of protective compounds in the typical U.S. diet. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods—such as savory beef liver patties and perfectly seared ribeye steak, made with two ribeye steaks (about one inch thick), two tablespoons of grass-fed butter, salt, freshly ground black pepper, one tablespoon of olive oil, and fresh herbs for garnish—into daily meals, individuals can not only reduce oxidative stress but also consider how can oxidative stress be reversed to promote healthy aging and vitality, thereby supporting the body’s resilience against age-related decline.
Current research indicates that a diet abundant in antioxidants can lower the risk of chronic diseases. Studies reveal that higher circulating concentrations of antioxidants correlate with a reduced risk of all-cause mortality. This highlights the importance of incorporating both plant and animal sources to achieve optimal health outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding oxidative stress is essential in the pursuit of better health and longevity. This article has explored the intricate relationship between oxidative stress, its causes, and potential reversal strategies. By recognizing the factors that contribute to oxidative imbalance, such as environmental pollutants and poor dietary choices, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate their effects and enhance overall well-being.
Key insights highlight the importance of a nutrient-rich diet, particularly one that includes antioxidants from both plant and animal sources. Furthermore, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and effective stress management are crucial components in combating oxidative stress. Emerging research suggests that innovative environmental interventions may offer new avenues for reversing oxidative damage and promoting cellular regeneration.
As the understanding of oxidative stress continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly clear that making informed lifestyle choices can significantly impact health outcomes. Embracing a balanced diet, engaging in consistent exercise, and considering appropriate supplementation can empower individuals on their journey toward improved health and vitality. The potential to reverse oxidative stress is not just a possibility; it is an actionable goal that underscores the significance of nutrition and lifestyle in fostering resilience against age-related decline and chronic diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress refers to the imbalance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to neutralize them or repair the resulting damage, leading to cellular damage.
What causes oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress occurs when the levels of reactive oxygen species exceed the body’s protective mechanisms, which can happen during metabolic processes.
What are the health implications of oxidative stress?
Oxidative stress is associated with various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders, and it significantly affects aging and the onset of chronic illnesses.
How can oxidative stress be addressed?
Understanding the imbalance of reactive oxygen species is crucial for investigating whether oxidative stress can be reversed. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods can help bolster the body’s antioxidant defenses.
What types of foods can help reduce oxidative stress?
Nutrient-rich foods, particularly those found in carnivore recipes, can provide essential vitamins and minerals that enhance the body’s antioxidant defenses.
How does quality animal-based nutrition relate to oxidative stress?
Prioritizing quality animal-based nutrition may enhance overall health and explore the potential for reversing oxidative stress, aligning with innovative therapies aimed at promoting longevity.






