Does Glycine Make You Sleepy? Discover Its Sleep Benefits
Overview
Glycine can contribute to improved sleep by enhancing sleep quality and promoting relaxation. This amino acid aids in lowering core body temperature and stabilizing sleep patterns. Studies support glycine’s effectiveness, demonstrating its ability to reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and improve overall rest. As a potential natural remedy for sleep difficulties, glycine presents a compelling option for those seeking better sleep.
Furthermore, its role in promoting relaxation makes glycine an appealing choice for individuals struggling with sleep-related issues. By incorporating glycine into your routine, you may experience a smoother transition into restful sleep. If you are interested in exploring natural solutions for sleep, consider learning more about glycine and its benefits.
Introduction
The quest for a good night’s sleep often leads individuals to explore various natural remedies, with glycine emerging as a noteworthy contender. This non-essential amino acid, abundant in protein-rich foods, has been linked to enhanced sleep quality and quicker sleep onset. Such findings pique the interest of those struggling with restless nights. Yet, does glycine truly make one sleepy, or is its role more complex? Delving into the science behind glycine’s calming effects reveals not only its potential benefits but also raises essential questions about its optimal use and safety in promoting restful slumber.
Understand Glycine: The Sleep-Enhancing Amino Acid
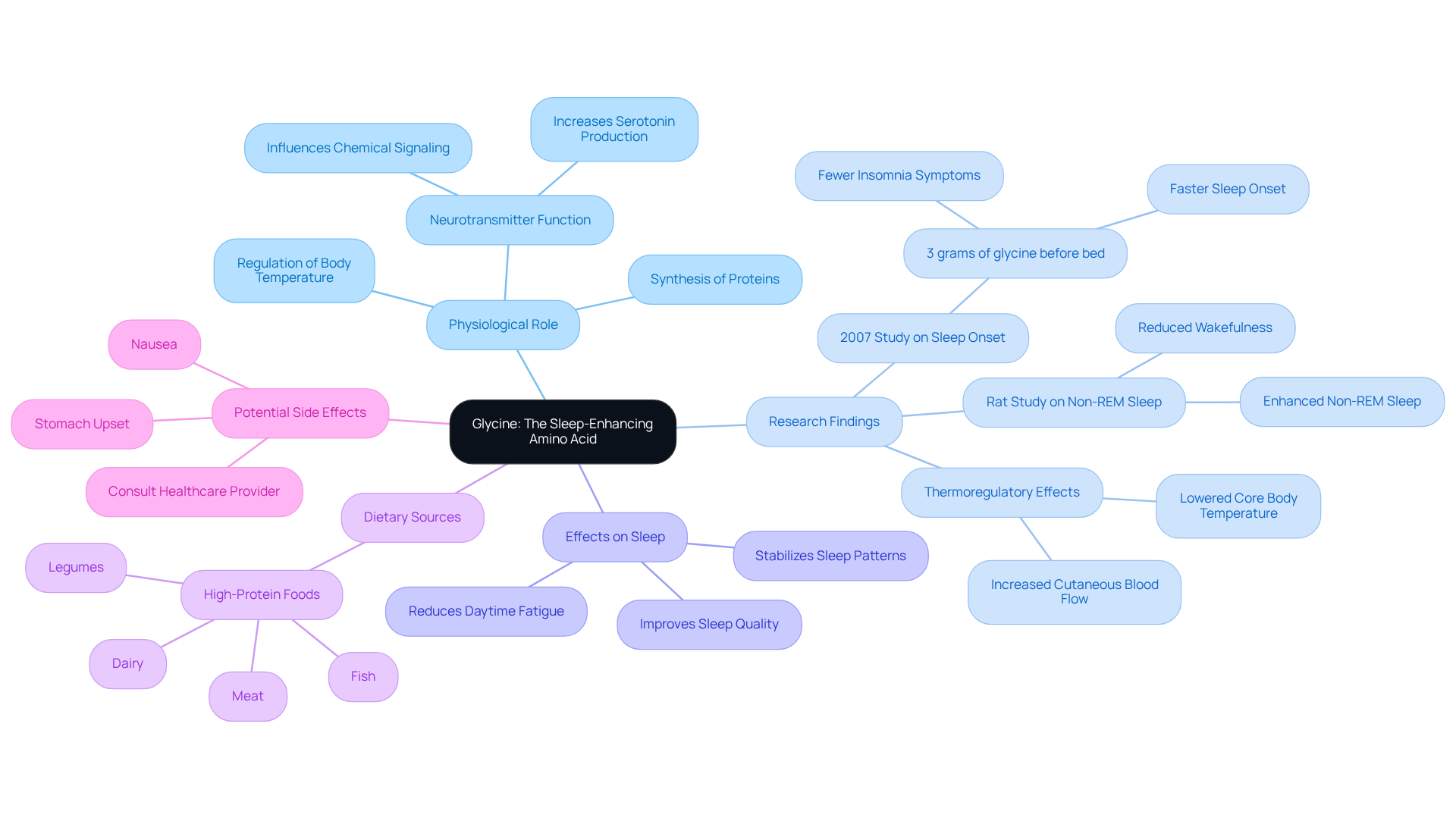
Glycine is a non-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including the synthesis of proteins and neurotransmitters. Naturally abundant in high-protein foods like meat, fish, dairy, and legumes, this amino acid raises the question of whether glycine makes you sleepy, as it is recognized for its soothing effects on the brain that can significantly enhance rest. Studies have demonstrated that glycine can reduce core body temperature, which is a vital element in initiating rest and promoting relaxation, raising the question of whether glycine does make you sleepy, making it an essential ally for individuals facing challenges with sleep.
Recent research has explored if glycine makes you sleepy, highlighting the amino acid’s effectiveness in improving sleep quality. For instance, a 2007 study found that volunteers who consumed 3 grams of glycine before bedtime experienced faster sleep onset and fewer insomnia symptoms, raising the question, does glycine make you sleepy? Moreover, the compound’s ability to stabilize sleep patterns without causing daytime fatigue raises the question of whether glycine does make you sleepy, as underscored in multiple studies, suggesting its potential as a safe alternative to conventional sleep aids.
Case studies further illustrate the impact of glycine on sleep. One study investigated the effects of glycine on sleep quality in rats, revealing that its administration significantly reduced wakefulness and enhanced non-REM sleep during the initial hours post-ingestion. This suggests that glycine not only aids in falling asleep but also raises the question of whether it does glycine make you sleepy and improves the restorative phases of sleep.
Additionally, glycine functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain, influencing chemical signaling and fostering a calming environment, leading to the question of does glycine make you sleepy. Its role in increasing serotonin production, a precursor to melatonin, further emphasizes its significance in regulating sleep cycles, which raises the question: does glycine make you sleepy?
While glycine is generally well-tolerated, potential side effects such as stomach upset and nausea have been reported. Therefore, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before considering long-term glycine supplementation.
In conclusion, the inquiry into whether glycine does make you sleepy reveals its diverse benefits for sleep enhancement, making it an appealing option for those seeking to improve their relaxation and overall well-being. By incorporating glycine-rich foods into your diet or considering supplementation, you may discover a natural remedy to enhance your sleep experience.
Explore How Glycine Promotes Sleep Quality
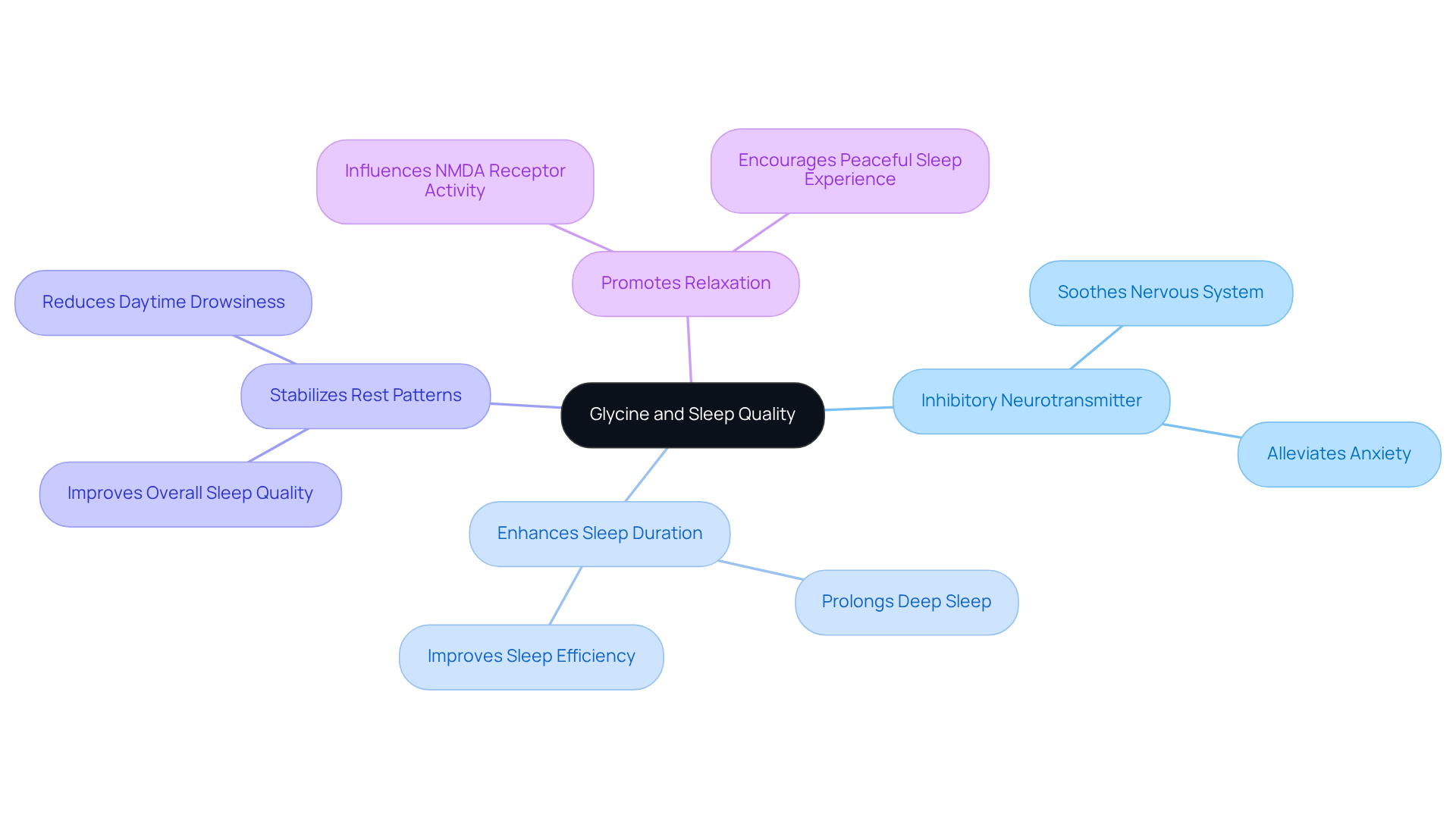
Glycine significantly improves rest quality through multiple mechanisms. As an inhibitory neurotransmitter, it soothes the nervous system and alleviates anxiety, which raises the question: does glycine make you sleepy by considerably decreasing the time it takes to fall asleep, allowing individuals to doze off more swiftly? Studies indicate that this supplement not only enhances rest efficiency but also prolongs the duration of deep slumber, a crucial phase for restorative recovery.
Research has shown that glycine can stabilize rest patterns, leading to an improved overall rest standard and heightened daytime alertness. For instance, a study revealed that consuming 3 grams of this amino acid before bedtime raised the question of whether glycine does make you sleepy, as it resulted in better perceived rest quality and reduced daytime drowsiness. Furthermore, glycine’s role in promoting relaxation is linked to its ability to influence NMDA receptor activity, which may enhance soothing sensations in the brain, thus encouraging a more peaceful rest experience.
Implement Glycine: Dosage and Timing for Optimal Sleep Benefits
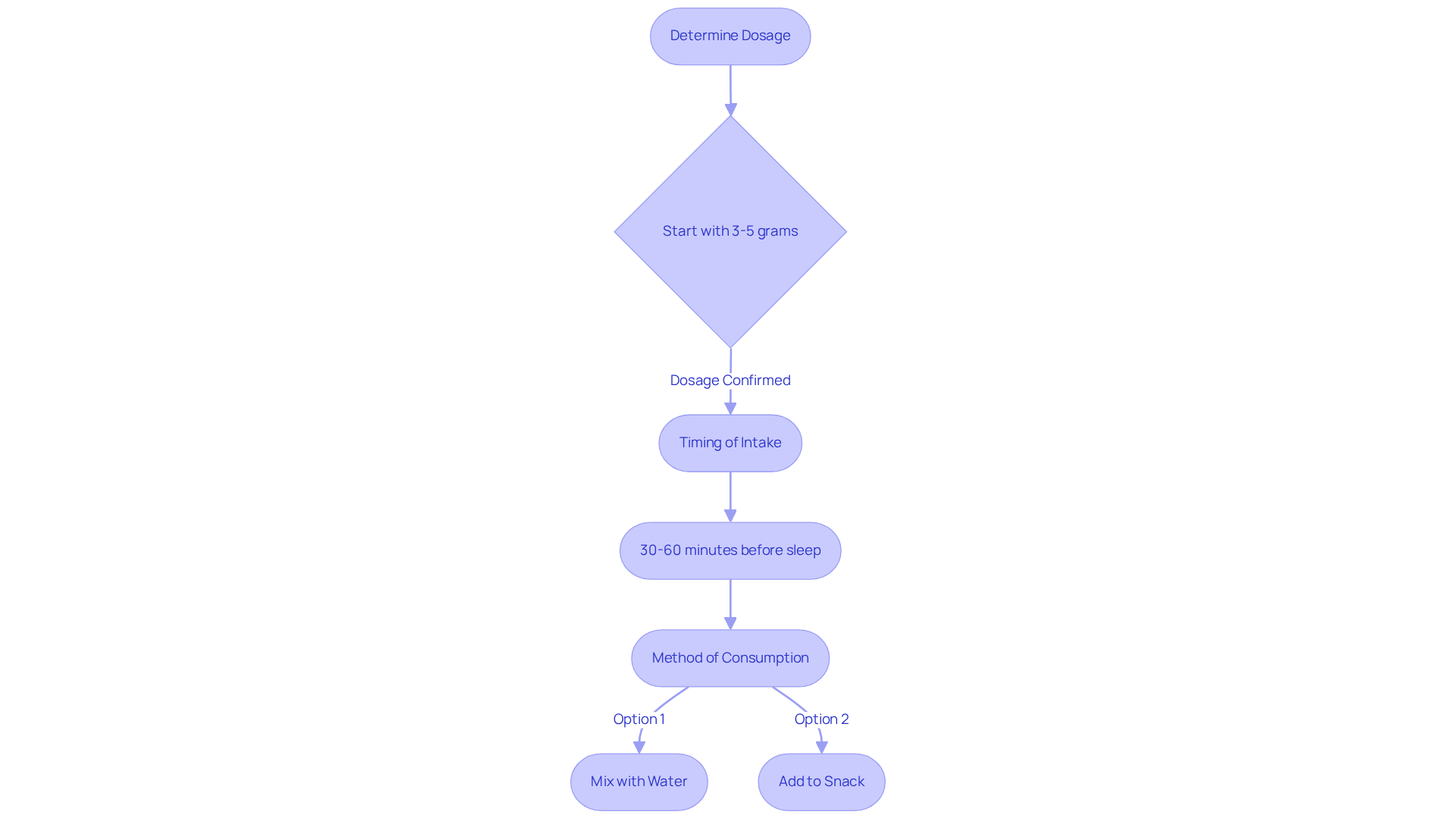
To determine if glycine does make you sleepy, it is typically advised to consume a dosage of 3 to 5 grams about 30 to 60 minutes before sleeping to enjoy its sleep-improving advantages. This timing allows glycine to exhibit its soothing properties as you prepare for rest, as it can lower core body temperature by approximately one degree Celsius during the night. Glycine can be taken in powder form mixed with water or added to a pre-bedtime snack, such as yogurt or a protein shake.
It’s important to start with a lower dose to assess individual tolerance and to adjust as necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. Potential side reactions, such as mild nausea or stomach discomfort, should also be considered. Significantly, this amino acid takes about 30 minutes to be absorbed into the brain after consumption, leading to the question of does glycine make you sleepy, which makes the timing of supplementation essential for optimal sleep benefits.
Consider Safety: Side Effects and Interactions of Glycine
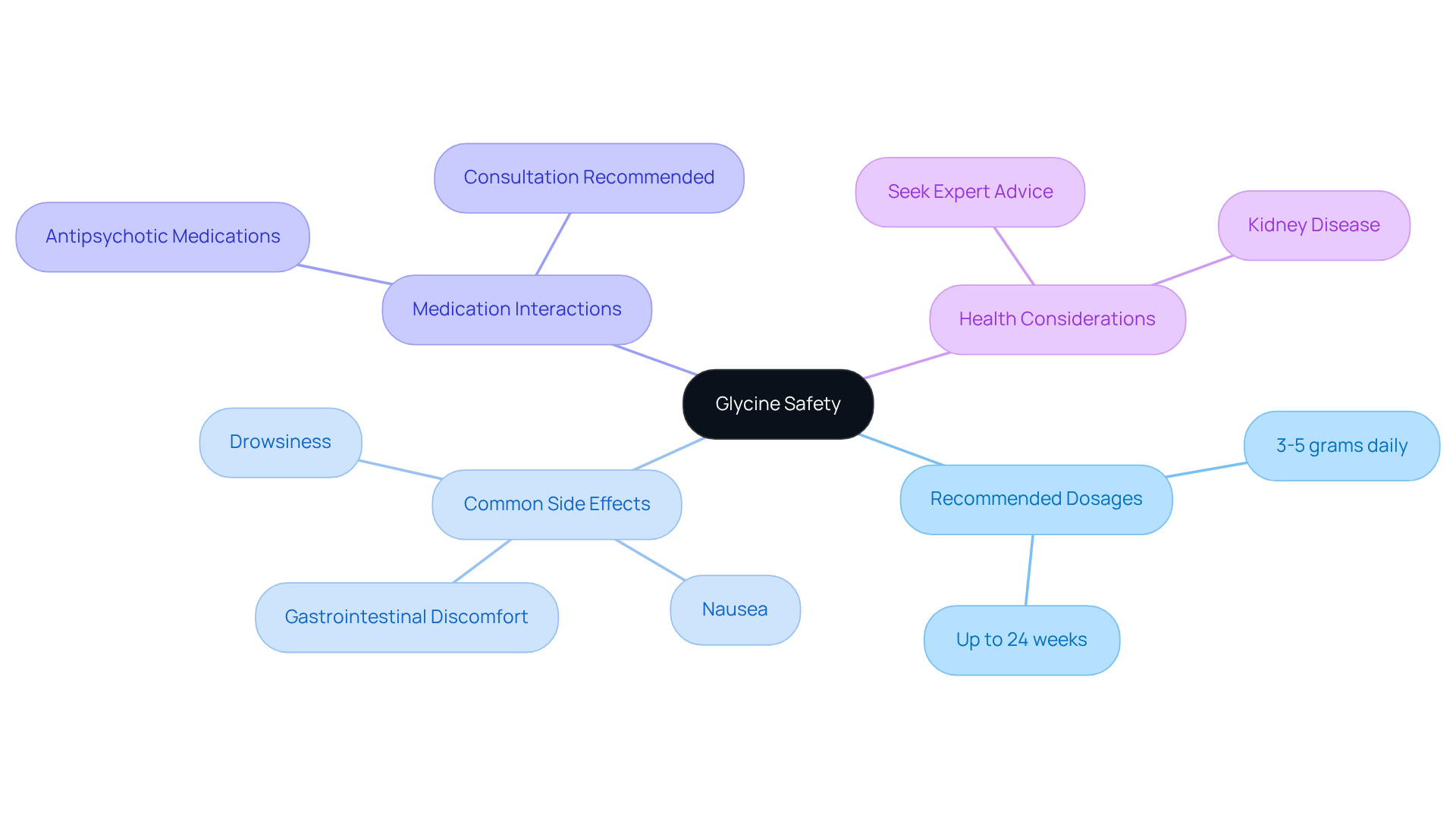
Glycine is widely regarded as safe for most individuals when consumed within recommended dosages, typically ranging from 3 to 5 grams daily. Most commonly, it is taken in doses of up to 3 grams daily for up to 24 weeks. However, some users may encounter mild reactions, including gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or drowsiness, leading to the query of whether glycine does make you sleepy. Caution is especially recommended for individuals using medications that affect the central nervous system, particularly when considering whether glycine does make you sleepy by enhancing their effects.
For instance, individuals on antipsychotic medications such as Clozaril (clozapine) should consult their healthcare provider before beginning amino acid supplements. Interactions may reduce the medication’s effectiveness and exacerbate symptoms. Interestingly, this amino acid supplementation may enhance symptoms of schizophrenia when taken with certain antipsychotic medications, highlighting the complexity of its interactions. Furthermore, individuals with particular health issues, like kidney disease, ought to seek expert advice before using this supplement.
Research has indicated that amounts of up to 90 grams of this amino acid daily have been utilized without significant adverse reactions. Nevertheless, observing your body’s reaction to it is crucial. If any negative reactions occur, it is recommended to stop usage and seek advice from a healthcare provider. Overall, while glycine supplementation can offer benefits, understanding its interactions and potential side effects is essential for safe usage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glycine emerges as a powerful ally in the quest for better sleep, showcasing its remarkable ability to enhance rest quality and promote relaxation. This non-essential amino acid not only aids in falling asleep faster but also stabilizes sleep patterns, making it a compelling option for those grappling with sleep disorders. The inquiry into whether glycine makes you sleepy underscores its multifaceted benefits, suggesting that incorporating this amino acid into one’s routine can lead to significant improvements in sleep quality.
Key insights highlight glycine’s role in reducing core body temperature, its calming effects as a neurotransmitter, and its ability to enhance deep sleep phases. Research supports the idea that consuming glycine before bedtime can lead to quicker sleep onset and a more restorative sleep experience. Furthermore, understanding the appropriate dosage and timing for glycine supplementation is crucial to maximizing its sleep-enhancing properties while minimizing potential side effects.
In light of these findings, those seeking natural solutions to improve their sleep should consider exploring glycine as a viable option. By integrating glycine-rich foods into their diet or opting for supplementation, individuals may unlock a pathway to more restful nights and rejuvenated days. Embracing this amino acid could be a transformative step toward achieving optimal sleep health and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is glycine?
Glycine is a non-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including the synthesis of proteins and neurotransmitters.
How does glycine affect sleep?
Glycine is recognized for its soothing effects on the brain, which can significantly enhance rest by reducing core body temperature, a vital element in initiating sleep and promoting relaxation.
What does research say about glycine and sleep quality?
Research indicates that glycine can improve sleep quality. A 2007 study found that volunteers who consumed 3 grams of glycine before bedtime experienced faster sleep onset and fewer insomnia symptoms.
Does glycine cause daytime fatigue?
Glycine has been shown to stabilize sleep patterns without causing daytime fatigue, making it a potential safe alternative to conventional sleep aids.
Are there any animal studies related to glycine and sleep?
Yes, studies on rats revealed that glycine administration significantly reduced wakefulness and enhanced non-REM sleep, suggesting it aids in falling asleep and improves the restorative phases of sleep.
What role does glycine play in the brain?
Glycine functions as a neurotransmitter, influencing chemical signaling in the brain and fostering a calming environment, which can contribute to sleep regulation.
Can glycine influence serotonin and melatonin production?
Yes, glycine increases serotonin production, which is a precursor to melatonin, further emphasizing its significance in regulating sleep cycles.
Are there any side effects associated with glycine?
While glycine is generally well-tolerated, potential side effects such as stomach upset and nausea have been reported. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before considering long-term glycine supplementation.
How can one incorporate glycine into their diet?
Glycine can be incorporated by consuming glycine-rich foods such as meat, fish, dairy, and legumes, or by considering supplementation to enhance sleep experience.






