Does Lithium Help with Anxiety? Understanding Its Impact and Mechanisms
Overview
Lithium has shown promise in alleviating anxiety symptoms, especially for individuals with mood disorders such as bipolar disorder. By stabilizing emotions and enhancing neurotransmitter balance in the brain, lithium can significantly improve emotional well-being.
Research supports these benefits, detailing lithium’s mechanisms of action and clinical studies that demonstrate substantial reductions in distress among patients. Furthermore, patient reports often indicate improvements in emotional stability, highlighting lithium’s potential as a valuable treatment option.
However, it is crucial to monitor potential side effects and risks associated with lithium use. Understanding these factors can empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their mental health treatment.
In conclusion, exploring lithium as a therapeutic option may offer significant benefits for managing anxiety and mood disorders. For those interested in learning more, consider consulting healthcare professionals or accessing further resources on this topic.
Introduction
The intricate relationship between mental health and treatment options has sparked renewed interest in the effects of lithium, particularly its potential to alleviate anxiety.
With a complex mechanism that influences neurotransmitter systems and promotes emotional stability, lithium may present a unique solution for those grappling with anxiety disorders.
However, the question remains: can this well-known mood stabilizer truly provide relief for anxiety, or do the risks and side effects overshadow its benefits?
Exploring this topic reveals not only the science behind lithium’s action in the brain but also the nuanced considerations necessary for effective mental health management.
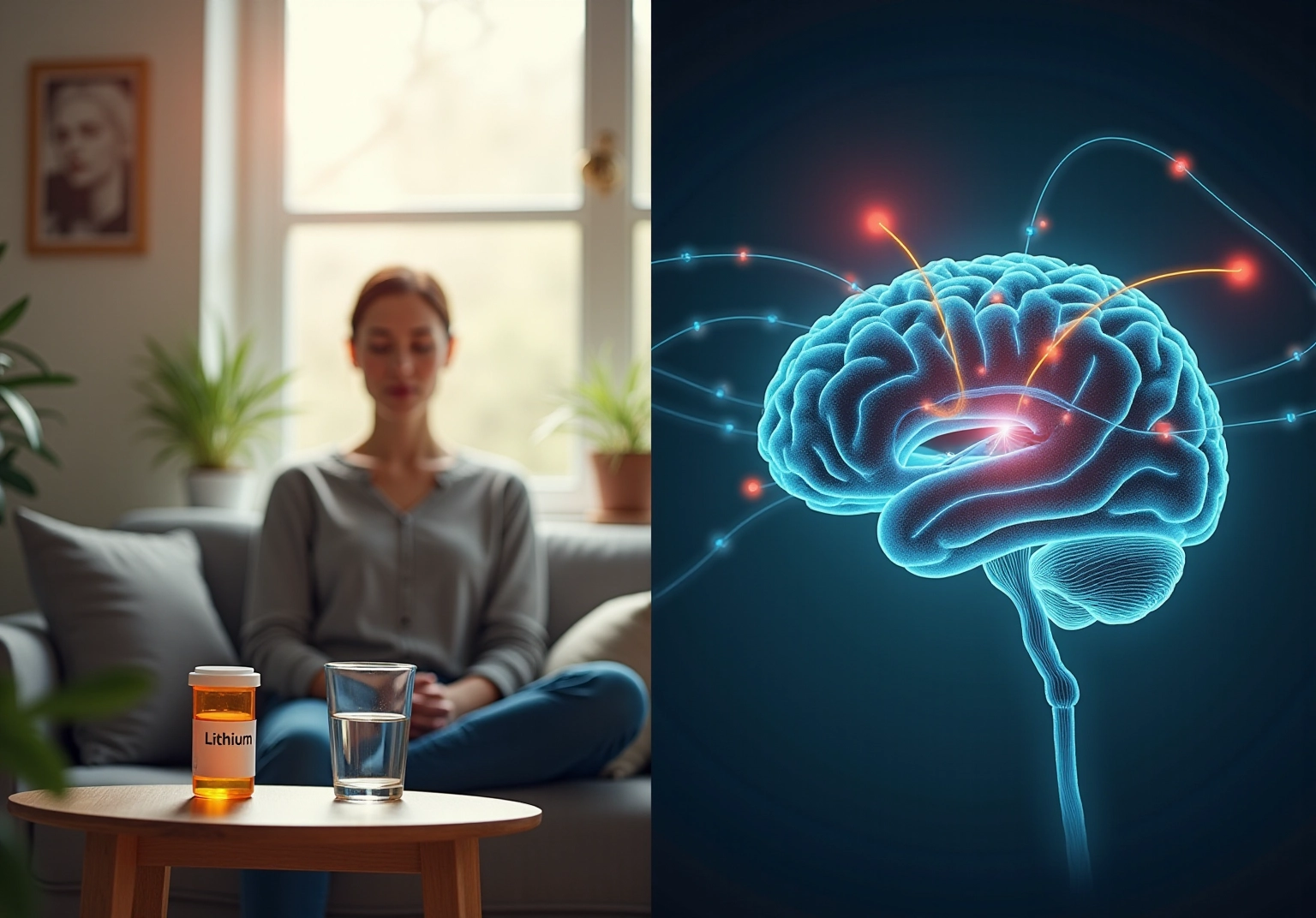
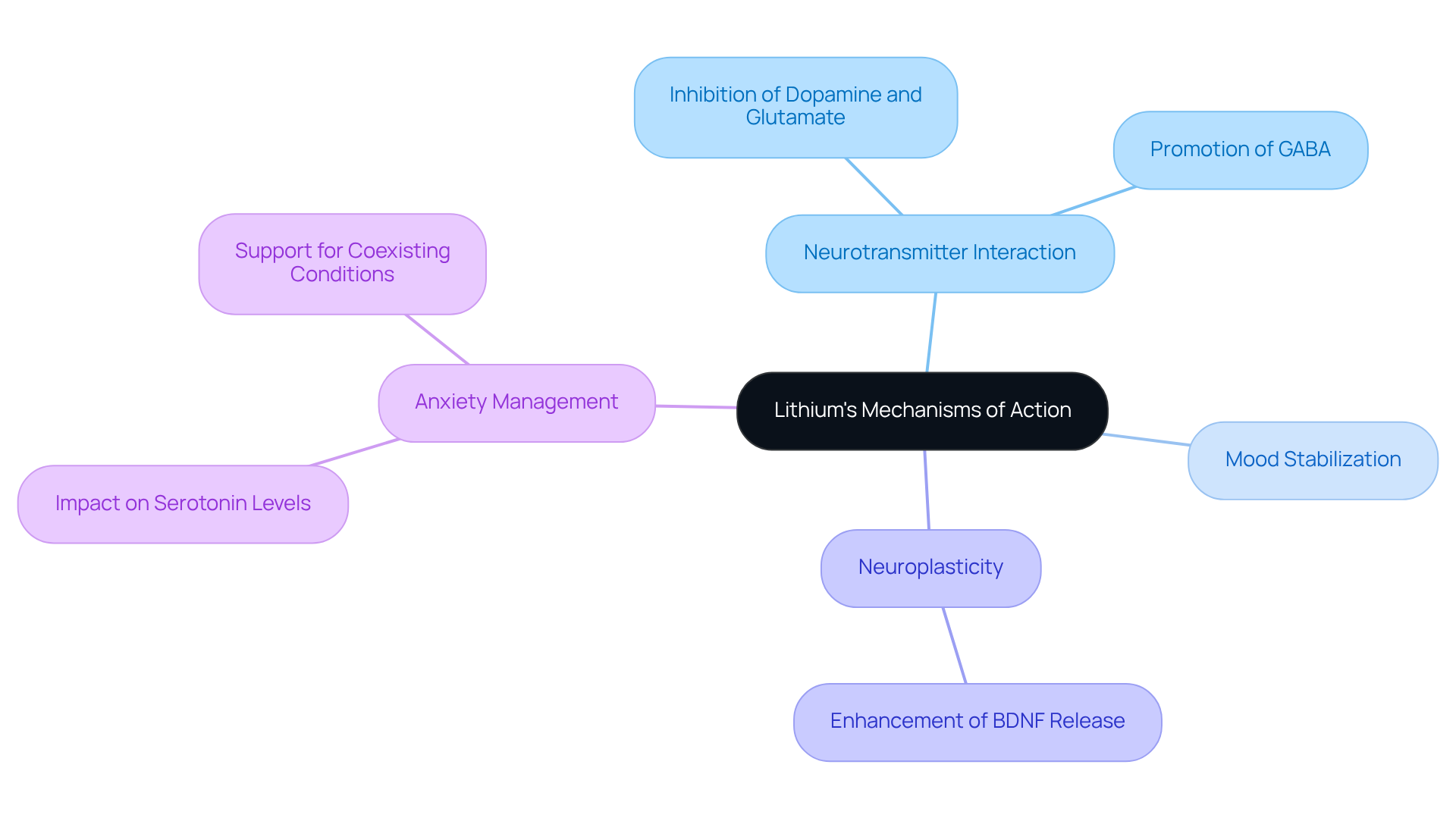
Understand Lithium’s Mechanisms of Action in the Brain
Lithium’s mechanisms of action are complex and multifaceted, primarily involving its interaction with neurotransmitter systems in the brain. It inhibits excitatory neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate while promoting GABA-mediated neurotransmission. This dual action helps stabilize emotions and decrease symptoms of worry, leading to the inquiry of whether lithium helps with anxiety. Furthermore, lithium has been shown to enhance the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is essential for neuroplasticity and overall brain health. By adjusting these neurotransmitter systems, lithium can assist in restoring equilibrium in individuals experiencing mood issues, leading to the inquiry of whether lithium helps with anxiety.
Studies suggest that this treatment can lead to significant changes in brain chemistry, including modifications in serotonin levels, frequently associated with stress-related conditions. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for recognizing how lithium helps with anxiety and can serve as a viable treatment alternative for managing stress, particularly in individuals with coexisting conditions such as bipolar syndrome. This knowledge empowers individuals to explore effective strategies for mood stabilization and overall mental health.
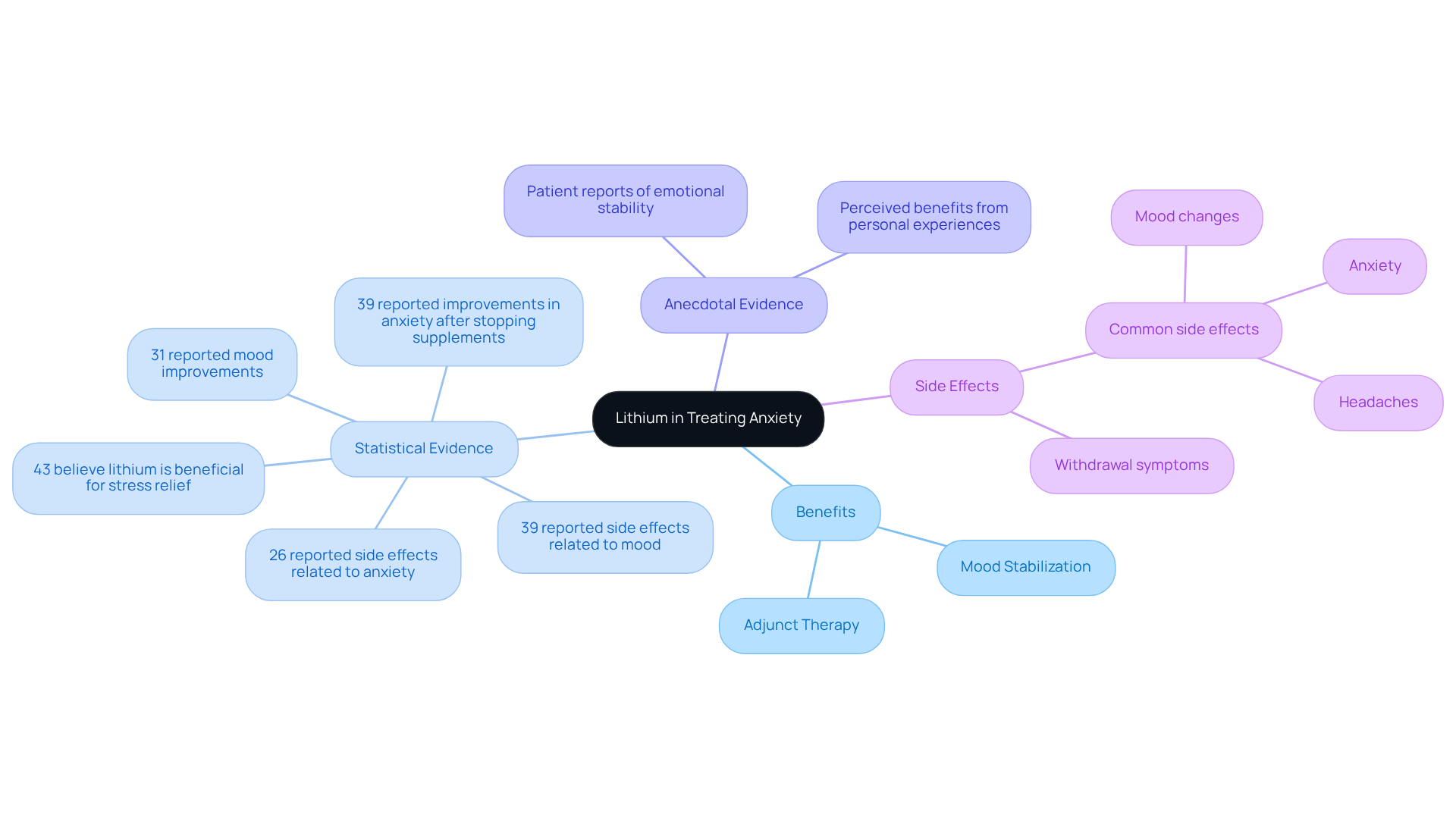
Examine Lithium’s Role in Treating Anxiety and Related Disorders
Lithium has long been recognized for its effectiveness in managing mood disorders, leading many to ask, does lithium help with anxiety? Clinical research indicates that this element can lead to significant reductions in distress symptoms, especially in individuals with bipolar disorder. For example, studies have shown that lithium treatment is linked to notable improvements in stress levels, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic option.
Furthermore, the element serves as an adjunct therapy for coexisting anxiety in bipolar patients, supported by numerous studies that demonstrate its efficacy both as a standalone treatment and in conjunction with other medications. This dual functionality allows lithium to stabilize mood and decrease the frequency of distress episodes, which leads to the consideration of whether does lithium help with anxiety-related challenges.
Anecdotal evidence from patients also suggests that this medication can effectively alleviate severe distress, promoting a sense of emotional stability and control. Notably, 43% of respondents in a recent survey believed that lithium was beneficial for stress relief, while 39% reported improvements in their condition after discontinuing its supplements.
However, it is crucial to consider the potential side effects and withdrawal symptoms, which were found to be more common than expected among participants. This highlights the importance of viewing lithium as a viable therapeutic option for managing stress and raises the question: does lithium help with anxiety, particularly in complex cases involving emotional difficulties?
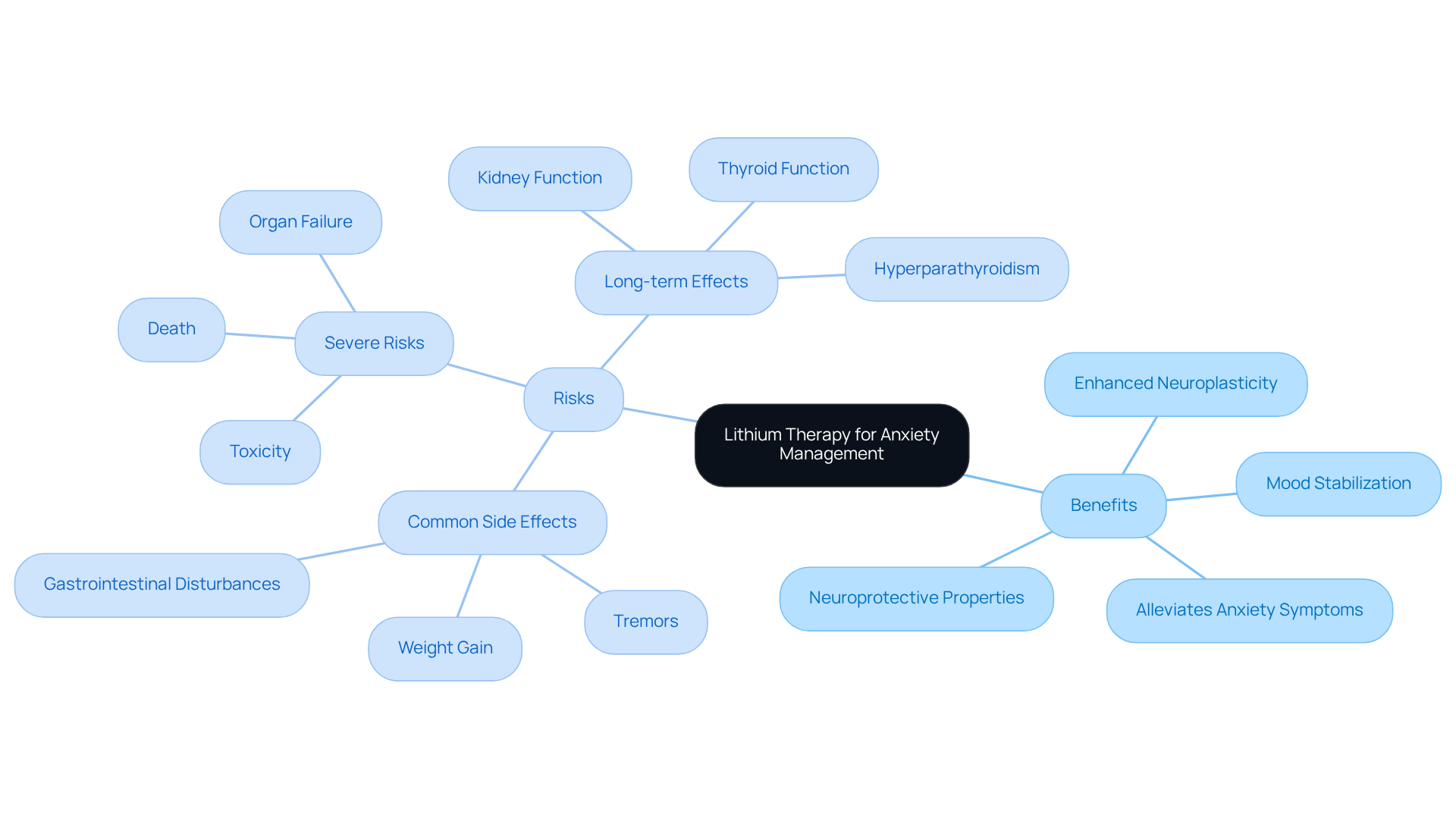
Evaluate the Benefits and Risks of Lithium for Anxiety Management
One of the key discussions around lithium therapy is whether it does lithium help with anxiety. It aids in mood stabilization, alleviates anxiety symptoms, and lowers the risk of suicide in patients with bipolar disorder. Additionally, its neuroprotective properties and ability to enhance neuroplasticity further enrich its therapeutic profile.
However, it is essential to weigh these benefits against potential risks. Common side effects include:
- Tremors
- Weight gain
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
Studies show that approximately 67-90% of individuals using this medication experience at least one side effect. More severe risks involve toxicity, which can lead to serious health complications, including organ failure or death if levels exceed 3.0 mEq/L. Therefore, routine blood examinations are crucial to ensure that medication levels remain within the therapeutic range, typically between 0.6-1.2 mEq/L.
Moreover, prolonged use of lithium may affect kidney and thyroid function, necessitating continuous medical oversight. This includes monitoring sodium levels and kidney performance. Interestingly, lithium-induced hyperparathyroidism occurs four times more frequently in females than in males. Given these considerations, it is vital for patients and healthcare professionals to engage in thorough discussions about whether does lithium help with anxiety management, carefully evaluating the benefits against potential risks.
Furthermore, ongoing research is investigating lithium’s possible effects on cellular repair, neurogenesis, and overall lifespan. Its combination with conventional antidepressants may also offer additional benefits for certain patients. Engaging in these discussions can lead to better-informed decisions regarding treatment options.
Conclusion
Lithium’s potential role in alleviating anxiety symptoms has garnered significant attention, particularly due to its multifaceted mechanisms of action within the brain. By influencing neurotransmitter systems, lithium stabilizes mood and promotes emotional balance. This suggests that it could be a valuable tool for those grappling with anxiety, especially in the context of mood disorders like bipolar disorder.
The article explores various aspects of lithium’s effectiveness, highlighting clinical research that supports its use in reducing distress symptoms and enhancing emotional stability. Furthermore, evidence of its role as an adjunct therapy for anxiety in individuals with coexisting conditions underscores its potential benefits. However, it is essential to consider the associated risks and side effects, which can impact patient outcomes and necessitate careful monitoring.
Ultimately, the exploration of lithium as a treatment for anxiety reveals both its promise and the complexities involved in its use. As ongoing research delves deeper into its effects on brain chemistry and potential applications, it becomes increasingly important for patients and healthcare professionals to engage in informed discussions about treatment options. Understanding the balance between benefits and risks is crucial for optimizing mental health management and improving quality of life for those affected by anxiety and related disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary mechanisms of action of lithium in the brain?
Lithium primarily interacts with neurotransmitter systems by inhibiting excitatory neurotransmitters like dopamine and glutamate, while promoting GABA-mediated neurotransmission.
How does lithium affect emotional stability?
By its dual action on neurotransmitter systems, lithium helps stabilize emotions and decrease symptoms of worry.
Does lithium help with anxiety?
Yes, lithium’s mechanisms of action suggest it can help with anxiety by stabilizing mood and adjusting neurotransmitter systems.
What role does brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) play in lithium’s effects?
Lithium enhances the release of BDNF, which is essential for neuroplasticity and overall brain health.
How does lithium influence serotonin levels?
Studies suggest that lithium can lead to modifications in serotonin levels, which are frequently associated with stress-related conditions.
Who might benefit from lithium treatment?
Individuals experiencing mood issues, particularly those with coexisting conditions such as bipolar syndrome, may find lithium to be a viable treatment alternative for managing stress and mood stabilization.