How to Improve Mitochondrial Function Through Diet and Exercise
Overview
To enhance mitochondrial function, individuals should prioritize a blend of dietary strategies, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications. Nutrient-dense foods play a vital role, while both aerobic and resistance training are essential components. Additionally, effective stress management and quality sleep are crucial for promoting mitochondrial health and optimizing overall cellular performance. Research supports the connection between these practices and improved energy metabolism, as well as reduced oxidative stress. By adopting these strategies, individuals can significantly boost their mitochondrial function and overall well-being.
Introduction
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for producing the energy that fuels nearly every biological process. Their proper functioning is critical not only for energy production but also for overall cellular health. Dysfunction in these organelles has been linked to various health issues, including metabolic disorders and accelerated aging.
This article delves into effective strategies for enhancing mitochondrial function through targeted dietary choices and exercise routines. By adopting these practices, readers can unlock greater vitality and well-being. However, with so much conflicting information available, how can one discern the most effective methods to support these vital cellular structures? Let’s explore this important topic together.
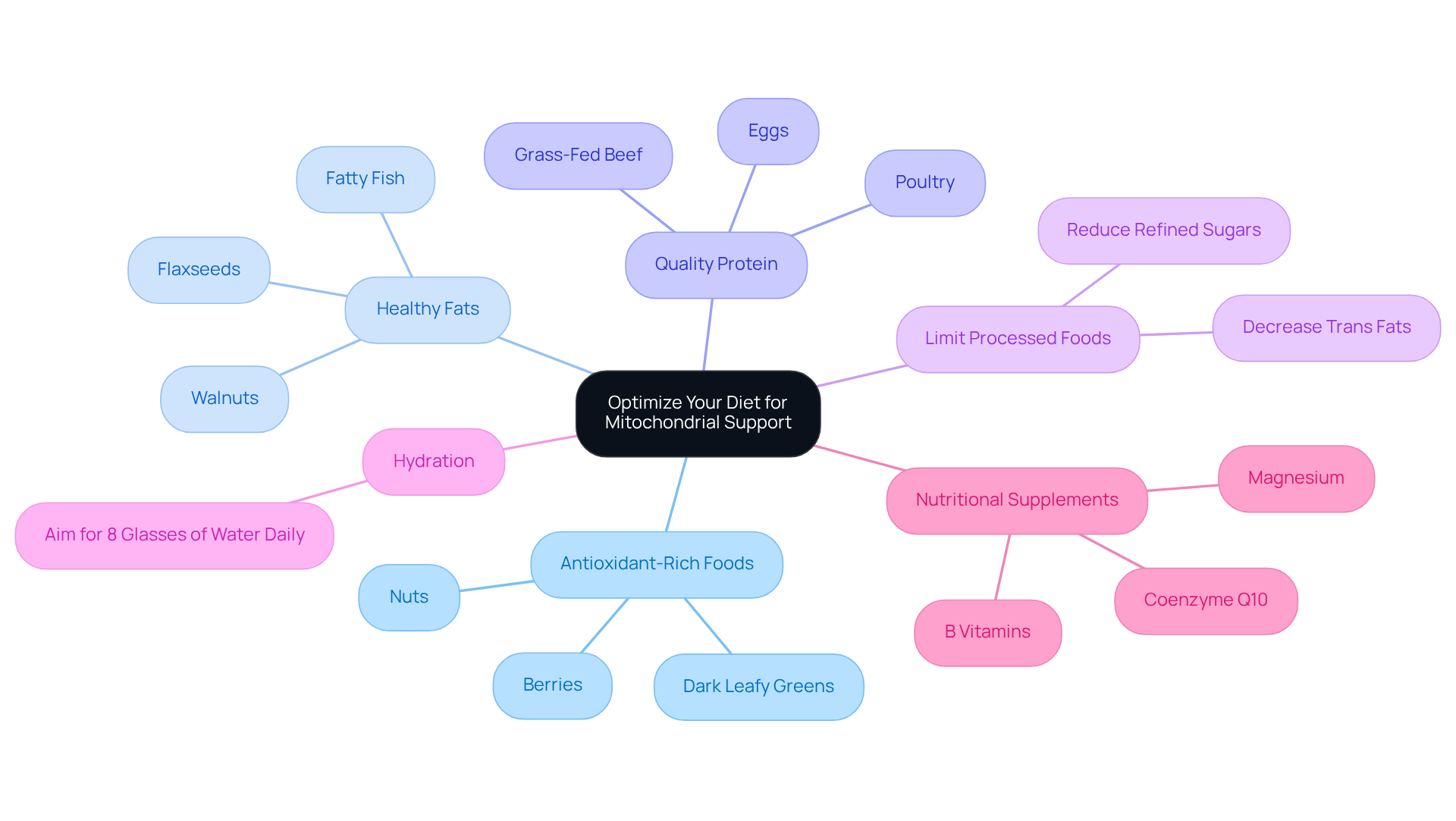
Understand Mitochondrial Function and Its Importance
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of nearly all eukaryotic cells, play a crucial role in producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell. Their importance extends beyond energy production; they are vital in cellular metabolism and sustaining overall cellular well-being. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to various wellness issues, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and even the aging process. Understanding how to improve mitochondrial function is essential for enhancing the health of these cellular structures through nutritional and physical activity strategies.
Key functions of mitochondria include:
- ATP Production: Mitochondria convert nutrients into ATP via oxidative phosphorylation, a process vital for energy supply. This underscores the significance of quality nutrition, particularly animal-based foods, which can provide essential nutrients for optimal cellular performance.
- Regulation of Metabolism: They are integral to the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, influencing overall metabolic health. The Hunza people, known for their longevity, often consume a diet rich in whole foods, supporting their metabolic health and cellular activity.
- Calcium Homeostasis: Mitochondria regulate intracellular calcium levels, crucial for various cellular activities, including muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release.
- Apoptosis Regulation: They play a key role in programmed cell death, a necessary process for maintaining healthy tissue and preventing cancerous growth.
Research indicates that dysfunction in these cellular energy factories can significantly impact aging. Studies show that reduced oxidative capacity in mitochondria correlates with increased cardiovascular disease risk. Furthermore, engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to enhance cellular function, potentially reducing the risk of age-related illnesses. By prioritizing how to improve mitochondrial function through informed lifestyle choices, including innovative dietary strategies like the carnivore diet, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and vitality. Personal experiences from those who have adopted a carnivore diet suggest that such dietary choices may lead to improved energy levels and overall health, further emphasizing the connection between nutrition and cellular processes.
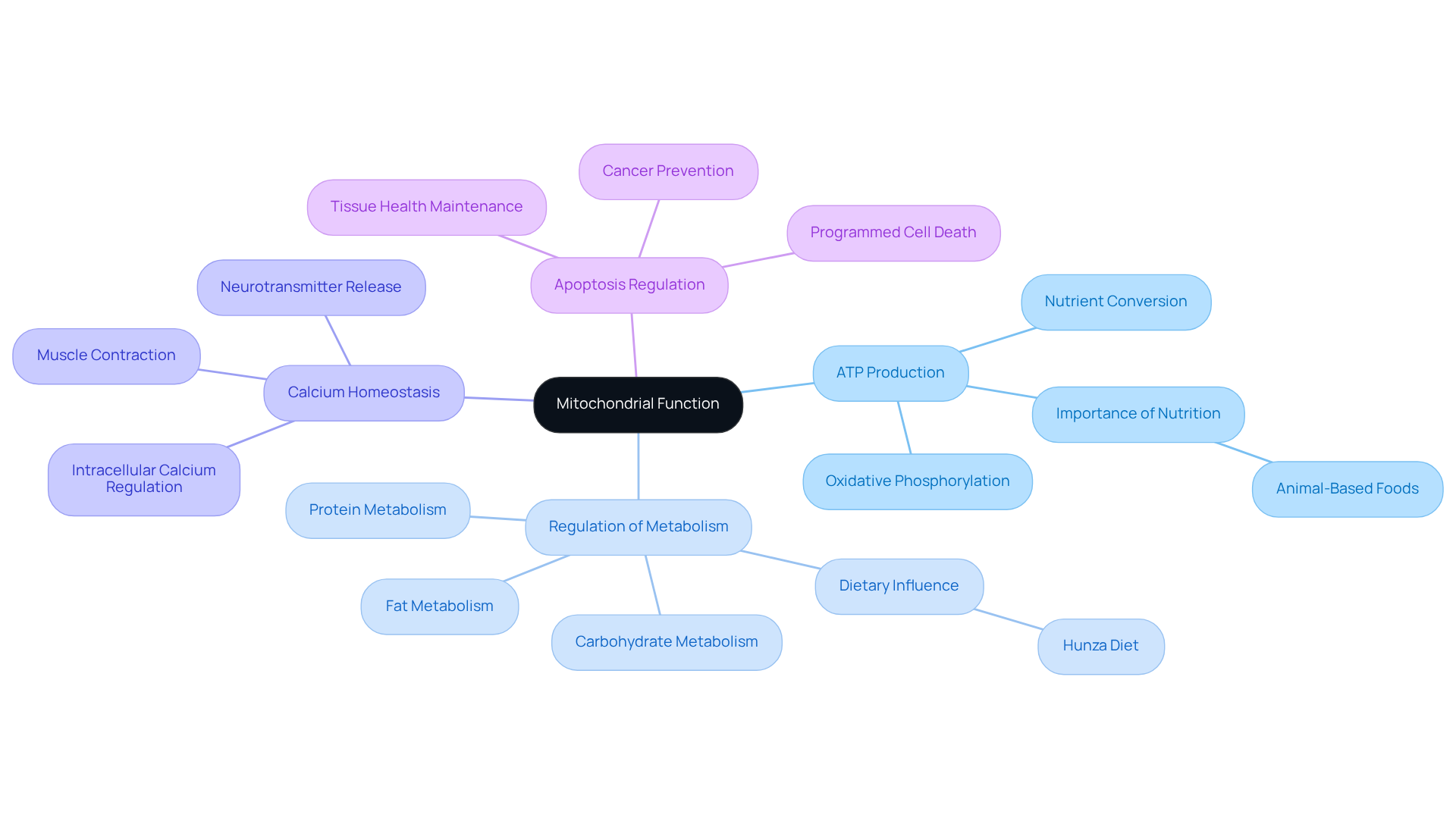
Optimize Your Diet for Mitochondrial Support
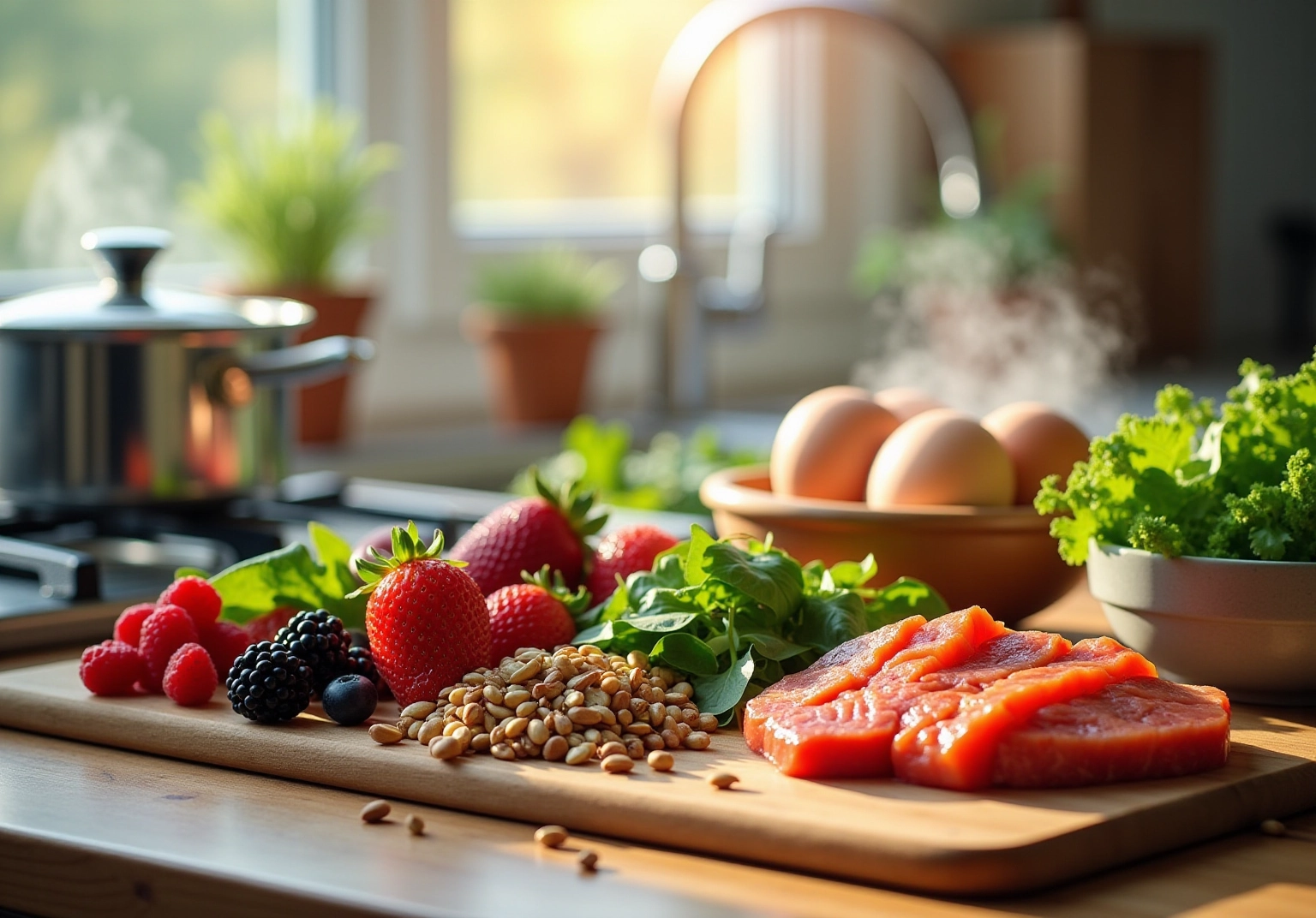
To enhance your diet for cellular support, focus on incorporating nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Here are some dietary strategies:
- Include Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, dark leafy greens, and nuts, help combat oxidative stress, which can damage mitochondria. Research indicates that diets abundant in antioxidants can significantly enhance cellular performance and provide knowledge on how to improve mitochondrial function while reducing oxidative harm.
- Prioritize Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These fats are essential for maintaining membrane integrity and improving overall performance. Research shows that omega-3 supplementation can lead to a 320% increase in DHA levels in cell membranes, enhancing energy metabolism.
- Consume Quality Protein: Include high-quality animal-based proteins, such as grass-fed beef, eggs, and poultry. These foods provide vital amino acids necessary for cellular activity and repair, which are important when considering how to improve mitochondrial function and supporting overall cellular health.
- Limit Processed Foods: Decrease the intake of highly processed foods that can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, negatively impacting cellular health. A diet low in trans fats and refined sugars is essential for understanding how to improve mitochondrial function.
Staying hydrated is vital for peak cellular performance and is an essential aspect of how to improve mitochondrial function, including energy production. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily to support metabolic processes. - Consider Nutritional Supplements: Supplements such as Coenzyme Q10, B vitamins, and magnesium can support cellular energy production, particularly if dietary intake is lacking. For example, CoQ10 is essential for ATP production and has been shown to enhance energy metabolism in individuals facing oxidative stress.
By focusing on these dietary approaches, you can create a nutrient-rich eating plan that promotes cellular health and overall well-being.
Incorporate Exercise to Enhance Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Incorporating consistent physical activity into your routine is vital for understanding how to improve mitochondrial function, the very process through which new mitochondria are created. Here are some effective exercise strategies to consider:
- Engage in Aerobic Exercise: Activities such as running, cycling, and swimming stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week. Research indicates that physical training can enhance cellular energy structures in skeletal muscle, with variations between 10% to 90% depending on the training method.
- Include Resistance Training: Strength training activities, including weight lifting or bodyweight routines, can also improve cellular health. Aim for at least two sessions per week.
- Try High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense activity followed by rest periods are an effective method for how to improve mitochondrial function. Incorporate HIIT workouts 1-2 times a week.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is crucial. Develop a physical activity regimen that you enjoy to ensure lasting commitment. As David Bishop noted, physical activity is one of the most economical ways to control and prevent various illnesses, making it a valuable component of your wellness routine.
- Monitor Progress: Track your workouts and gradually increase intensity or duration to continue challenging your mitochondria. Consider metrics such as endurance levels, recovery times, and overall energy levels to assess improvements in cellular performance.
By integrating these activity techniques, you can effectively boost cellular biogenesis and enhance overall energy generation, which demonstrates how to improve mitochondrial function, leading to improved well-being and vitality as you age.
Prioritize Lifestyle Changes for Mitochondrial Health
In addition to diet and exercise, several lifestyle changes can significantly show how to improve mitochondrial function.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic stress adversely affects mitochondrial function, leading to oxidative stress and cellular damage. Incorporating stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine can lessen these effects and enhance cellular resilience.
-
Prioritize Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for cellular repair and optimal performance. Strive for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted rest each night. Studies show that poor sleep quality is associated with diminished cellular activity and heightened oxidative stress.
-
Limit Toxin Exposure: Environmental toxins, such as heavy metals and pollutants, can hinder cellular activity. Reducing exposure by using air purifiers and opting for organic produce can help protect your mitochondria from harmful substances.
-
Stay Socially Active: Participating in social events not only improves mental well-being but also decreases stress, positively affecting cellular function. A helpful social network can promote emotional resilience, which is essential for sustaining cellular activity.
-
Consider Fasting: Intermittent fasting has been demonstrated to enhance cellular energy production and improve metabolic well-being. Trying fasting methods that suit your way of life can enhance cellular processes and overall vitality.
By prioritizing these lifestyle changes, you can create an environment conducive to how to improve mitochondrial function, which enhances their performance and promotes overall well-being.
Conclusion
Improving mitochondrial function is essential for enhancing overall health and vitality. By understanding the pivotal role that mitochondria play in energy production and cellular well-being, individuals can adopt effective dietary and lifestyle strategies that bolster these cellular powerhouses. Emphasizing quality nutrition, regular physical activity, and mindful lifestyle choices can lead to significant improvements in mitochondrial health.
Key insights from the article highlight the importance of:
- Nutrient-dense foods rich in antioxidants
- Healthy fats
- Quality proteins
- Reduction in processed foods
Incorporating consistent exercise—particularly:
- Aerobic activity
- Resistance training
- High-intensity interval training
is crucial for stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis. Furthermore, prioritizing:
- Stress management
- Quality sleep
- Social engagement
further supports mitochondrial function, creating a holistic approach to health.
Ultimately, the journey to enhancing mitochondrial function is multifaceted, requiring a commitment to informed dietary choices, regular exercise, and positive lifestyle changes. By taking actionable steps toward optimizing mitochondrial health, individuals can not only improve their energy levels and metabolic performance but also pave the way for a healthier, more vibrant life. Embrace these strategies today to unlock the full potential of your cellular powerhouses and enhance your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are mitochondria and why are they important?
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of nearly all eukaryotic cells, crucial for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell. They are vital for cellular metabolism and overall cellular well-being.
What are the key functions of mitochondria?
Key functions of mitochondria include ATP production, regulation of metabolism (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins), calcium homeostasis, and regulation of apoptosis (programmed cell death).
How do mitochondria contribute to energy production?
Mitochondria convert nutrients into ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, which is essential for supplying energy to cells. This highlights the importance of quality nutrition for optimal mitochondrial function.
What is the relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and health issues?
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to various wellness issues, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and the aging process. Reduced mitochondrial function can significantly impact aging and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
How can one improve mitochondrial function?
Improving mitochondrial function can be achieved through informed lifestyle choices, including nutritional strategies (like the carnivore diet) and regular physical activity, which enhances cellular function and may reduce the risk of age-related illnesses.
What dietary strategies are suggested for enhancing mitochondrial function?
Innovative dietary strategies, such as a diet rich in whole foods or the carnivore diet, are suggested to support mitochondrial function and overall metabolic health, as seen in the dietary habits of the Hunza people known for their longevity.
What personal experiences have been reported regarding the carnivore diet and mitochondrial health?
Personal experiences from individuals who have adopted a carnivore diet suggest improvements in energy levels and overall health, highlighting the connection between nutrition and mitochondrial function.