Low Dose Naltrexone Anxiety: Understand Dosage, Benefits, and Side Effects
Overview
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) presents a promising option for treating anxiety. By enhancing endorphin levels, LDN not only improves mood but also reduces symptoms of worry and depression. Clinical studies underscore its effectiveness, particularly for individuals facing anxiety linked to chronic pain or autoimmune conditions. This dual approach addresses both the psychological and physiological dimensions of anxiety, making it a comprehensive treatment choice.
The benefits of LDN are noteworthy. It offers a unique solution that targets the root causes of anxiety while promoting overall well-being. For those struggling with anxiety, exploring LDN could be a valuable step toward relief. As research continues to unfold, it is essential to stay informed about such innovative treatments.
Introduction
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) is emerging as a potential game-changer in anxiety treatment, offering a unique approach that intertwines mental and physical health. By harnessing the power of this opioid receptor antagonist, individuals grappling with anxiety may find relief not only from their mental burdens but also from the chronic pain and inflammation that often accompany these conditions.
However, with its promise comes a set of questions:
- How exactly does LDN work to alleviate anxiety symptoms?
- What should patients be aware of regarding dosage and potential side effects?
Exploring these facets can illuminate the path toward a more balanced state of well-being. As a result, understanding LDN’s role in anxiety treatment becomes essential for those seeking effective solutions.
Understand Low Dose Naltrexone: Mechanism and Benefits
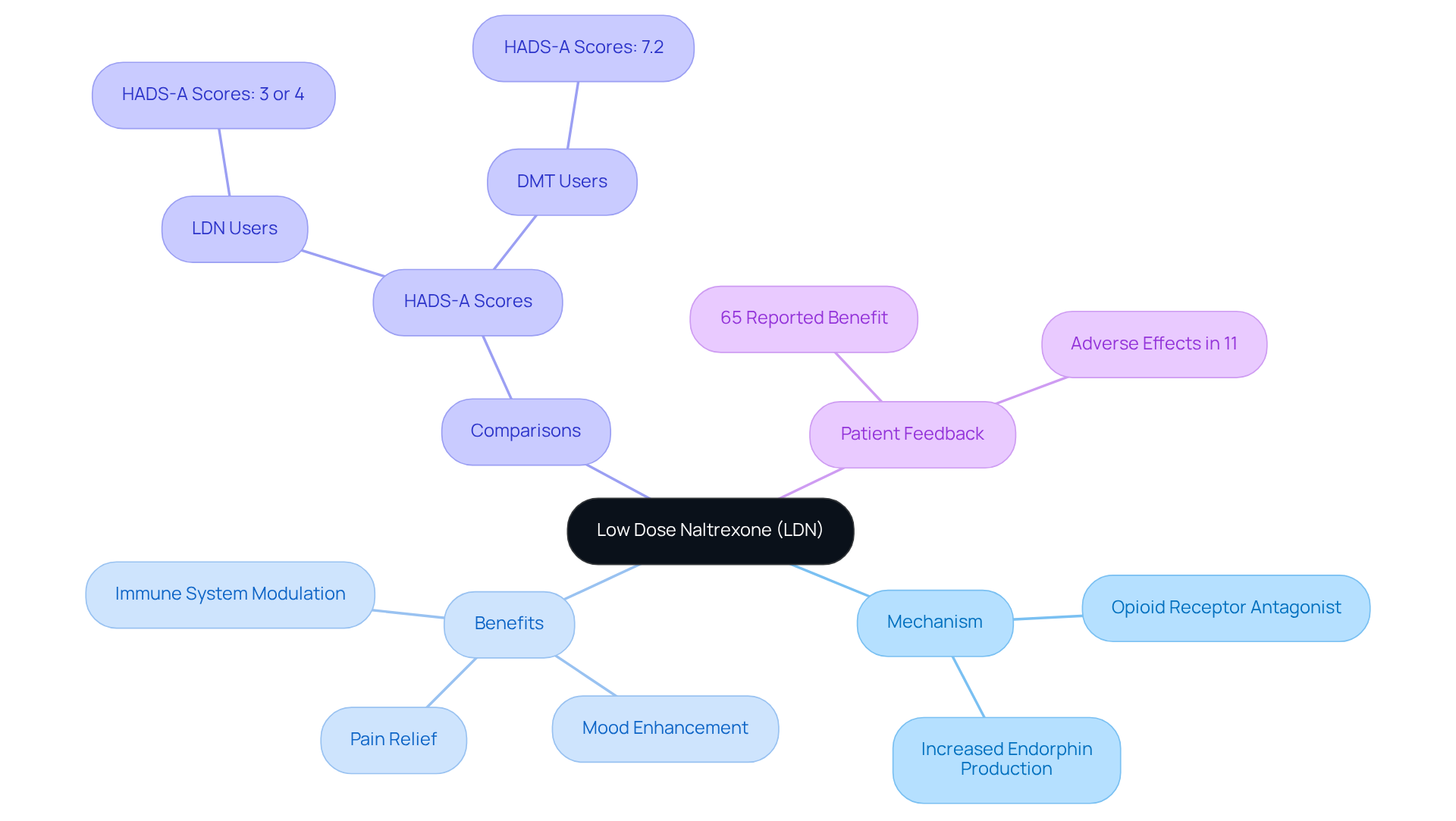
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) serves as an opioid receptor antagonist, typically administered in doses ranging from 1.5 mg to 4.5 mg. At these low doses, LDN temporarily blocks opioid receptors, leading to a compensatory increase in endorphin production. This mechanism not only alleviates pain but also significantly reduces symptoms of worry and depression associated with low dose naltrexone anxiety, thereby enhancing mood and fostering a sense of well-being.
Recent studies indicate that LDN can effectively modulate the immune system, making it particularly beneficial for conditions characterized by inflammation, such as autoimmune disorders. For instance, a study revealed that individuals with multiple sclerosis (PwMS) prescribed low dose naltrexone anxiety reported significantly lower levels of worry and depression compared to those on standard disease-modifying therapies, with HADS-A scores of 3 or 4 for LDN users versus 7.2 for those on oral DMTs. This highlights low dose naltrexone anxiety’s potential as a valuable resource for managing stress and enhancing overall mental health.
Furthermore, 65% of patients taking LDN for chronic pain reported a perceived benefit in their symptoms, underscoring its efficacy in enhancing quality of life. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for identifying how low dose naltrexone anxiety can be a beneficial approach for managing stress and associated mental health concerns. It is important to note that while LDN is generally well-tolerated, adverse effects were reported in 11% of patients, and the study was conducted under protocol #9784, emphasizing the necessity for further research.
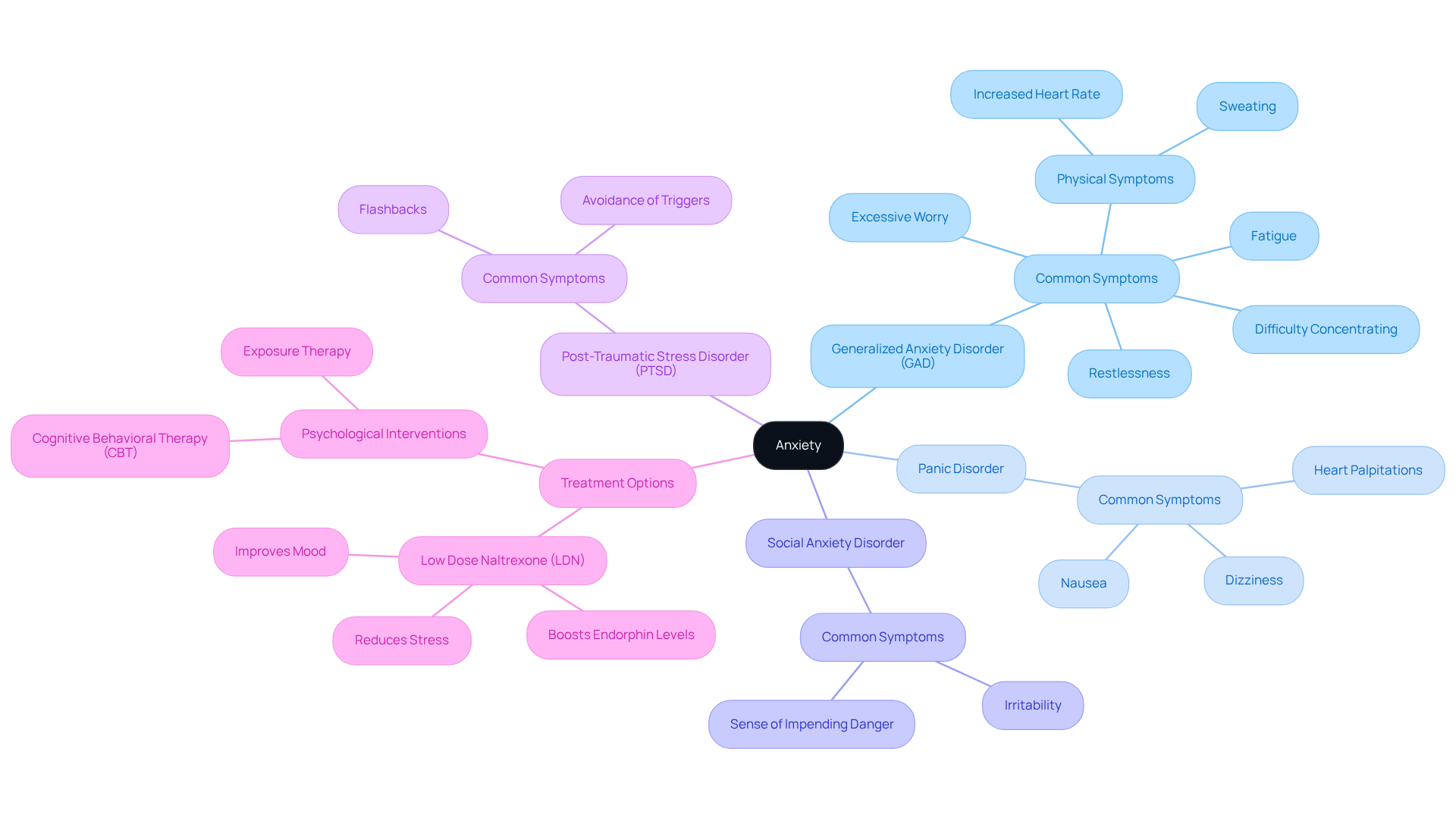
Identify Anxiety Symptoms and Conditions Treated by LDN
Nervousness can manifest in various forms, such as:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Panic disorder
- Social anxiety disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Common signs include:
- Excessive worry
- Restlessness
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Physical symptoms like increased heart rate and sweating
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) has shown potential in alleviating low dose naltrexone anxiety by boosting endorphin levels, which can improve mood and reduce stress. Clinical studies indicate that low dose naltrexone anxiety may be particularly effective for individuals who are experiencing anxiety related to chronic pain or autoimmune conditions, as it addresses both the psychological and physiological aspects of anxiety.
If you or someone you know struggles with anxiety, exploring treatment options such as low dose naltrexone anxiety could be beneficial. Understanding the interplay between mental and physical health is crucial for effective management. For more information, consider consulting a healthcare professional or researching further resources.
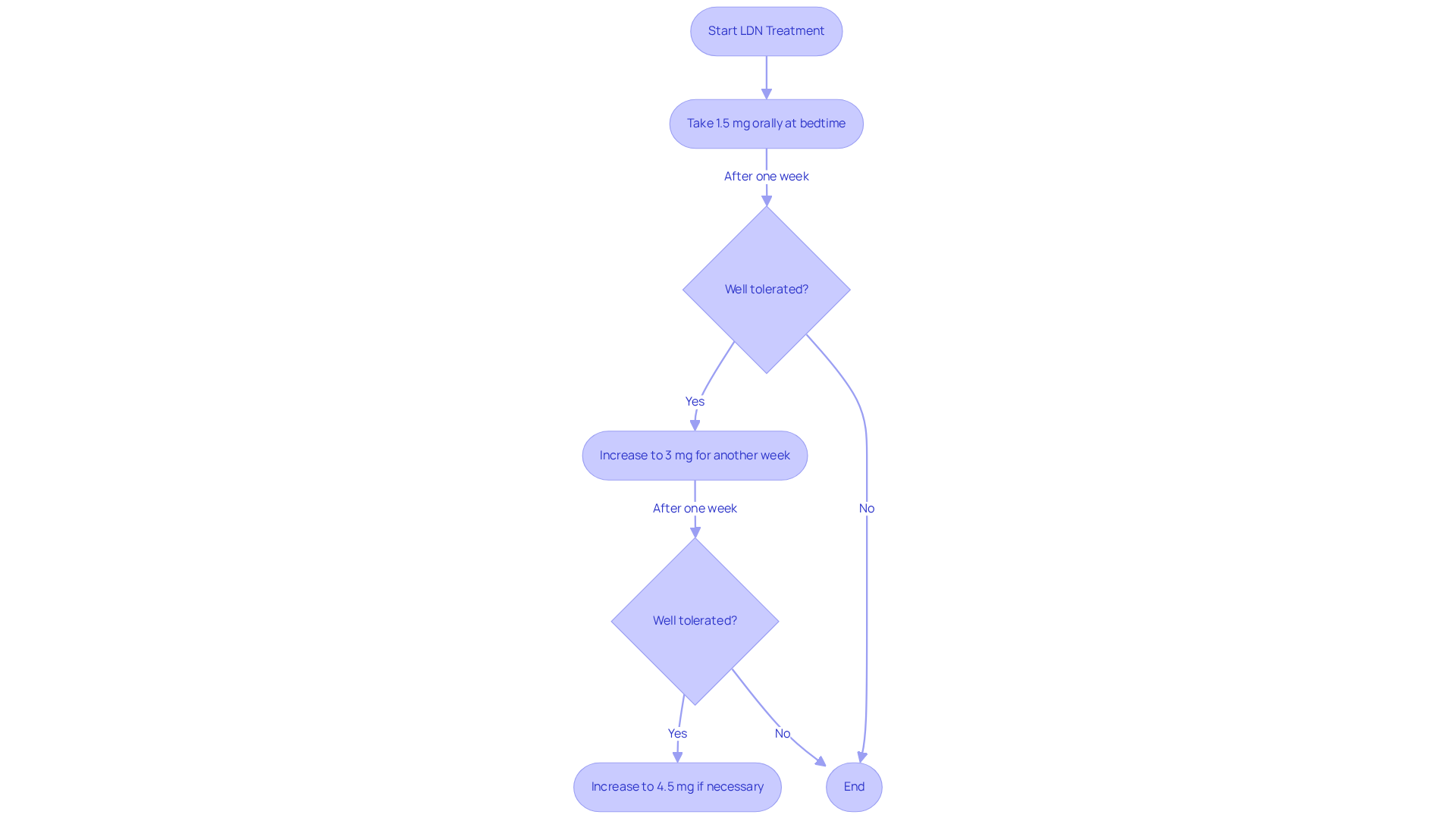
Follow Dosage Guidelines and Administration Steps for LDN
When beginning Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN), it is essential to follow a gradual titration plan to minimize potential adverse reactions. A common starting dose is 1.5 mg taken orally at bedtime. If well tolerated after one week, the dose can be increased to 3 mg for another week, followed by a potential increase to 4.5 mg if necessary.
Furthermore, it is recommended to consume LDN on an empty stomach, preferably at night, to enhance absorption and reduce the likelihood of gastrointestinal issues. Always consult with a healthcare provider before adjusting the dosage or administration schedule, as individual responses can vary significantly. This careful approach ensures a safer and more effective experience with LDN.
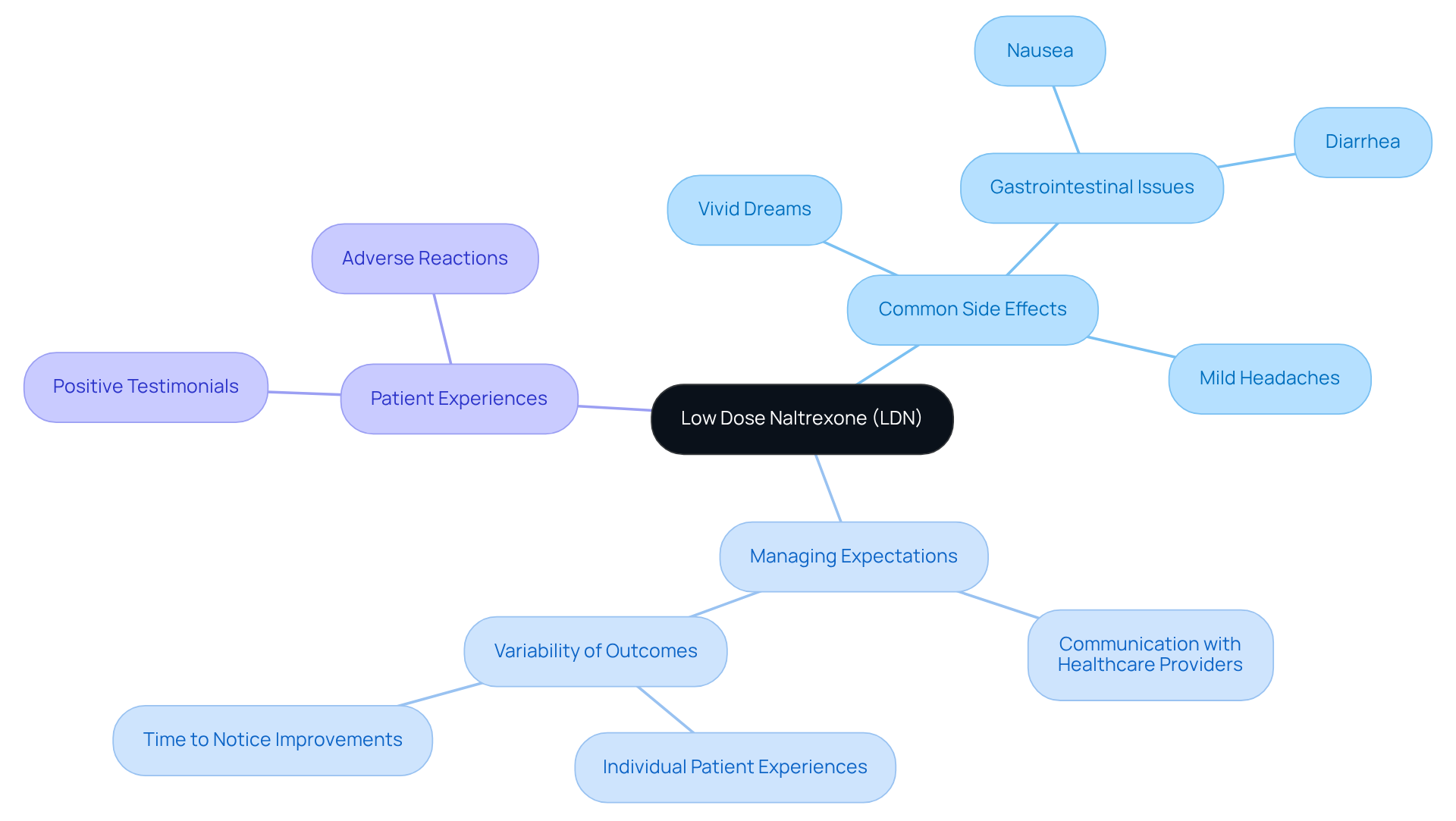
Recognize Side Effects and Manage Expectations with LDN
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) is generally well accepted among patients; however, some individuals may experience adverse reactions, especially during the initial treatment phase. Commonly reported adverse reactions include:
- Vivid dreams
- Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and diarrhea
- Mild headaches
Typically, these reactions diminish as the body adjusts to the medication.
It is essential to maintain open communication with healthcare providers to address concerns and adjust dosages as necessary. Setting realistic expectations is crucial; while some individuals may notice improvements in low dose naltrexone anxiety symptoms within a few weeks, others might require more time to experience the full benefits of LDN. Regular follow-ups are vital for optimizing treatment outcomes.
Patient testimonials illustrate the variability in experiences. For instance, one individual reported significant improvements in sleep and pain after adjusting their dosage, while another noted mild side effects that were manageable. Understanding these dynamics can empower patients to navigate their treatment journey more effectively.
Conclusion
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) offers a promising approach for managing anxiety, especially for those facing chronic pain or autoimmune disorders. Acting as an opioid receptor antagonist at low doses, LDN not only enhances endorphin production but also effectively alleviates symptoms of anxiety and depression. This dual mechanism not only promotes mental well-being but also supports physical health, positioning LDN as a valuable alternative treatment option.
The article emphasizes several critical insights, such as:
- The significance of appropriate dosage and administration
- Potential side effects
- The range of anxiety disorders that LDN may alleviate
With evidence backing its effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms—particularly among patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis—LDN stands out as a viable treatment choice. Furthermore, understanding the gradual titration process and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers are essential for optimizing treatment outcomes.
Ultimately, exploring Low Dose Naltrexone for anxiety highlights the interconnectedness of mental and physical health. For individuals battling anxiety, considering LDN as a treatment option could lead to substantial improvements in quality of life. Engaging with healthcare professionals to discuss this therapy empowers individuals to take informed steps toward managing their anxiety effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) and how is it administered?
Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) is an opioid receptor antagonist typically administered in doses ranging from 1.5 mg to 4.5 mg.
How does LDN work in the body?
At low doses, LDN temporarily blocks opioid receptors, which leads to a compensatory increase in endorphin production. This mechanism helps alleviate pain and reduces symptoms of worry and depression.
What benefits does LDN provide for mental health?
LDN significantly reduces symptoms of worry and depression associated with anxiety, thus enhancing mood and fostering a sense of well-being.
What conditions can LDN help with?
LDN can effectively modulate the immune system and is particularly beneficial for conditions characterized by inflammation, such as autoimmune disorders.
Are there any studies supporting the effectiveness of LDN?
Yes, studies indicate that individuals with multiple sclerosis (PwMS) who were prescribed LDN reported significantly lower levels of worry and depression compared to those on standard disease-modifying therapies.
What percentage of patients reported benefits from LDN for chronic pain?
65% of patients taking LDN for chronic pain reported a perceived benefit in their symptoms.
Are there any adverse effects associated with LDN?
While LDN is generally well-tolerated, adverse effects were reported in 11% of patients according to the study conducted under protocol #9784.
Why is further research on LDN necessary?
Further research is necessary to better understand the mechanisms of LDN and its potential benefits for managing stress and associated mental health concerns.






