Rapamycin Dosage for Anti Aging: Guidelines and Integration
Overview
This article examines the recommended dosage of rapamycin for anti-aging, highlighting that a starting dosage of 2 to 3 mg once per week is advisable. Adjustments may be necessary based on individual tolerance and health factors. Evidence supports the notion that optimal dosing can promote cellular health and longevity while reducing side effects. Therefore, it is essential to customize the dosage according to personal health profiles and to monitor responses closely.
Introduction
The quest for longevity has captivated humanity for centuries. Scientific advancements have continually reshaped our understanding of aging. Among the most promising discoveries is rapamycin, a compound that not only inhibits the mTOR pathway but also enhances autophagy. This dual action has the potential to extend lifespan and improve healthspan.
This article delves into the intricacies of rapamycin dosage for anti-aging. It offers guidelines that can help individuals navigate this complex treatment. However, with the promise of longevity comes the challenge of balancing efficacy with safety. How can one determine the optimal dosage while managing potential side effects? Exploring these questions is essential for anyone interested in harnessing the benefits of rapamycin.
Define Rapamycin and Its Role in Anti-Aging
Sirolimus is a macrolide compound that inhibits the mechanistic target of mTOR, a crucial regulator of cell growth and metabolism. By inhibiting mTOR, this compound enhances autophagy, a vital process that removes damaged cellular components, promoting cellular health and longevity. Recent studies reveal that sirolimus can prolong lifespan across various species, including mice, by delaying the onset of age-related illnesses and improving overall healthspan.
Significantly, research indicates that sirolimus can enhance median lifespan by as much as 14% when administered at different life stages. This underscores its potential as a powerful strategy involving rapamycin dosage for anti-aging. Notably, sirolimus mimics the effects of caloric restriction, a well-documented method for extending lifespan, highlighting the importance of rapamycin dosage for anti-aging in the realm of anti-aging research.
Furthermore, combining a specific mTOR inhibitor with other compounds, such as metformin and acarbose, has been shown to promote lifespan extension, particularly in male subjects. This suggests a multifaceted approach to longevity therapies that could lead to significant advancements in healthspan and lifespan enhancement.
Determine Appropriate Dosage Guidelines for Rapamycin
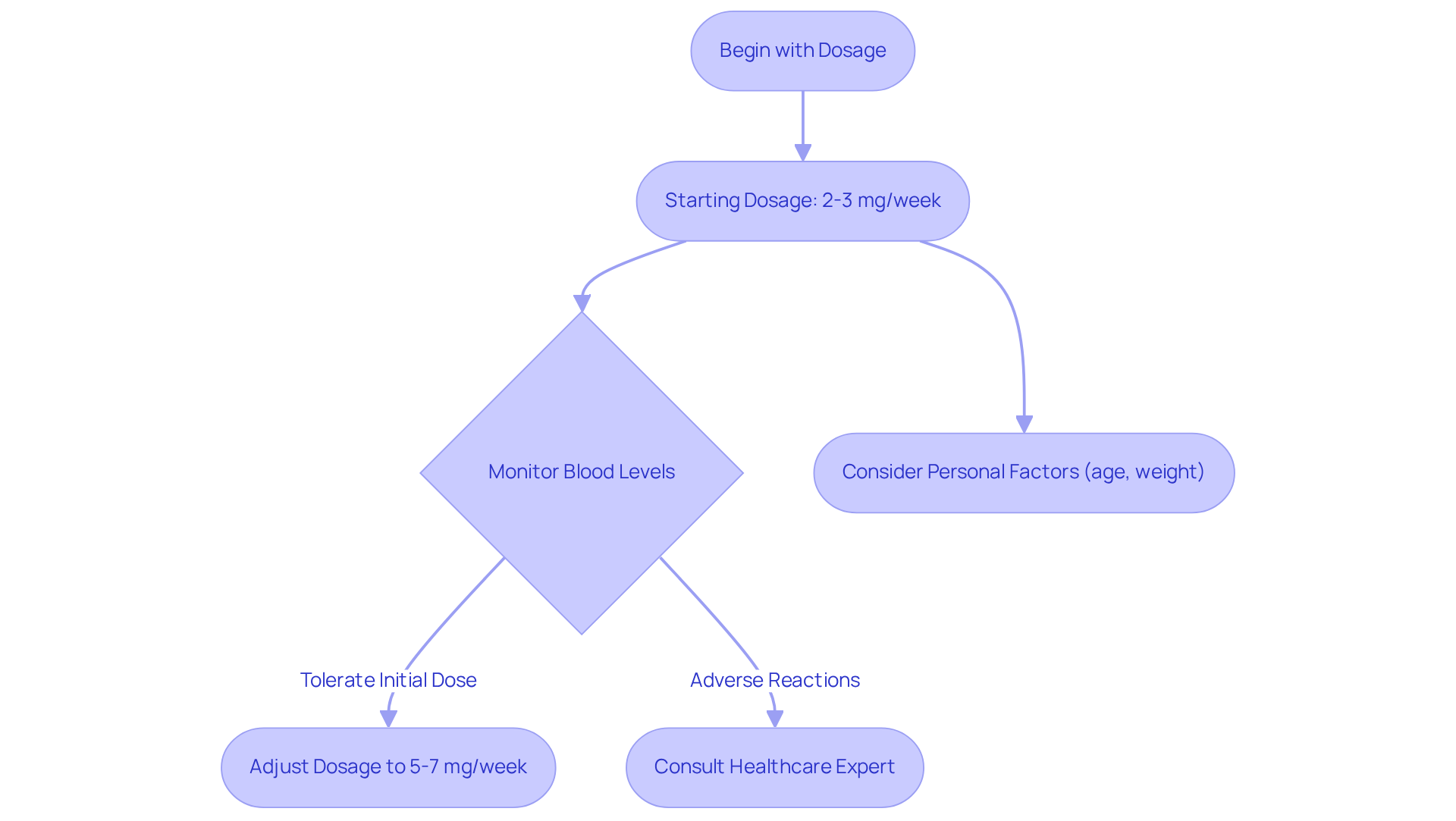
Determining the appropriate rapamycin dosage for anti aging is crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential side effects. The recommended starting rapamycin dosage for anti aging typically ranges from 2 to 3 mg once per week, allowing the body to adjust to the medication. As tolerance builds, individuals may gradually increase their rapamycin dosage for anti aging to between 5 and 7 mg weekly. Furthermore, monitoring blood levels is essential; optimal therapeutic ranges should see peak levels above 10 ng/ml a few hours after dosing, with levels dropping below 1 ng/ml within 24 to 48 hours before the next dose.
Personal factors such as age, weight, and general well-being significantly affect the ideal rapamycin dosage for anti aging. For instance, older adults may benefit from a higher rapamycin dosage for anti aging due to increased mTOR activity associated with aging. Conversely, younger adults often require lower doses, as their bodies are more efficient at cellular repair and regeneration. Consulting with a healthcare expert specializing in extended life medicine is strongly advised to customize the rapamycin dosage for anti aging according to individual wellness profiles and treatment objectives.
Recent studies suggest that a properly adjusted rapamycin dosage for anti aging can effectively support cellular health and longevity. For individuals unfamiliar with rapamycin, beginning with a cautious strategy enables close observation of any adverse reactions, which are typically mild and reversible. By following these guidelines and adjusting based on individual responses, users can effectively optimize their anti-aging treatment by determining the right rapamycin dosage for anti aging.
Identify and Manage Side Effects of Rapamycin
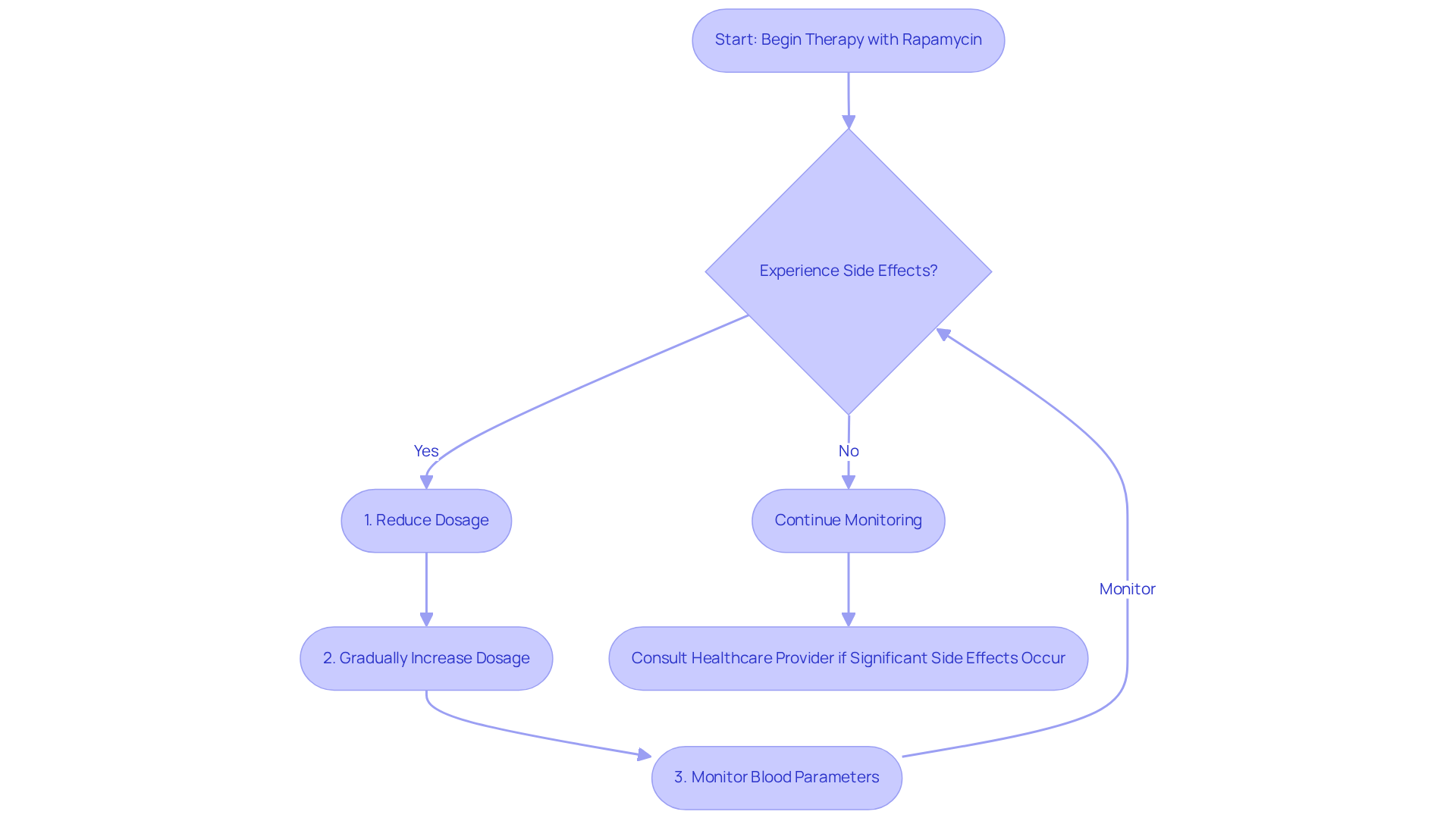
Rapamycin is generally well-accepted, yet some users may experience symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and increased cholesterol levels. Severe adverse reactions, although less common, can involve immune suppression, significantly increasing the risk of infections. Research indicates that patients using rapamycin may face a higher likelihood of developing infections, including those caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
To effectively manage these reactions, it is advisable to:
- Initiate therapy with a reduced dosage.
- Gradually increase the dosage, allowing the body to adjust.
- Consistently monitor blood parameters, such as lipid profiles and immune function, for early identification of any adverse effects.
If significant side effects occur, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to modify the dosage or consider alternative therapies.
This proactive approach can help mitigate risks while enhancing the benefits of the rapamycin dosage for anti-aging in protocols. Have you considered how your body might respond to rapamycin? Understanding these potential reactions can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
Integrate Rapamycin into a Holistic Anti-Aging Plan
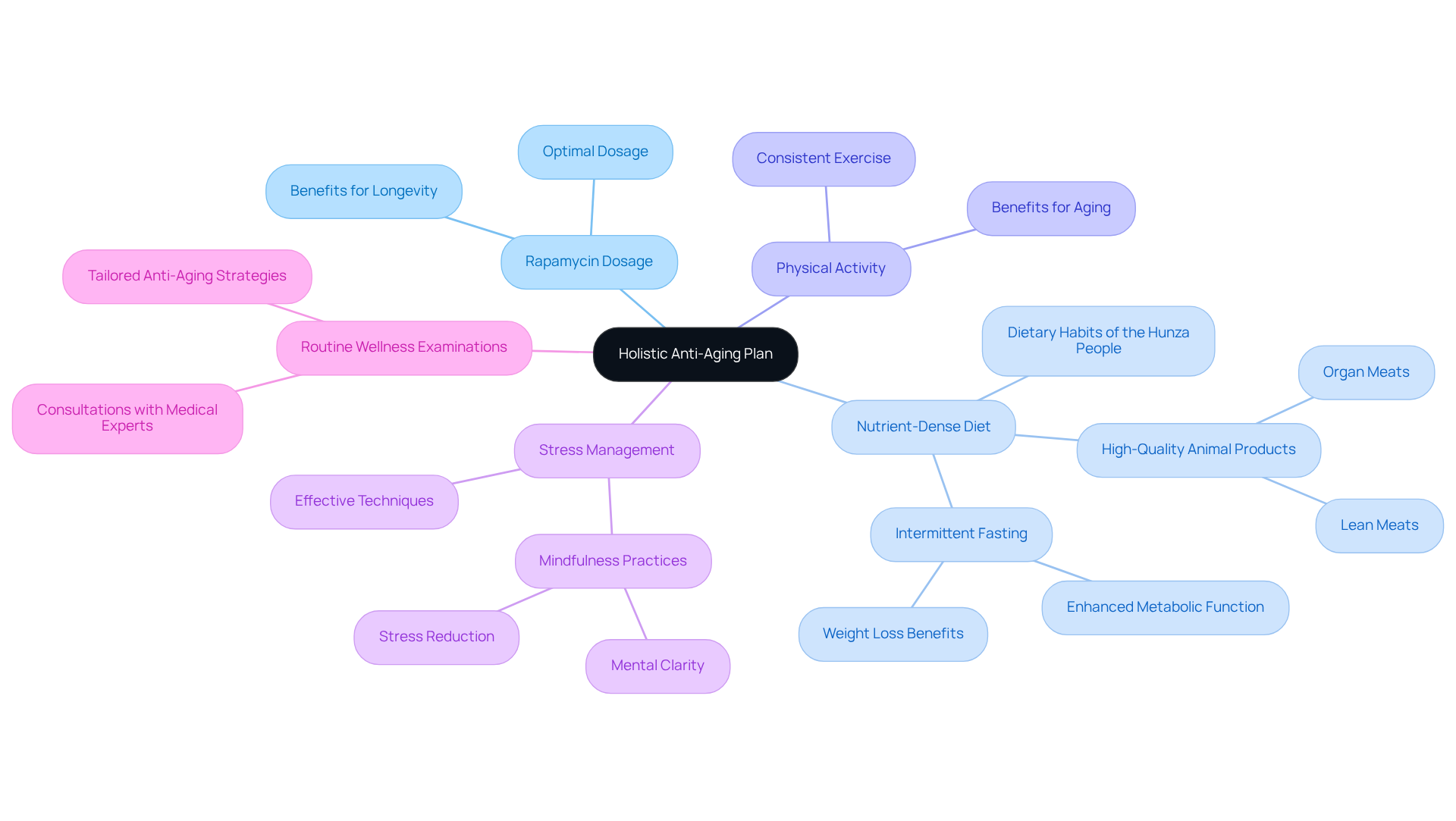
To fully harness the benefits of rapamycin, incorporating the appropriate rapamycin dosage for anti-aging into a holistic anti-aging strategy that includes:
- A nutrient-dense diet
- Consistent physical activity
- Effective stress management techniques
is essential. A diet rich in high-quality animal products, such as lean meats and organ meats, provides essential nutrients that enhance cellular well-being. This corresponds with the dietary habits seen in the Hunza people, recognized for their impressive lifespan and vibrant lifestyle, often credited to their nutrient-rich diet. Research suggests that nutrient-rich diets can considerably improve the effectiveness of the rapamycin dosage for anti-aging treatment, promoting optimal wellness results.
In addition to dietary considerations, practices such as intermittent fasting have shown promising results in supporting longevity. Research indicates that intermittent fasting can result in weight loss and enhanced metabolic function, with around 85% of trials showing statistically significant weight reduction. This dietary method not only encourages autophagy but also lessens oxidative stress, further enhancing the impacts of the compound.
Moreover, integrating mindfulness practices can enhance overall well-being, contributing to a balanced lifestyle that supports healthy aging. For instance, Dr. Dituri’s underwater research emphasizes the importance of mental clarity and stress reduction, achievable through mindfulness techniques. Routine wellness examinations and discussions with medical experts focused on longevity are essential for tailoring the anti-aging strategy, ensuring it aligns with personal well-being requirements and objectives. This comprehensive approach empowers individuals to take control of their health journey, maximizing the potential benefits of rapamycin dosage for anti-aging and fostering a vibrant, youthful life.
Conclusion
Rapamycin presents a compelling avenue for anti-aging therapies, primarily through its ability to inhibit mTOR and enhance autophagy. This macrolide compound not only shows promise in extending lifespan across species but also highlights the importance of precise dosage guidelines to maximize its benefits while minimizing side effects. By understanding the role of rapamycin in cellular health, individuals can make informed decisions about integrating this powerful compound into their longevity strategies.
Key insights from the article emphasize the significance of:
- Starting with a conservative rapamycin dosage.
- Gradually adjusting it based on individual tolerance and health factors.
- Monitoring blood levels.
- Consulting healthcare professionals as crucial steps in ensuring safe and effective use.
Furthermore, the potential side effects, while generally mild, necessitate a proactive management approach to enhance the overall experience of those seeking longevity.
Ultimately, integrating rapamycin into a holistic anti-aging plan that includes:
- A nutrient-dense diet.
- Regular physical activity.
- Stress management practices.
can significantly amplify its benefits. Embracing such a comprehensive approach empowers individuals to take charge of their health journey, leveraging the latest research on rapamycin to foster a vibrant and youthful life. As interest in longevity therapies continues to grow, staying informed about the latest developments and personalizing strategies will be essential for anyone looking to enhance their healthspan and lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is rapamycin and what role does it play in anti-aging?
Rapamycin, also known as sirolimus, is a macrolide compound that inhibits the mechanistic target of mTOR, which regulates cell growth and metabolism. By inhibiting mTOR, rapamycin enhances autophagy, promoting cellular health and longevity.
How does rapamycin affect lifespan?
Research indicates that rapamycin can prolong lifespan across various species, including mice, by delaying the onset of age-related illnesses and improving overall healthspan. It has been shown to enhance median lifespan by as much as 14% when administered at different life stages.
How does rapamycin mimic caloric restriction?
Rapamycin mimics the effects of caloric restriction, which is a well-documented method for extending lifespan. This similarity highlights the importance of rapamycin dosage in anti-aging research.
Can rapamycin be combined with other compounds for enhanced effects?
Yes, combining a specific mTOR inhibitor like rapamycin with other compounds, such as metformin and acarbose, has been shown to promote lifespan extension, particularly in male subjects. This suggests a multifaceted approach to longevity therapies.






