Should I Take NMN or NAD? A Step-by-Step Supplementation Guide
Overview
The article explores the question of whether to take NMN or NAD supplements. It emphasizes that NMN supplementation is generally recommended for boosting NAD+ levels, which tend to decline with age and are associated with various health benefits. NMN can enhance energy metabolism and cognitive function, making it a compelling choice for those interested in maintaining their health as they age.
Furthermore, the article advises on appropriate dosage and timing for NMN supplementation. It highlights the importance of consulting healthcare professionals to manage any potential side effects effectively. By following these guidelines, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Introduction
Navigating the world of dietary supplements can be overwhelming. In particular, understanding the roles of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) presents unique challenges. As research continues to unveil their potential benefits for energy metabolism and healthy aging, many individuals find themselves questioning which supplement might best suit their needs.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide, detailing the advantages and considerations of NMN versus NAD supplementation. It addresses common queries and challenges that arise in this evolving field. With the stakes high for those seeking to enhance their well-being, how can one make an informed choice between these two powerful compounds?
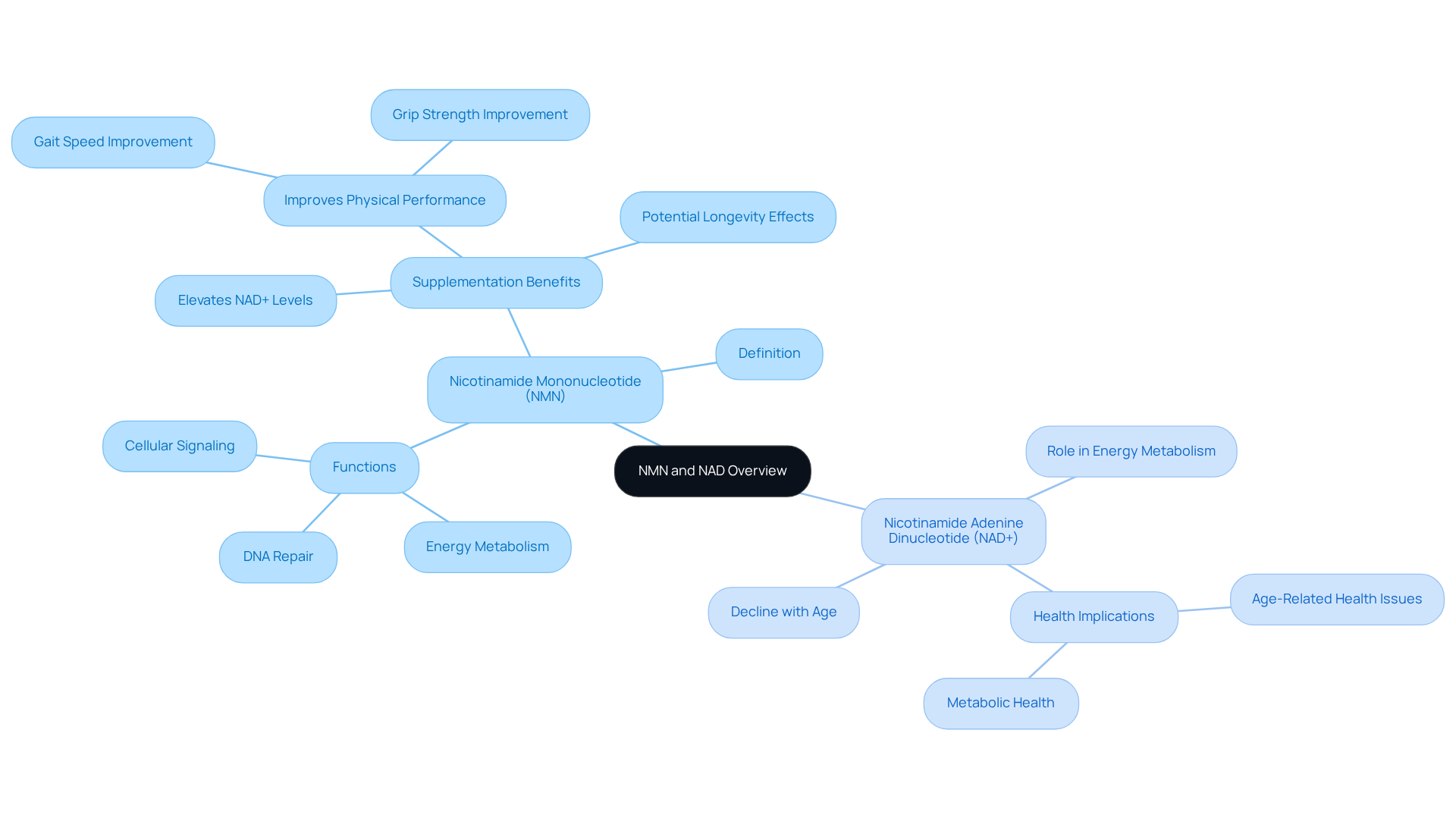
Understand NMN and NAD: Key Definitions and Functions
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) serves as a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide, functioning as a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+). This critical coenzyme is present in every cell and plays an integral role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular signaling. As we age, our levels of NAD+ naturally decline, which can contribute to various age-related health issues.
Recent studies suggest that supplementing with NMN can effectively elevate NAD+ levels, thereby enhancing cellular function and potentially promoting longevity. For instance, clinical trials have shown significant improvements in physical performance, including a nominally significant increase in gait speed (p = 0.033) and left grip test performance (p = 0.019) among participants taking NMN. Health professionals stress the importance of maintaining NAD+ levels, highlighting that “as the NAD concentration in human skin, blood, liver, muscle, and brain are thought to decrease with age, finding ways to increase NAD status could possibly influence the aging process and associated metabolic sequelae.”
Understanding these definitions and functions is essential for evaluating the benefits and factors related to NMN usage, especially when considering the question, should I take NMN or NAD in the context of healthy aging. Ongoing clinical trials continue to investigate the safety and efficacy of NMN, with doses ranging from 300 mg to 900 mg demonstrating promising results.
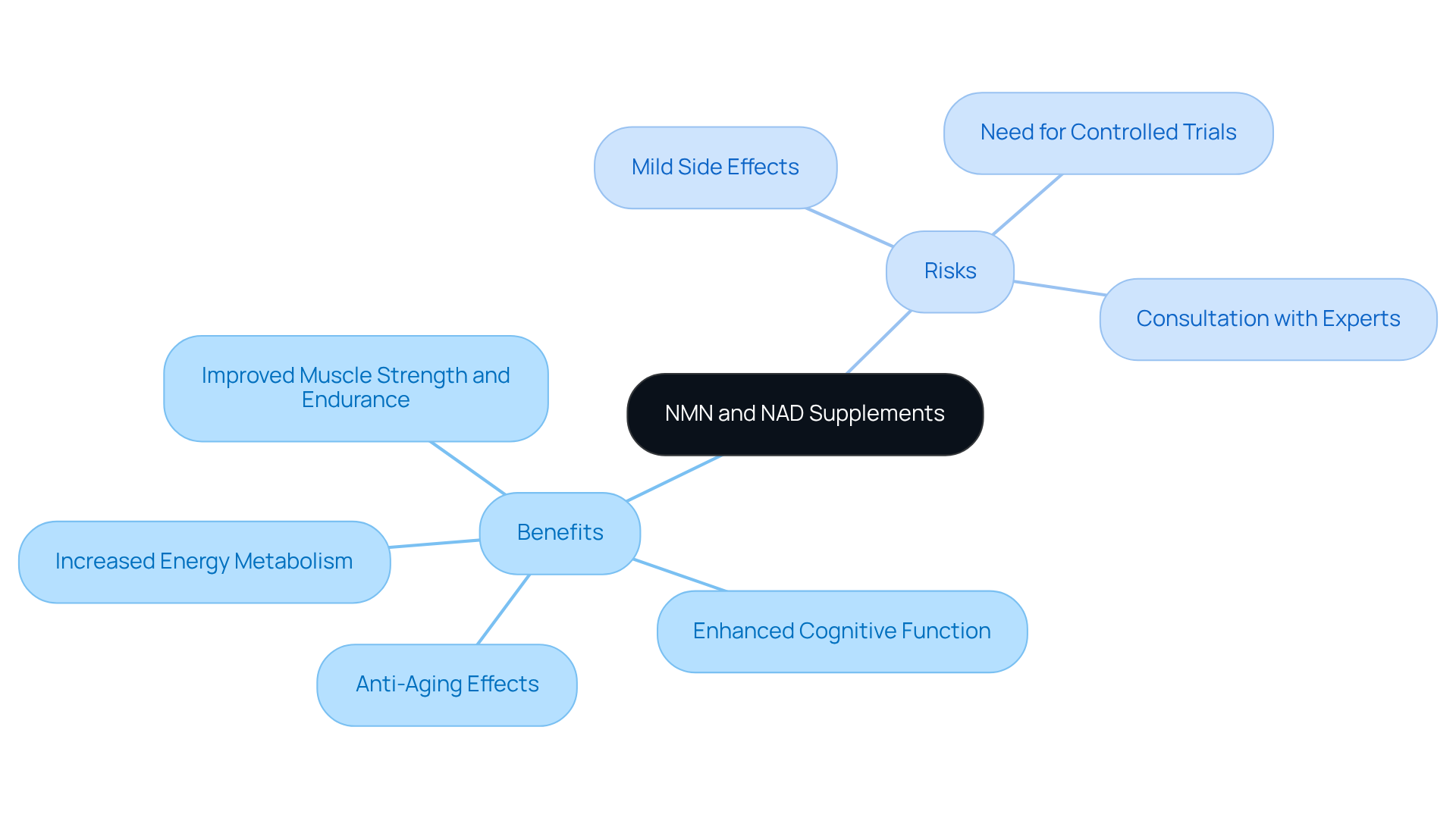
Evaluate the Benefits and Risks of NMN and NAD Supplements
NMN and NAD intake may offer numerous benefits, such as increased energy metabolism, enhanced cognitive function, and potential anti-aging effects. Recent research indicates that NMN effectively raises NAD+ levels, which can help counteract age-related declines in physical performance and metabolic function. For instance, clinical trials involving healthy individuals aged 18-70 years have shown that NMN intake can lead to significant improvements in muscle strength and endurance, particularly in older adults.
One study revealed that daily doses of up to 1,200 mg of NMN are safe for consumption, further supporting its potential advantages. However, it is important to consider the possible risks associated with supplements, such as when deciding should I take NMN or NAD. Mild side effects, including gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, and dizziness, have been reported in various studies. Furthermore, current research underscores the need for more rigorously controlled clinical trials to assess the long-term safety and effectiveness of NMN and NAD, especially regarding their effects on cognitive function and metabolic health.
Before starting any supplements, it is crucial to consult a medical expert, particularly for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications. This ensures a secure and informed approach to enhancing well-being.
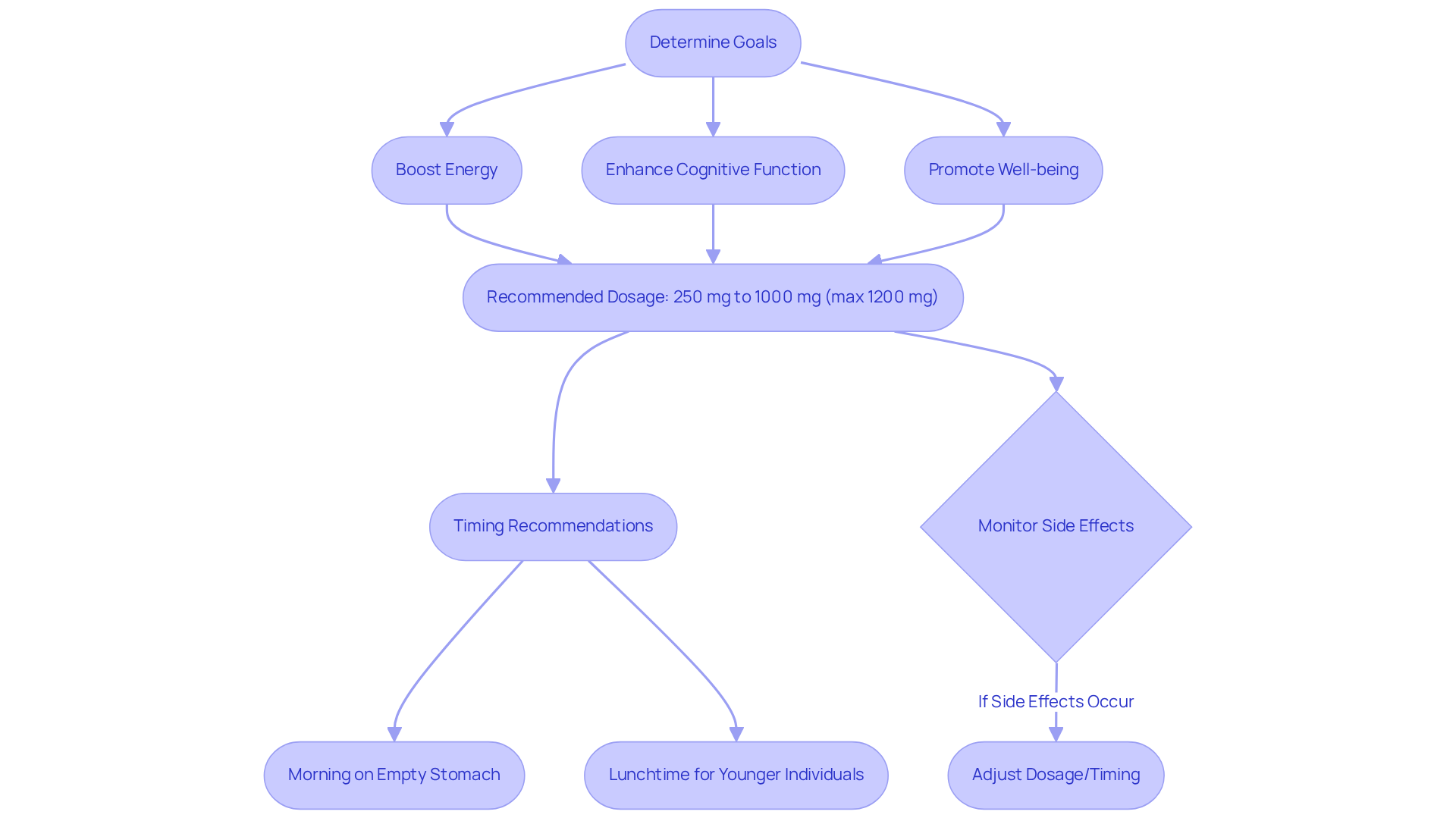
Determine Your Supplementation Strategy: Dosage, Timing, and Goals
Establishing clear goals is crucial when determining what I should take, NMN or NAD supplementation. What do you hope to achieve? Whether your aim is to boost energy levels, enhance cognitive function, or promote overall well-being, understanding your objectives will help you determine if you should take NMN or NAD. Recommended dosages for NMN typically range from 250 mg to 1000 mg daily, tailored to individual health needs and responses, with a maximum limit of 1200 mg daily.
Experts recommend taking NMN in the morning on an empty stomach to maximize absorption and align with the body’s natural NAD+ production cycle. As noted by Dr. Kahn, starting with a conservative dose allows for gradual adjustments based on how your body reacts. Tracking your reaction is crucial for enhancing nutritional strategies; as Professor Martens advises, “For most individuals, it’s wise to begin modestly and gradually escalate according to how your body reacts.”
Some individuals may find that taking NMN around lunchtime enhances its effectiveness, particularly if they are younger. Consistency in timing and dosage is key to achieving desired outcomes, making it important to personalize your regimen based on individual experiences and health indicators. Additionally, while NMN is generally well tolerated, some users may experience mild side effects such as headaches or digestive discomfort, which should be monitored closely.
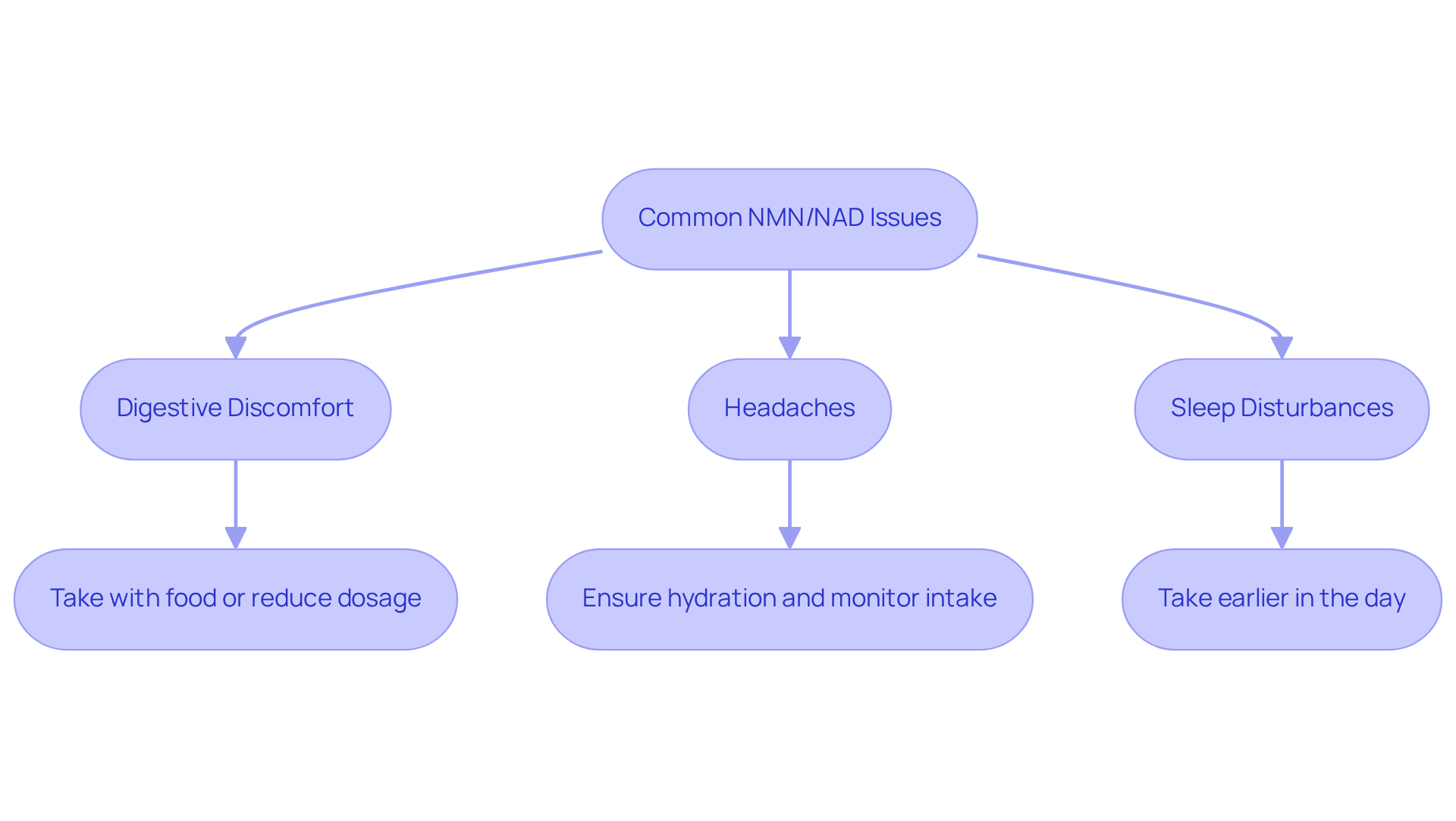
Troubleshoot Common Issues with NMN and NAD Supplementation
Common issues with NMN and NAD intake may include digestive discomfort, headaches, or difficulty sleeping. If you experience gastrointestinal issues, consider taking the supplement with food or reducing the dosage. Research indicates that some individuals experience digestive upset, with mild side effects such as nausea and bloating being reported. For headaches, ensure you are well-hydrated and monitor your intake. If sleep disturbances occur, try taking the supplement earlier in the day. Always listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional if problems persist or worsen.
It’s essential to consider that NMN may interact with blood pressure medications like beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors. In rare cases, it may cause increased heart rate. Additionally, some users report feeling tired or having brain fog after stopping NMN supplementation. To minimize side effects, starting with a lower dose of NMN (250-300 mg daily) is recommended. Individual responses to supplements can vary, so what works for one person may not work for another.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between NMN and NAD supplements is crucial for anyone considering supplementation for health and longevity. NMN serves as a precursor to NAD+, which plays vital roles in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and overall cellular function. As NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, supplementing with NMN has emerged as a promising strategy to bolster these essential processes and potentially mitigate age-related health issues.
Key insights reveal that NMN supplementation can lead to significant improvements in physical performance and cognitive function, particularly in older adults. While the benefits are compelling, it is equally important to weigh potential risks and side effects, which may include:
- Mild gastrointestinal discomfort
- Headaches
Establishing a personalized supplementation strategy based on individual health goals, dosage, and timing is essential for maximizing benefits while minimizing adverse effects.
Ultimately, the decision to take NMN or NAD should be made with careful consideration and, ideally, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. As research continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest scientific findings will empower individuals to make educated choices about their health. Embracing this proactive approach to supplementation can lead to enhanced well-being and a more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)?
NMN is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide, functioning as a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+).
What role does NAD+ play in the body?
NAD+ is a critical coenzyme present in every cell, playing an integral role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular signaling.
How does aging affect NAD+ levels?
As we age, our levels of NAD+ naturally decline, which can contribute to various age-related health issues.
Can NMN supplementation help with NAD+ levels?
Yes, recent studies suggest that supplementing with NMN can effectively elevate NAD+ levels, enhancing cellular function and potentially promoting longevity.
What improvements have been observed in clinical trials involving NMN?
Clinical trials have shown significant improvements in physical performance, including increased gait speed and left grip test performance among participants taking NMN.
Why is it important to maintain NAD+ levels?
Maintaining NAD+ levels is important because the concentration of NAD in human skin, blood, liver, muscle, and brain is thought to decrease with age, and increasing NAD status could influence the aging process and associated metabolic issues.
What are the typical dosages of NMN used in clinical trials?
Ongoing clinical trials have investigated doses of NMN ranging from 300 mg to 900 mg, which have shown promising results.
What considerations should be made when deciding to take NMN or NAD?
Understanding the definitions and functions of NMN and NAD is essential for evaluating their benefits, particularly in the context of healthy aging.






