Sodium Butyrate Benefits: Understanding Its Health Impact and Mechanisms
Overview
Sodium butyrate presents notable health benefits, especially for gut health. It plays a vital role in:
- Reducing inflammation
- Enhancing intestinal integrity
- Improving metabolic functions, including insulin sensitivity
What mechanisms contribute to these effects? The article delves into its action pathways, such as:
- The inhibition of histone deacetylases
- The activation of G protein-coupled receptors
These processes collectively underscore its therapeutic potential in managing conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and various metabolic disorders. By understanding these mechanisms, one can appreciate sodium butyrate’s role in promoting overall health.
Introduction
Sodium butyrate is a powerful short-chain fatty acid that emerges from the fermentation of dietary fibers in the gut. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining intestinal health. This compound not only serves as a vital energy source for colon cells but also boasts impressive anti-inflammatory and metabolic benefits. As a result, it is a key player in the fight against various gastrointestinal disorders and metabolic diseases. However, as research continues to unveil its mechanisms of action, the question remains: how can sodium butyrate be effectively harnessed to enhance overall health and well-being?
Define Sodium Butyrate: Composition and Sources
Sodium butanoate, the salt of butyric acid, is a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) represented by the chemical formula Na(C3H7COO). This compound is predominantly produced in the colon through the fermentation of dietary fibers by beneficial gut bacteria. Foods rich in fermentable fibers, such as whole grains, legumes, and specific fruits, greatly aid in the production of short-chain fatty acids in the gut. Furthermore, a salt of butyric acid is found in minor amounts in dairy items like butter and cheese.
Its critical role as a primary energy source for colonocytes—the cells lining the colon—highlights its significance in maintaining gut health. Recent studies suggest that ideal amounts of sodium salt can improve intestinal integrity, promote microbial diversity, and lessen inflammation, highlighting the sodium butyrate benefits as an essential part of a health-focused diet. Additionally, the salt of butyric acid functions as a histone deacetylase inhibitor and transmits signals via G-protein coupled receptors, which are crucial for its molecular processes.
Clinical efforts to elevate short-chain fatty acid levels in humans have demonstrated varied outcomes, emphasizing the necessity for additional investigation. Crucially, the salt of butyric acid, known for its sodium butyrate benefits, has protective effects against intestinal disorders like inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. Reduced levels of butyric acid are associated with worse health outcomes, underscoring the importance of sustaining optimal levels for overall well-being.
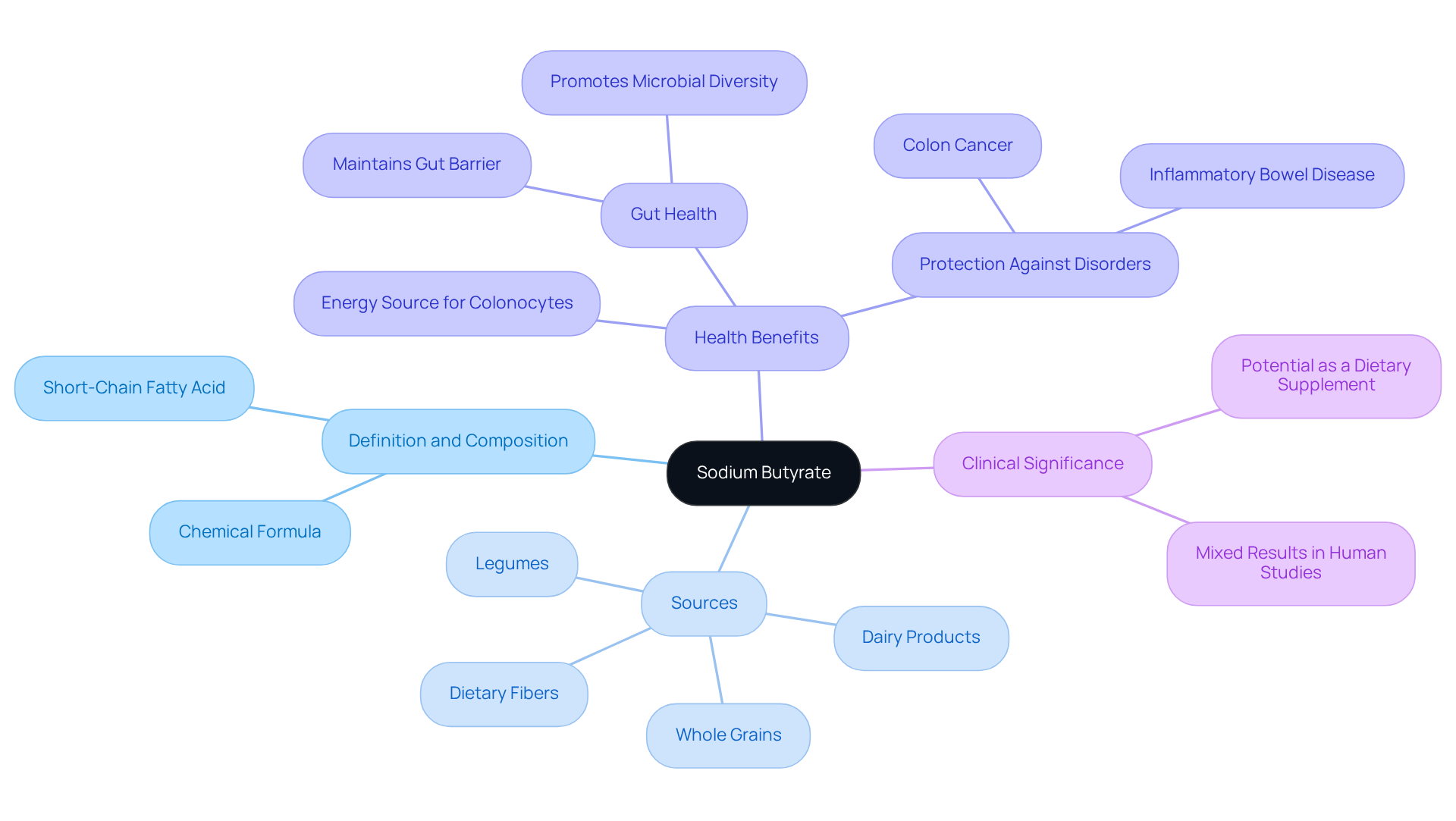
Explore Health Benefits: Anti-Inflammatory and Metabolic Effects
Sodium butyrate benefits are widely recognized for their potent anti-inflammatory properties, which are particularly helpful in alleviating conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Research indicates that butyric acid effectively reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6. This reduction enhances gut barrier function and helps prevent ‘leaky gut.’
Furthermore, butyric acid plays a significant role in metabolic health by improving insulin sensitivity and regulating blood sugar levels. Studies suggest that it can aid in weight loss and reduce fat accumulation, making it a vital component of dietary strategies for managing obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Importantly, sodium supplementation has been shown to diminish the inflammatory traits of circulating monocytes in individuals with metabolic syndrome, highlighting its potential in reducing inflammation associated with these conditions.
In addition, clinical trials, including those registered under NTR4392, have demonstrated its effectiveness in improving colitis scores and restoring microbial diversity in patients with IBD. This underscores its therapeutic potential in both gastrointestinal and metabolic health, prompting further exploration of the sodium butyrate benefits.
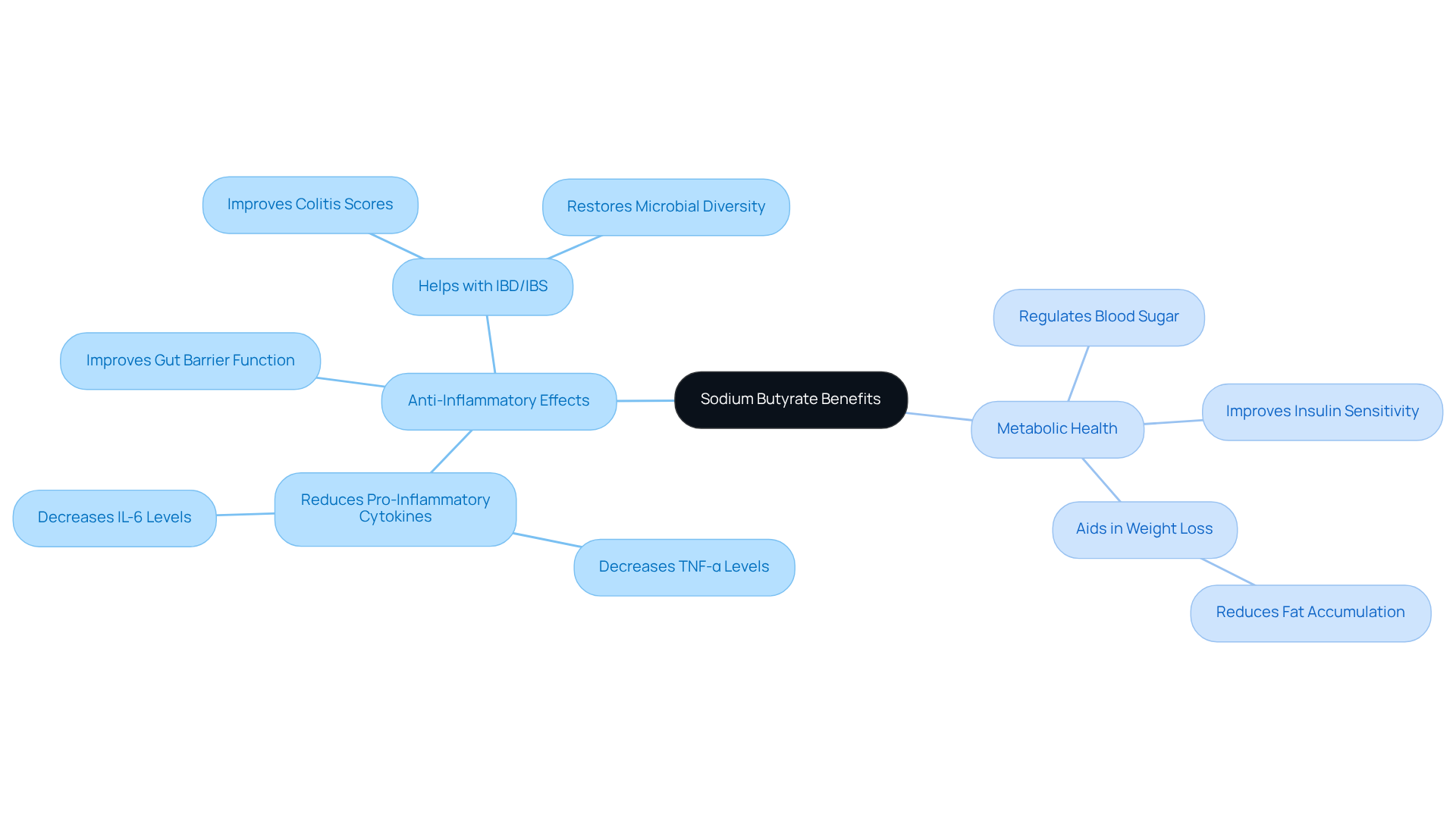
Understand Mechanisms of Action: How Sodium Butyrate Works
Sodium primarily exerts its effects through the inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs), which leads to increased histone acetylation and significant alterations in gene expression. This mechanism is vital for regulating inflammation and cellular metabolism. Notably, a salt of butyric acid has been demonstrated to improve the expression of acetylated histone proteins, including AcH3 and AcH4, which are linked to transcriptional activation. In studies, treatment involving butyric acid resulted in a remarkable 188% increase in RGC survival at a concentration of 0.1 mM.
Furthermore, sodium butyric acid activates G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which play crucial roles in various signaling pathways related to gut motility and immune response. This activation contributes to the modulation of gut microbiota and enhances intestinal barrier integrity, thereby promoting overall gut health and systemic well-being. Research indicates that supplementation with butyric acid can enhance glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, further highlighting its metabolic advantages.
In clinical environments, a type of salt derived from butyric acid has shown promise in addressing obesity and insulin resistance. Research indicates notable decreases in body weight and fat mass in high-fat diet models. For example, treatment with a certain fatty acid consistently resulted in reduced fasting glucose and insulin levels, emphasizing its therapeutic significance for metabolic disorders. Overall, the diverse mechanisms of action associated with this compound highlight the sodium butyrate benefits, making it a promising option for improving well-being and addressing age-related decline.
Examine Clinical Applications: Research and Future Directions
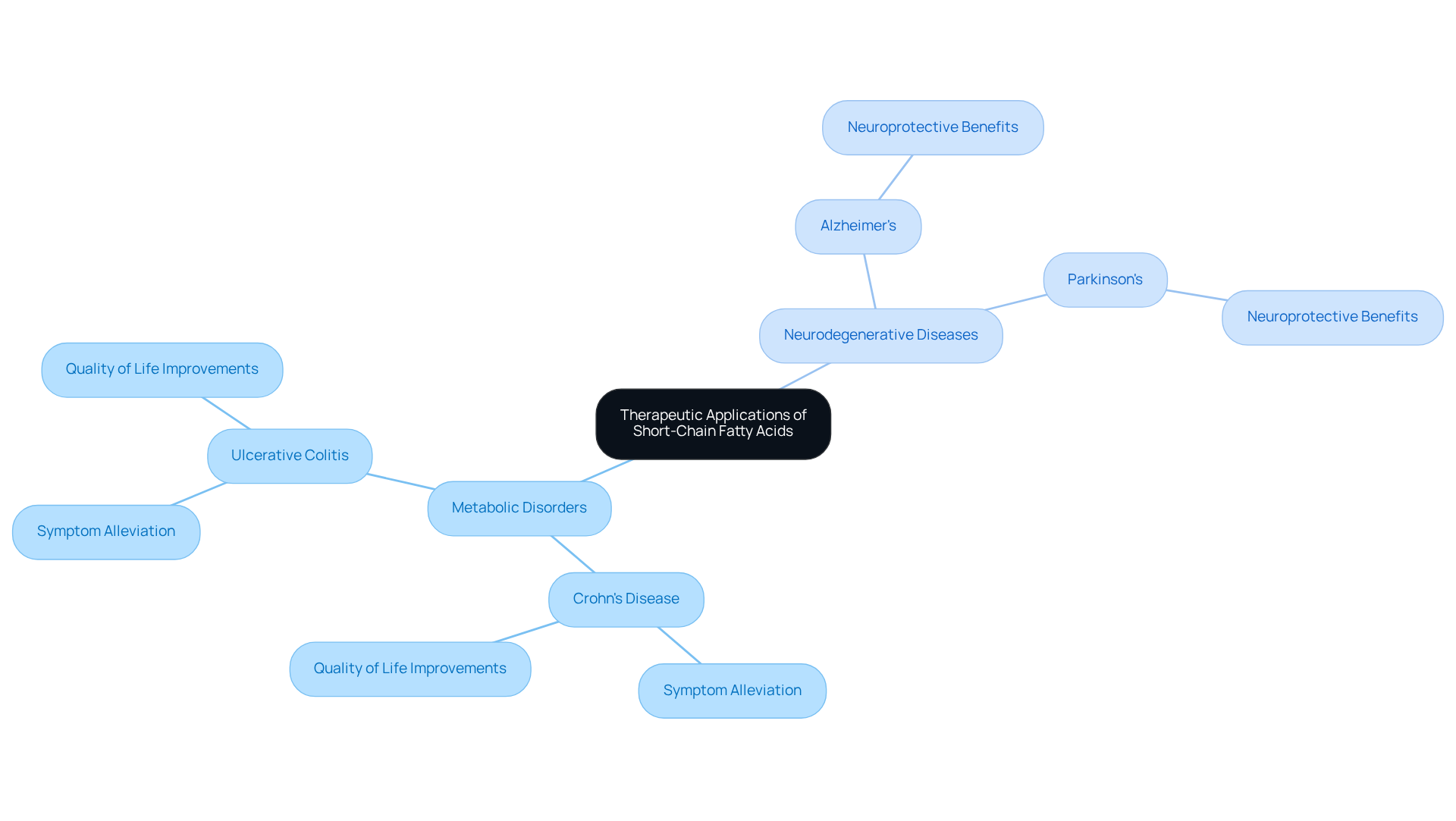
Recent clinical studies have illuminated the therapeutic potential of a specific short-chain fatty acid in addressing various health conditions, particularly metabolic disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. For example, supplementation with a specific salt of butyric acid has demonstrated effectiveness in alleviating symptoms associated with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, leading to significant improvements in patient quality of life. In the realm of neurodegenerative disorders, ongoing research indicates that this short-chain fatty acid may offer neuroprotective benefits, particularly for conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
A study involving 2,990 patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported an impressive 99.7% response rate, highlighting the compound’s efficacy in managing gastrointestinal symptoms. Furthermore, this salt’s ability to enhance autophagy and modify gut microbiota composition has been linked to improved cognitive function and reduced neuroinflammation in animal models. As research continues to uncover the mechanisms behind sodium butyrate benefits, it presents promising avenues for developing innovative therapeutic strategies that leverage its properties for enhanced health outcomes.
Conclusion
Sodium butyrate emerges as a vital compound with significant implications for health, particularly in gut health and metabolic regulation. As a short-chain fatty acid produced through the fermentation of dietary fibers, its importance in maintaining intestinal integrity and promoting microbial diversity cannot be overstated. Moreover, the benefits of sodium butyrate extend beyond the gut, highlighting its potential in mitigating inflammation and enhancing metabolic health.
This article delves into key insights surrounding sodium butyrate, illustrating its anti-inflammatory properties that are crucial for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and metabolic syndrome. Furthermore, the mechanisms through which sodium butyrate operates—such as inhibiting histone deacetylases and activating G protein-coupled receptors—reveal its multifaceted approach to improving health outcomes. Clinical studies reinforce its therapeutic potential, showcasing promising results in managing gastrointestinal disorders and possibly neurodegenerative diseases.
In light of the compelling evidence presented, it becomes clear that sodium butyrate is not just a dietary supplement but a promising candidate for therapeutic applications. As ongoing research continues to unfold its mechanisms and benefits, embracing dietary sources rich in fermentable fibers can be a proactive step toward enhancing overall well-being. The significance of sodium butyrate in health management is profound, making it an essential area for further exploration and application in clinical settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sodium butyrate?
Sodium butyrate, or sodium butanoate, is the salt of butyric acid, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) with the chemical formula Na(C3H7COO).
How is sodium butyrate produced in the body?
Sodium butyrate is predominantly produced in the colon through the fermentation of dietary fibers by beneficial gut bacteria.
What foods are rich in fermentable fibers that promote sodium butyrate production?
Foods rich in fermentable fibers include whole grains, legumes, and specific fruits.
Where else can sodium butyrate be found?
Sodium butyrate can also be found in minor amounts in dairy products such as butter and cheese.
Why is sodium butyrate important for gut health?
Sodium butyrate serves as a primary energy source for colonocytes, the cells lining the colon, and is significant in maintaining gut health by improving intestinal integrity, promoting microbial diversity, and reducing inflammation.
What are the potential benefits of sodium butyrate?
Sodium butyrate may have protective effects against intestinal disorders like inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer and is associated with better health outcomes when maintained at optimal levels.
How does sodium butyrate function at a molecular level?
Sodium butyrate acts as a histone deacetylase inhibitor and transmits signals through G-protein coupled receptors, which are important for its molecular processes.
What does current research say about sodium butyrate levels in humans?
Clinical efforts to elevate short-chain fatty acid levels in humans have shown varied outcomes, indicating the need for further investigation into its effects and benefits.