Topical Rapamycin: Benefits, Application, and Precautions Explained
Overview
Topical rapamycin presents significant advantages for skin health. It is particularly effective in reducing signs of aging and enhancing overall dermal condition, thanks to its anti-inflammatory and cellular rejuvenation properties. This article explores its mechanism of action, which includes promoting collagen production and increasing cellular turnover. Furthermore, clinical evidence supports its efficacy, showing improved complexion and diminished age-related blemishes in users.
Why consider topical rapamycin? The benefits are compelling. By stimulating collagen and enhancing skin renewal, it addresses common concerns associated with aging. Users have reported noticeable improvements in skin texture and vitality. As a result, topical rapamycin stands out as a promising option for those seeking to rejuvenate their skin.
In conclusion, if you’re looking to improve your skin’s health and appearance, topical rapamycin could be worth exploring further. Its scientifically-backed benefits make it a valuable addition to skincare regimens aimed at combating the visible effects of aging.
Introduction
Rapamycin, a compound originally discovered for its antifungal properties, has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment in dermatology, particularly for its potential to rejuvenate aging skin. This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of topical rapamycin, exploring its:
- Mechanism of action
- Application techniques
- Precautions necessary for safe use
Furthermore, as with any treatment, questions arise:
- What are the potential side effects?
- How can users maximize its effectiveness while minimizing risks?
Understanding these aspects is crucial for anyone considering this innovative approach to skincare.
Define Rapamycin and Its Mechanism of Action
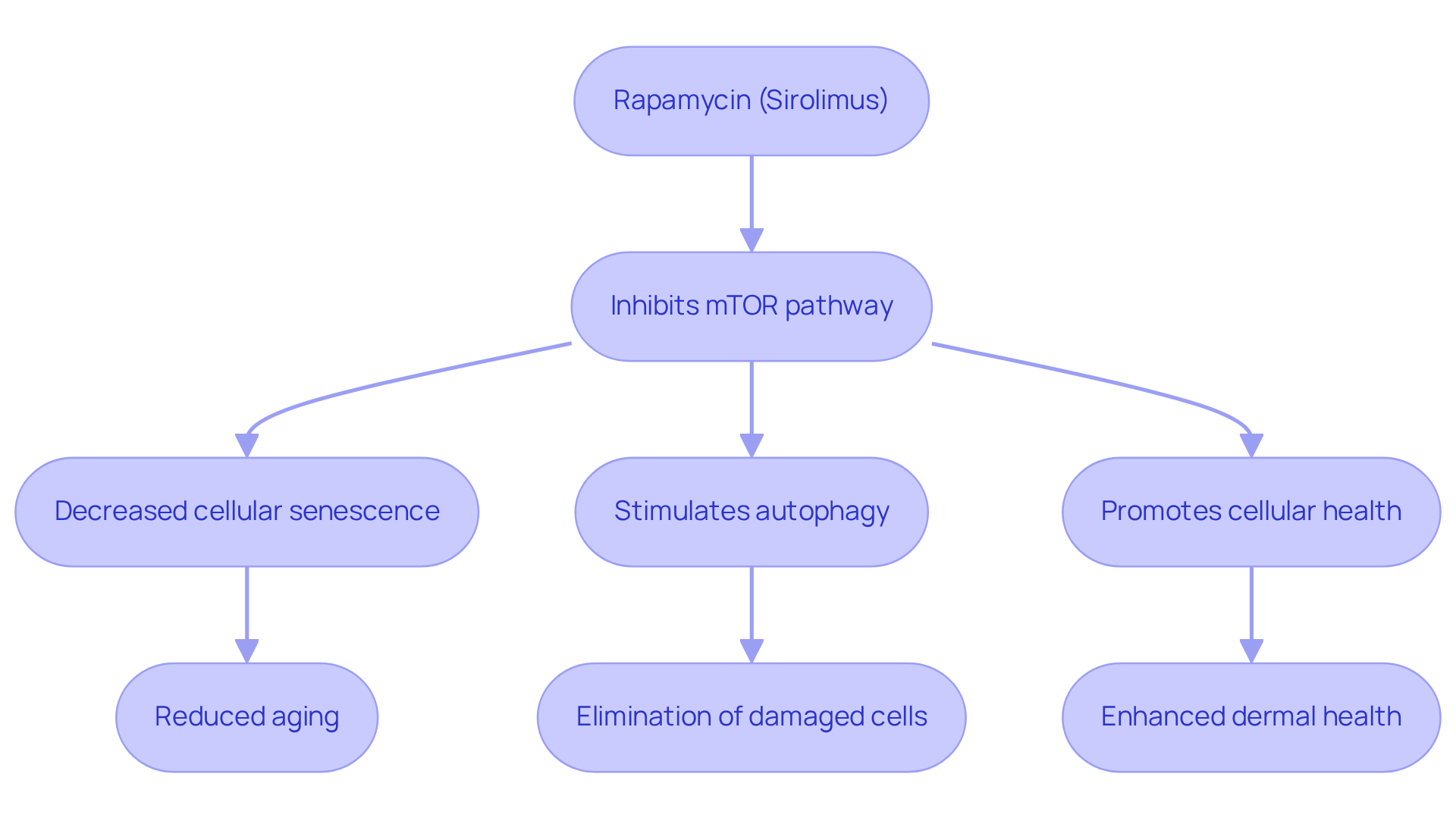
Rapamycin, also known as sirolimus, is a macrolide compound that was initially identified for its antifungal properties. Its primary role is as an inhibitor of the mammalian target of a specific compound, a crucial protein kinase that regulates cell growth, proliferation, and survival. By blocking this particular pathway, rapamycin effectively simulates caloric limitation, a thoroughly researched method for prolonging lifespan across various organisms. This inhibition leads to decreased cellular senescence and stimulates autophagy, a vital process that eliminates damaged cells and proteins, thereby promoting overall cellular health.
This mechanism is essential as it lays the foundation for the drug’s therapeutic applications in dermatology and anti-aging therapies. Recent studies underscore the significance of inhibiting the target of rapamycin in fostering longevity. Findings suggest that reduced activity of this pathway may enhance the likelihood of achieving extraordinary lifespans. Furthermore, dermatologists have observed that mTOR inhibition can result in improved dermal health by promoting cellular regeneration and resilience, further highlighting the potential of rapamycin in anti-aging treatments.
Explore the Benefits of Topical Rapamycin for Skin Health
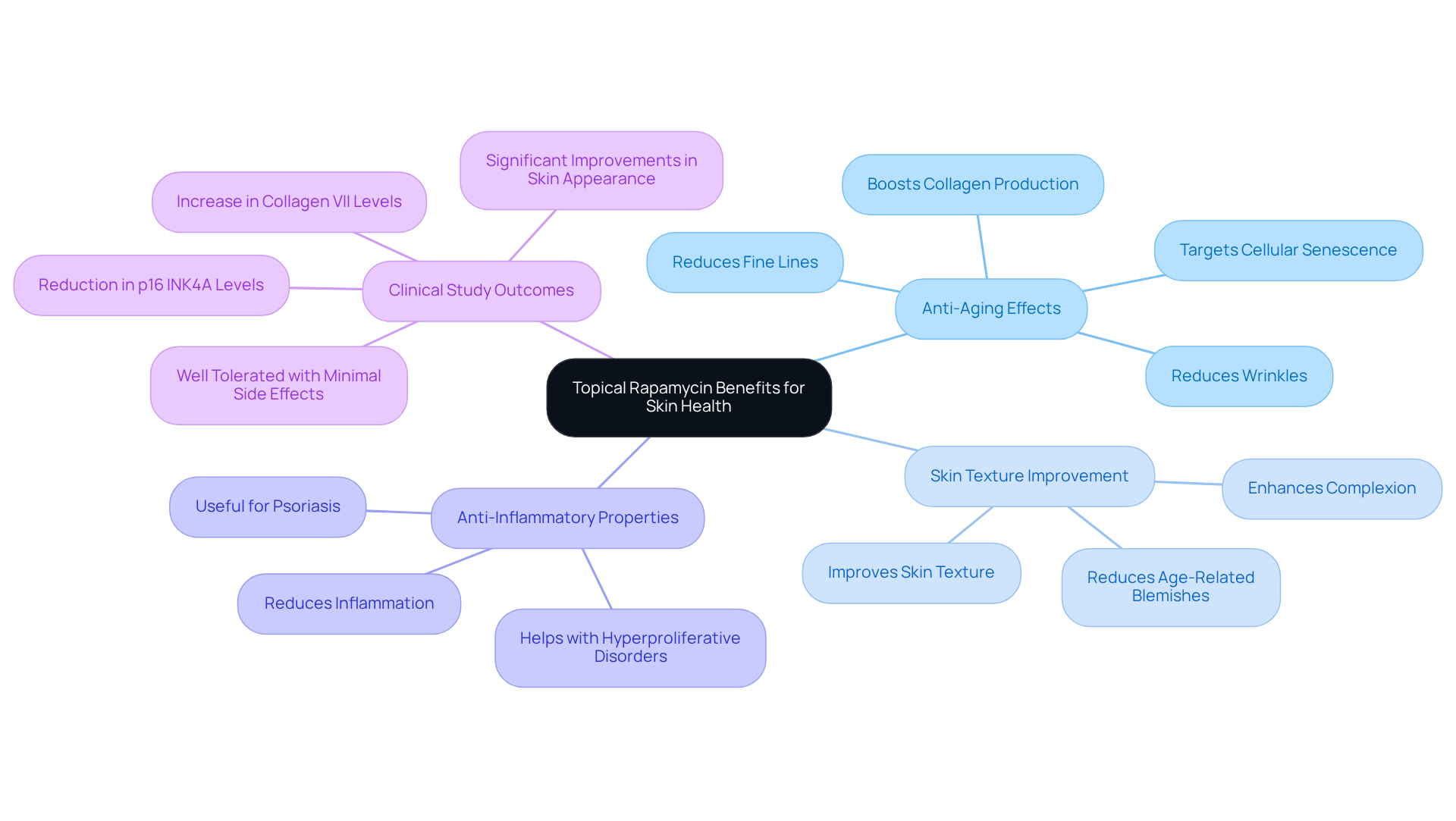
Topical rapamycin treatment has emerged as a significant factor in enhancing dermal health, especially in addressing the effects of photoaging. Research shows its capability to reduce signs of aging, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging. By effectively targeting cellular senescence, topical rapamycin rejuvenates the surface by facilitating the turnover of aged cells and boosting collagen production.
Furthermore, clinical studies suggest that patients using a cream with topical rapamycin reported significant enhancements in complexion and texture, along with a reduction in inflammation and age-related blemishes. Its anti-inflammatory characteristics enhance its usefulness, establishing it as a valuable treatment choice for conditions like psoriasis and other hyperproliferative disorders.
In general, the use of topical treatment offers a hopeful approach for preserving a youthful and radiant complexion.
Guide to Applying Topical Rapamycin: Dosage and Techniques
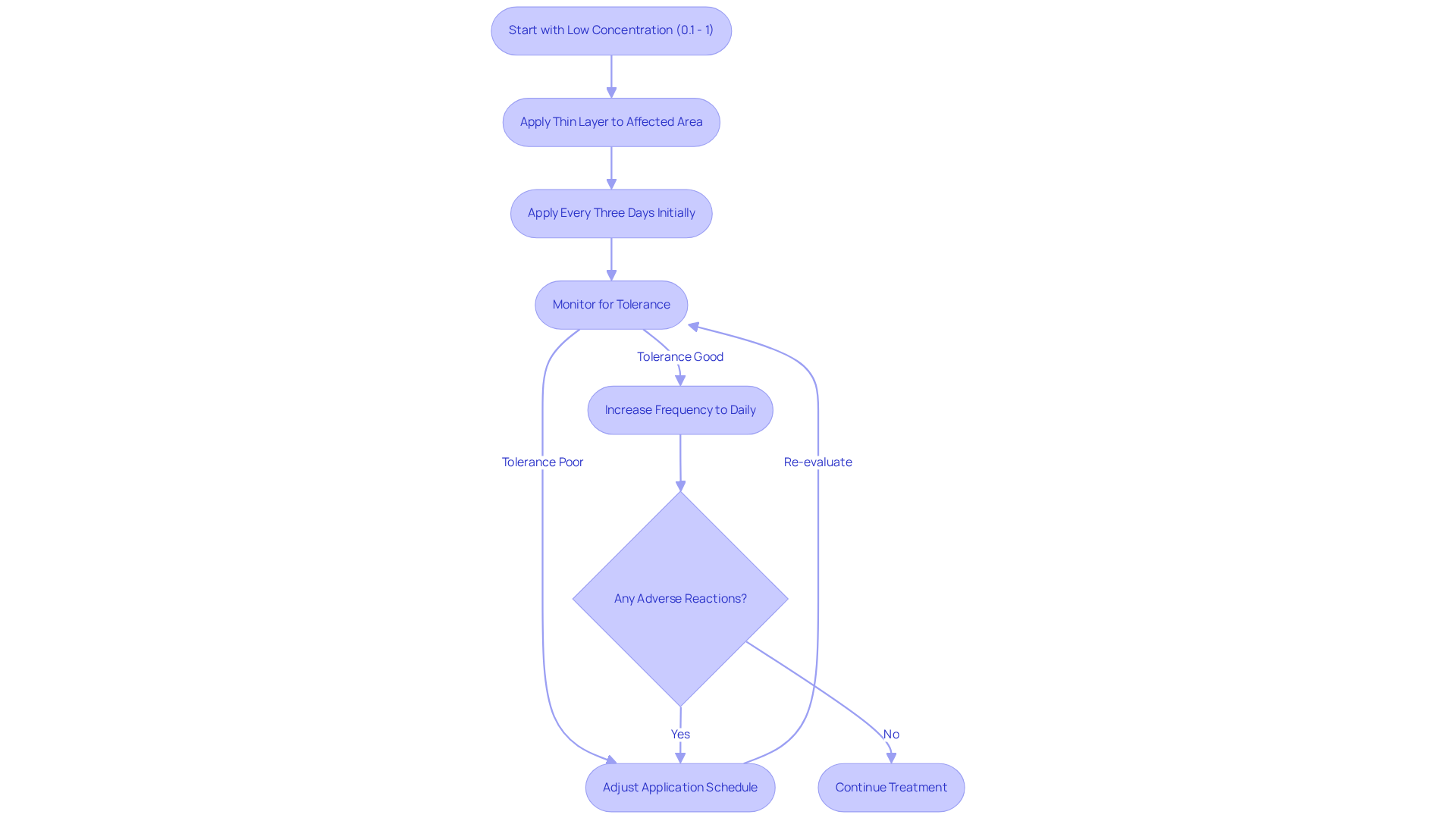
Adherence to specific usage guidelines is crucial to achieve optimal results with topical rapamycin. Start with a low concentration, typically between 0.1% and 1%, and apply a thin layer directly to the affected area. Beginning with applications every three days allows for evaluation of tolerance before increasing the frequency. Most users find that applying topical rapamycin daily yields effective results.
Make certain the skin is clean and dry before use, and gently rub the cream into the skin. Avoid covering the area with bandages or occlusive dressings, as this can hinder absorption. It is important to monitor for any adverse reactions, such as irritation or redness. Adjust the application schedule as needed based on individual responses.
By adhering to these guidelines, users can improve their compliance with the treatment plan and optimize the advantages of topical rapamycin. Are you ready to enhance your treatment experience?
Understand Side Effects and Precautions of Topical Rapamycin
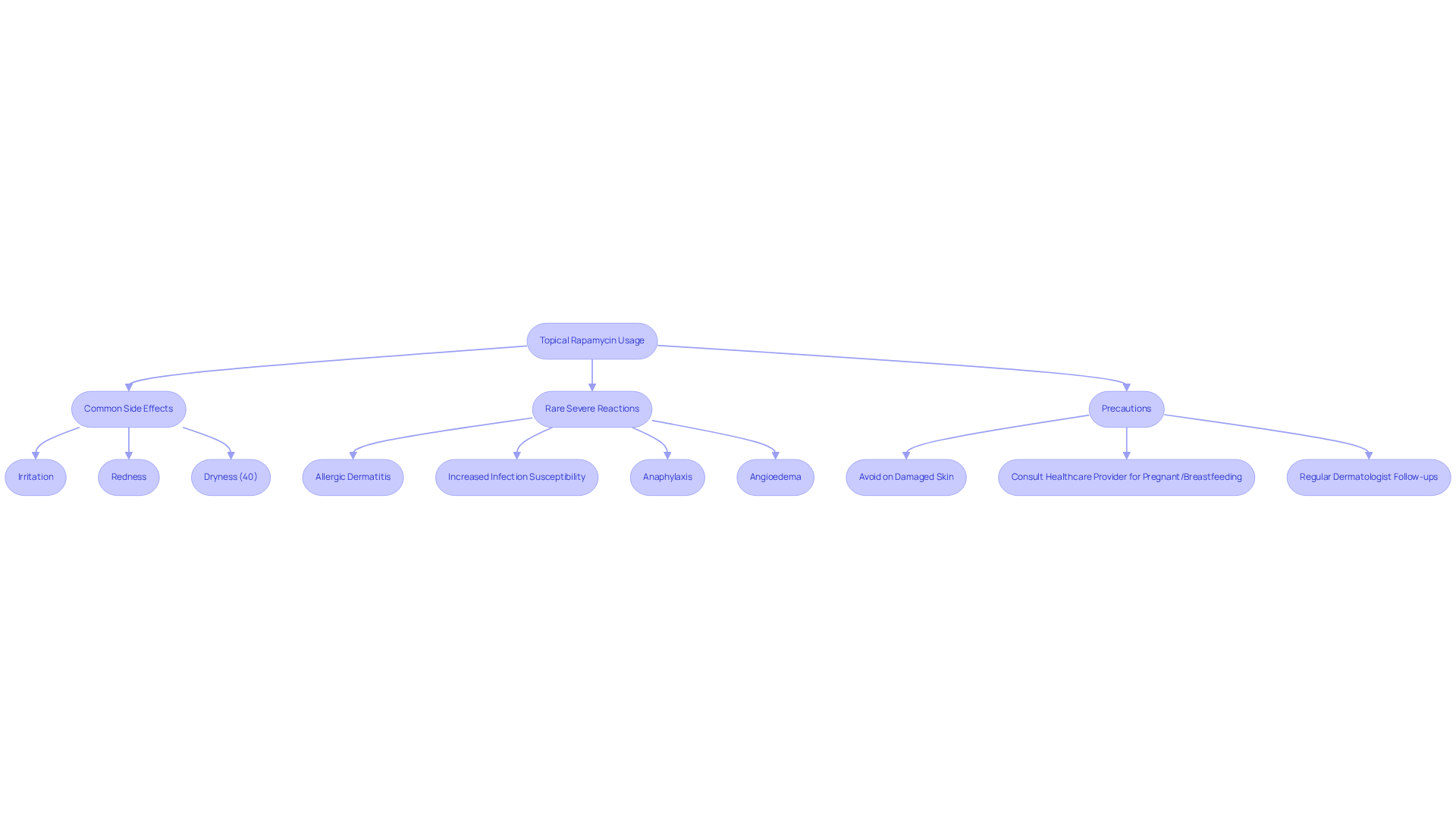
While topical rapamycin is generally well-tolerated, users may still encounter some side effects. Typical responses include irritation, redness, and dryness at the site of use, with around 40% of patients noting dry dermis as a dermatologic adverse event. The most predominant drug-related adverse events were application site irritation and dryness.
In rare instances, more severe reactions such as allergic dermatitis or increased susceptibility to infections may occur, including serious allergic reactions like anaphylaxis and angioedema. To reduce risks, it is crucial to refrain from using the drug on damaged or infected tissue. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare provider before using this medication, as its safety in these populations has not been established.
Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist can help monitor skin health and adjust treatment as necessary, especially considering that the primary safety endpoint incidence was 2.1%, affecting 2 patients. By understanding these precautions, users can safely incorporate topical rapamycin into their skincare routine, ensuring both efficacy and safety.
Notably, 73% of patients treated with topical sirolimus reported subjective improvement in angiofibromas compared to 38% for placebo, highlighting the treatment’s effectiveness. This information underscores the importance of informed usage and highlights the potential benefits of using topical rapamycin.
Conclusion
Topical rapamycin represents a groundbreaking advancement in dermatological treatments, particularly for enhancing skin health and combating the visible signs of aging. By inhibiting the mTOR pathway, rapamycin not only promotes cellular health but also rejuvenates the skin, offering a promising solution for those seeking to maintain a youthful appearance.
Furthermore, the article delves into the multifaceted benefits of topical rapamycin, highlighting its efficacy in reducing fine lines, wrinkles, and other age-related skin issues. It emphasizes the importance of proper application techniques and dosage to maximize results while minimizing potential side effects. Understanding the precautions and side effects associated with its use is crucial for anyone considering this treatment, ensuring both safety and effectiveness.
As a result, the insights shared about topical rapamycin underscore its potential as a revolutionary treatment for skin health. For those interested in exploring this innovative approach, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to tailor the treatment to individual needs. Embracing the possibilities of topical rapamycin could lead to significant improvements in skin health and overall appearance, making it a valuable addition to modern skincare regimens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is rapamycin?
Rapamycin, also known as sirolimus, is a macrolide compound that was initially identified for its antifungal properties.
What is the primary function of rapamycin?
The primary function of rapamycin is to act as an inhibitor of the mammalian target of a specific compound, a crucial protein kinase that regulates cell growth, proliferation, and survival.
How does rapamycin affect cellular processes?
By blocking a specific pathway, rapamycin simulates caloric limitation, leading to decreased cellular senescence and stimulating autophagy, which eliminates damaged cells and proteins, promoting overall cellular health.
What are the therapeutic applications of rapamycin?
Rapamycin has therapeutic applications in dermatology and anti-aging therapies, as its mechanism supports cellular regeneration and resilience.
How does rapamycin relate to longevity?
Recent studies suggest that inhibiting the target of rapamycin may enhance the likelihood of achieving extraordinary lifespans by reducing activity in the mTOR pathway.
What benefits does mTOR inhibition have for skin health?
Dermatologists have observed that mTOR inhibition can improve dermal health by promoting cellular regeneration and resilience.






