Understanding Elastin Structure: Key to Skin Health and Vitality
Overview
Elastin structure plays a crucial role in skin health and vitality. It provides the necessary elasticity that helps maintain a youthful appearance by allowing the skin to stretch and return to its original shape. Furthermore, the production of elastin decreases with age, leading to sagging and wrinkles. This decline emphasizes the importance of nutrition and lifestyle choices. A diet rich in antioxidants and proper hydration can significantly support elastin levels and enhance overall skin resilience. By making informed choices, you can contribute to the maintenance of your skin’s elasticity and youthfulness.
Introduction
Elastin is a vital protein found in connective tissues, playing a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity and overall vitality. As the foundation for youthful skin, understanding its structure and function provides insights into effective anti-aging strategies.
However, with age and environmental factors threatening elastin levels, how can individuals safeguard their skin’s resilience and appearance?
Exploring the intricacies of elastin not only reveals its importance but also presents actionable steps for preserving dermal health in a rapidly aging world.
Define Elastin: The Essential Protein for Skin Elasticity
Elastin is a crucial protein found in connective tissues, particularly in the dermis, lungs, and blood vessels. It provides the necessary elasticity for tissues to stretch and return to their original shape. Composed mainly of amino acids, elastin is produced by fibroblasts and plays an essential role in maintaining the firmness and elasticity of the epidermis. Unlike collagen, which offers structural support, elastin enables the epidermis to revert to its form after stretching or contracting, making it vital for a youthful, healthy appearance.
Statistics indicate that elastin comprises approximately 2% to 4% of the dry weight of the dermis in adults, highlighting its significance in skin composition. As individuals age, the production of this key protein diminishes, leading to noticeable signs of aging, such as sagging and wrinkles. Recent studies underscore the importance of elastin in preserving the flexibility of various tissues, revealing that environmental factors like UV exposure and smoking can accelerate the breakdown of this protein.
Furthermore, hydration is essential for the suppleness of the dermis, which consists of 64% water; a lack of moisture can result in reduced flexibility. Protective measures, such as applying sunscreen and avoiding smoking, are crucial for maintaining skin elasticity. Insights from the Hunza people’s lifestyle, known for their nutrient-rich diet abundant in antioxidants, suggest that such eating habits can enhance the firmness of the dermis and overall vitality.
Understanding the role of elastin is essential for developing effective anti-aging strategies and preserving dermal health. What steps will you take to protect your skin’s elasticity?
Examine Elastin Structure: Composition and Functional Properties
Elastin is primarily made up of tropoelastin, a soluble precursor that polymerizes to create elastic fibers. These fibers are notable for their high concentration of hydrophobic amino acids, which contribute to their extraordinary ability to stretch and recoil. The unique cross-linking of elastic fibers not only enhances their flexibility but also bolsters their durability, allowing them to endure significant mechanical stress. This structural configuration is crucial for maintaining the youthful appearance of the dermis, as elastic fibers can stretch over twice their length before breaking and return to their original dimensions without hysteresis.
Understanding the intricate elastin structure and its functional characteristics is essential for appreciating its vital role in tissue elasticity and overall vitality. Recent studies highlight that the mechanical performance of elastin is influenced by its spatial organization within the extracellular matrix, which varies across different tissues. As the production of elastin diminishes with age, leading to visible signs of aging such as wrinkles and sagging skin, exploring innovative therapies aimed at replenishing this protein becomes increasingly important for dermal health.
Significantly, the Hunza people’s diet, rich in high-quality animal-based nutrients, demonstrates how nutrition can enhance elastin production and overall health. This insight underscores the importance for health-conscious individuals to consider such dietary practices in their anti-aging strategies.
Explore Elastin’s Role in Skin Health: Benefits and Mechanisms
Elastin: The Key to Youthful Skin
Elastin is crucial for preserving the health of the dermis, offering the elasticity and resilience required for a youthful appearance. This protein enables the surface to stretch without tearing, effectively avoiding sagging and the creation of wrinkles. Studies show that the presence of elastin structure in the dermis is essential for maintaining the outer layer’s integrity, allowing it to withstand environmental stressors like UV rays and pollution. Furthermore, elastin plays an important role in wound healing by encouraging tissue regeneration, which is vital for preserving a youthful look.
Moreover, elastin’s capacity to hold moisture is another critical element in hydration and overall vitality. Research indicates that increased levels of elastin are linked to better moisture retention in the dermis, leading to a full and vibrant appearance. For example, participants in clinical trials reported notable enhancements in dermal hydration and elasticity following therapies designed to boost protein generation. These findings highlight the elastin structure’s role not only in preserving the dermis but also in improving its moisture and durability.
Real-world examples emphasize the significance of elastin in preventing wrinkles. Individuals receiving microneedling procedures, for instance, have noted an impressive 400% rise in collagen and elasticity production, resulting in a smoother surface and a decrease in visible signs of aging. This non-invasive procedure has gained popularity due to its effectiveness in stimulating the body’s natural healing processes, crucial for maintaining elasticity and preventing sagging.
In summary, elastin is a vital component of dermal health, aiding in hydration, resilience, and the prevention of wrinkles. Understanding its mechanisms can empower individuals to implement effective skincare strategies that promote a youthful, vibrant appearance.
Analyze Aging Effects on Elastin: Implications for Skin Vitality
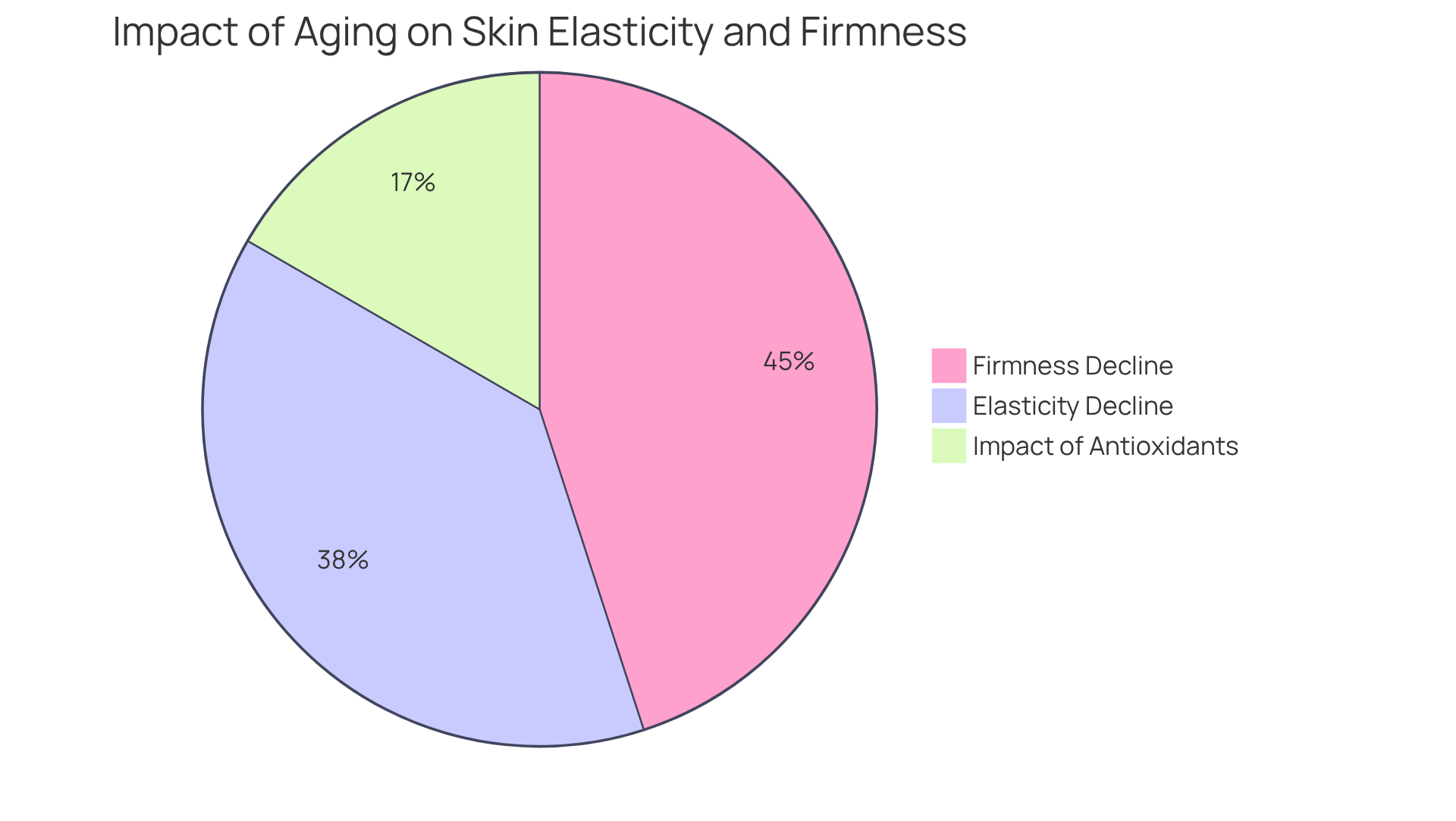
As individuals age, the elastin structure production decreases significantly, leading to a reduction in the suppleness and firmness of the dermis. Studies indicate that the elasticity of the dermis declines by approximately 23% with age, while firmness can diminish by as much as 27%. Furthermore, factors such as sun exposure, smoking, and inadequate nutrition can accelerate this decline. Chronic sun exposure, for instance, causes solar elastosis, which is characterized by a disorganized elastin structure and a reduction in tissue resilience. The deterioration of connective fibers results in noticeable signs of aging, including wrinkles, sagging tissue, and diminished overall vitality.
Research suggests that individuals who consume foods rich in antioxidants experience 10% less photoaging over 15 years compared to those with lower antioxidant intake. This highlights the importance of diet in maintaining skin elasticity. Understanding these impacts of aging is crucial for developing effective anti-aging strategies that focus on preserving the elastin structure of connective tissue and enhancing dermal vitality.
A consistent skincare routine, which includes the use of sunscreen, is essential for maintaining the health of the dermis as it matures. By prioritizing these practices, individuals can support their skin’s resilience and appearance over time.
Implement Strategies to Support Elastin Production: Nutrition and Lifestyle Tips
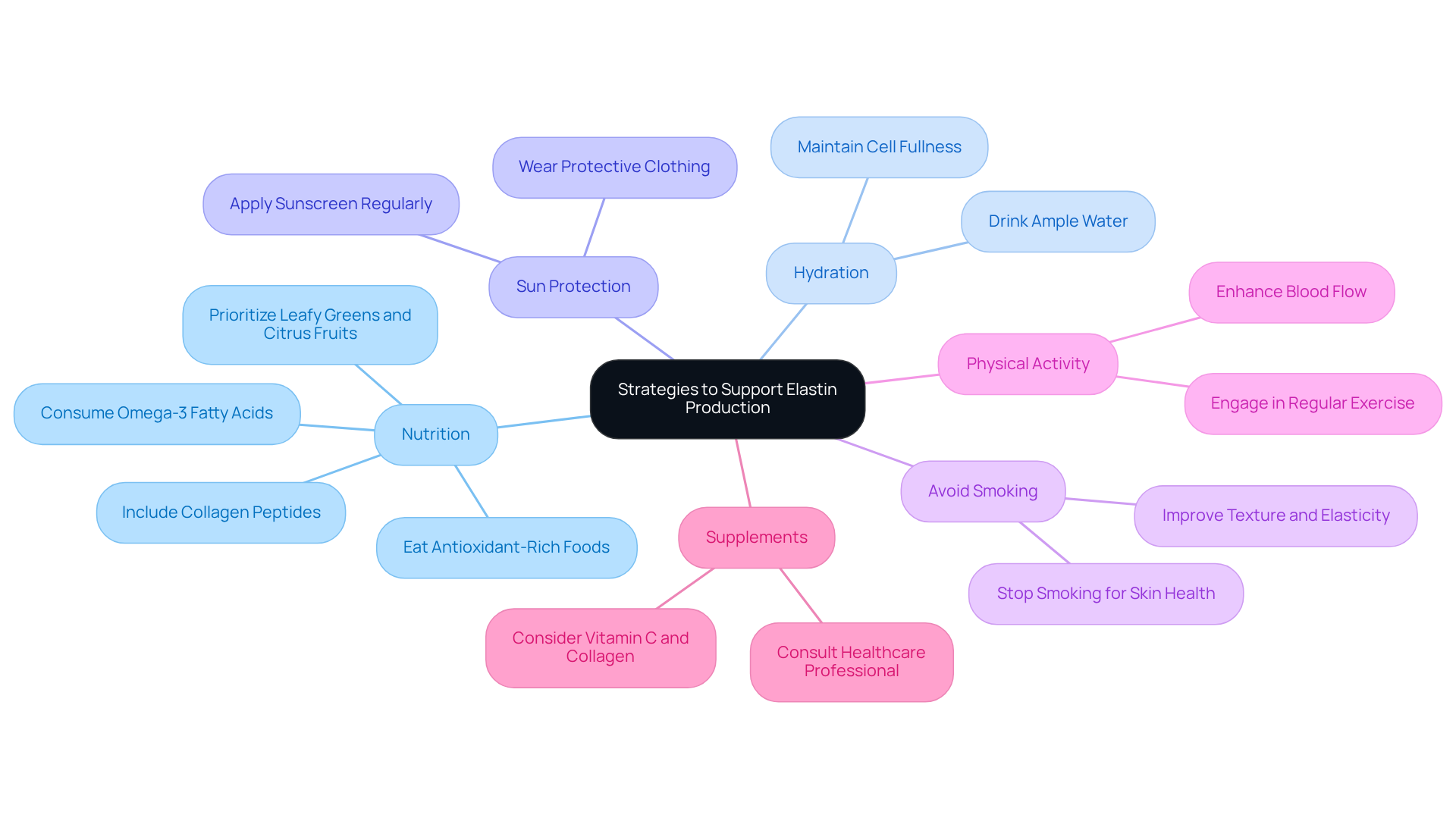
To support elastin production and maintain skin health, consider these nutrition and lifestyle tips:
-
Consume a Nutrient-Rich Diet: Prioritize foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins C and E, and omega-3 fatty acids. Leafy greens, citrus fruits, berries, and fatty fish such as trout and salmon, along with nuts, are outstanding options that can enhance the elastin structure and overall vitality. Furthermore, including dietary supplements like collagen peptides and vitamin C can further enhance the flexibility and health of the dermis.
-
Stay Hydrated: Sufficient hydration is essential for preserving the elasticity of the dermis. Consuming ample water aids in maintaining cell fullness and promotes their regenerative functions.
-
Limit Sun Exposure: Shield your dermis from harmful UV rays, which can harm elasticity and collagen. Regularly applying sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can mitigate these effects.
-
Avoid Smoking: Smoking accelerates the aging of the dermis and significantly decreases the levels of connective tissue proteins. Stopping smoking can lead to notable enhancements in texture and elasticity over time.
-
Include Consistent Physical Activity: Participating in exercise improves blood flow, facilitating nutrient supply to the dermis and aiding in collagen production. Exercise also enhances overall health, which is essential for preserving a youthful appearance.
-
Consider supplements that may assist in the elastin structure and collagen production, such as vitamin C and collagen peptides, by consulting with a healthcare professional. Personal experiences from individuals who have incorporated these supplements into their routines often highlight significant improvements in skin texture and resilience.
Conclusion
Elastin is a fundamental protein that plays an indispensable role in maintaining skin elasticity and overall dermal health. This essential component allows the skin to stretch and return to its original shape, significantly contributing to a youthful appearance. As individuals age, the decline in elastin production becomes evident, leading to sagging and wrinkles. Understanding the importance of elastin and its structural properties is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their skin’s vitality.
Throughout the article, key insights reveal how elastin not only supports the skin’s flexibility but also aids in moisture retention and wound healing. The impact of lifestyle choices, such as diet and sun exposure, on elastin levels emphasizes the need for proactive measures to protect and promote skin health. Nutrient-rich foods, hydration, and protective habits can significantly influence the integrity of elastin, thereby enhancing the skin’s resilience against aging and environmental stressors.
In light of these findings, adopting a holistic approach to skin care that prioritizes elastin preservation can lead to remarkable improvements in skin vitality. Embracing nutritious diets, staying hydrated, and avoiding harmful habits are vital steps toward maintaining a youthful appearance. By understanding and implementing strategies to support elastin production, individuals can empower themselves to combat the signs of aging and promote lasting skin health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is elastin and where is it found in the body?
Elastin is a crucial protein found in connective tissues, particularly in the dermis, lungs, and blood vessels. It provides elasticity for tissues to stretch and return to their original shape.
What role does elastin play in skin health?
Elastin is essential for maintaining the firmness and elasticity of the epidermis. It allows the skin to revert to its original form after stretching or contracting, contributing to a youthful and healthy appearance.
How much of the dermis is made up of elastin?
Elastin comprises approximately 2% to 4% of the dry weight of the dermis in adults, highlighting its significance in skin composition.
What happens to elastin production as we age?
As individuals age, the production of elastin diminishes, leading to noticeable signs of aging, such as sagging and wrinkles.
What factors can accelerate the breakdown of elastin?
Environmental factors like UV exposure and smoking can accelerate the breakdown of elastin.
Why is hydration important for skin elasticity?
Hydration is essential for the suppleness of the dermis, which consists of 64% water. A lack of moisture can result in reduced flexibility of the skin.
What protective measures can help maintain skin elasticity?
Protective measures include applying sunscreen and avoiding smoking to help maintain skin elasticity.
How does diet influence elastin production and skin health?
A nutrient-rich diet abundant in antioxidants, such as that of the Hunza people, can enhance the firmness of the dermis and overall vitality, suggesting that dietary practices can be beneficial for skin health.
What is the structure of elastin and its functional properties?
Elastin is primarily made up of tropoelastin, a soluble precursor that polymerizes to create elastic fibers. These fibers have a high concentration of hydrophobic amino acids, allowing them to stretch and recoil effectively.
How does the spatial organization of elastin affect its performance?
The mechanical performance of elastin is influenced by its spatial organization within the extracellular matrix, which varies across different tissues.
What innovative therapies are being explored for elastin replenishment?
As elastin production diminishes with age, exploring innovative therapies aimed at replenishing this protein becomes increasingly important for dermal health.