Understanding Insulin Resistance Vitamins and Their Role in Health
Overview
Insulin resistance vitamins, such as B vitamins, vitamin D, and vitamin E, play a crucial role in enhancing glucose sensitivity and managing blood sugar levels. By doing so, they help reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic disorders.
Have you ever considered how deficiencies in these vitamins might impact your glucose metabolism? This article details the significant effects of vitamin deficiencies and emphasizes the importance of adequate intake, whether through diet or supplementation.
Improving insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health is essential for everyone. Therefore, exploring ways to incorporate these vitamins into your daily routine can be a beneficial step towards better health.
Introduction
The intricate relationship between vitamins and insulin resistance represents a growing area of interest in health research. This highlights the essential nutrients that support the body’s ability to manage glucose effectively. Understanding the role of vitamins—particularly B vitamins, D, and E—can empower individuals to enhance their metabolic health and reduce the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
However, with rising rates of insulin resistance across various demographics, one pressing question emerges:
- How can specific vitamin deficiencies contribute to this condition?
- What proactive measures can be taken to mitigate these risks?
Exploring these questions can lead to actionable insights that promote better health outcomes.
Define Insulin Resistance Vitamins and Their Importance
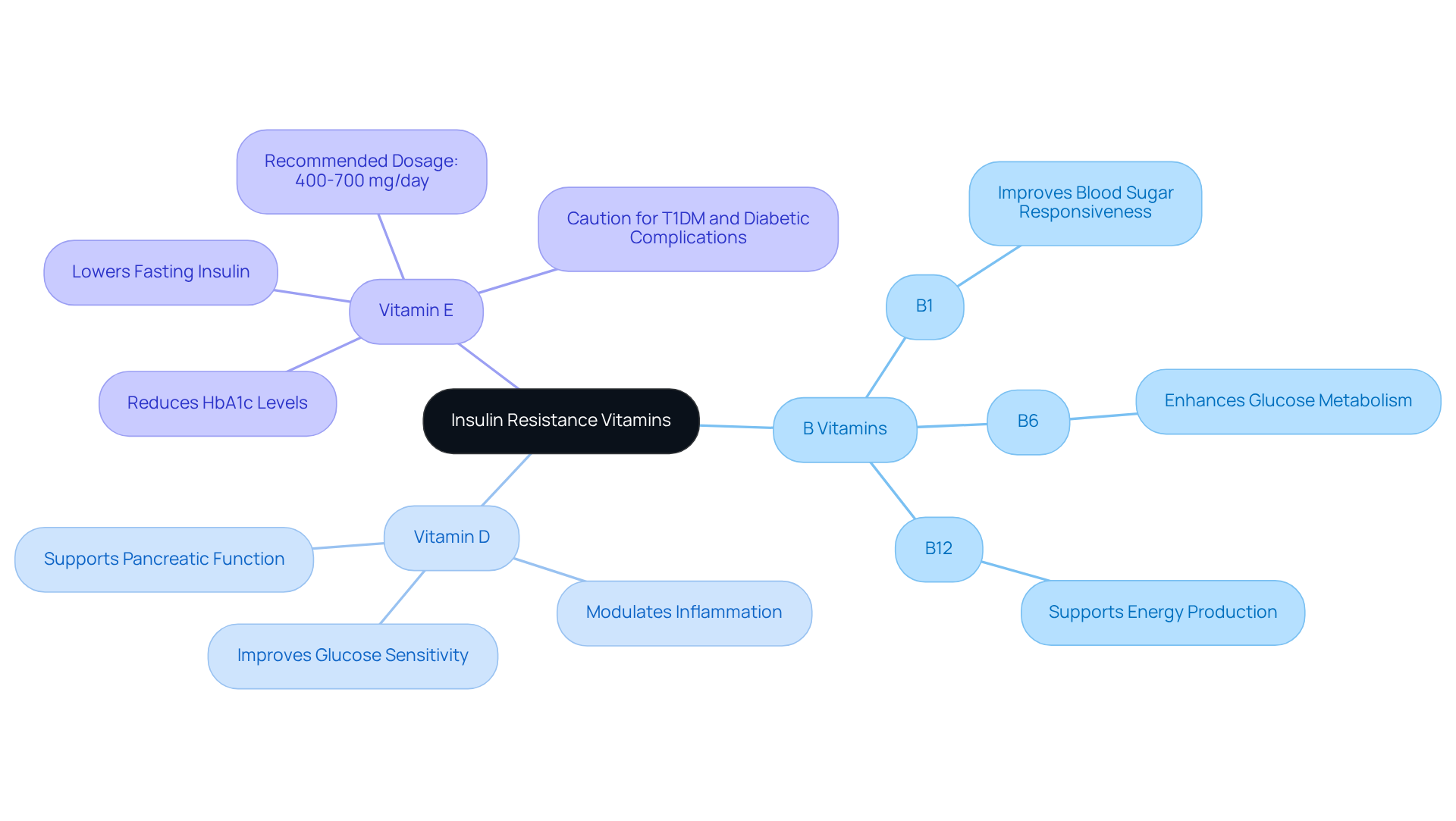
Nutrients associated with insulin resistance vitamins represent a critical collection of substances necessary for the body’s ability to utilize glucose effectively. These nutrients, which encompass insulin resistance vitamins as well as B vitamins, D, and E, play vital roles in regulating blood sugar levels. Their importance lies in their capacity to enhance glucose sensitivity, thereby reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. Research indicates that B vitamins, particularly B1, B6, and B12, significantly improve blood sugar responsiveness. Studies have shown that adequate intake can lead to improved glucose metabolism and a decreased likelihood of metabolic issues.
Furthermore, vitamin D is recognized as a key player in glucose sensitivity. Case studies reveal that individuals with sufficient levels of vitamin D often experience better glucose responses and lower fasting blood sugar levels. This nutrient’s role in modulating inflammation and supporting pancreatic function underscores its importance in metabolic health.
In addition, vitamin E, especially at doses between 400 to 700 mg/day, has demonstrated a significant impact on reducing HbA1c levels, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR in diabetic patients. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials has highlighted that vitamin E supplementation can lead to substantial improvements in glycemic control, particularly for those with type 2 diabetes.
However, caution is warranted for individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) and those suffering from diabetic nephropathy or neuropathy due to the limited research available regarding dietary supplementation effects in these groups.
The combined benefits of B vitamins, D, and E illustrate their essential roles as insulin resistance vitamins in enhancing glucose sensitivity. As individuals seek to manage their blood sugar levels and overall health—especially as they age—understanding the functions of these nutrients becomes increasingly important. Experts consistently recommend a balanced intake of these nutrients as part of a holistic health approach, emphasizing that ‘short-term interventions with vitamin E have resulted in lower fasting blood glucose in these patients’ (Omid Asbaghi, Nutrition Journal).
Contextualize Insulin Resistance: Causes and Health Implications
The body’s cells exhibit reduced sensitivity to hormones, which leads to increased blood sugar levels. Several factors influence this condition, particularly obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, and genetic predisposition. The consequences of hormonal dysfunction are significant, serving as a precursor to type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and various metabolic disorders. Recent research indicates that nearly 40% of young American adults aged 18-44 face hormonal challenges, often without excess weight. This highlights the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in this demographic and underscores the urgent need for early intervention and lifestyle changes.
Obesity significantly affects glucose resistance, as excess body fat—especially around the abdomen—can disrupt hormonal signaling. Additionally, a lack of physical activity exacerbates this issue, further diminishing sensitivity to glucose. Conversely, engaging in regular physical exercise and achieving weight loss can substantially improve glucose sensitivity, thereby reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
Real-life examples underscore the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications. Individuals who adopt a balanced diet rich in non-starchy vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins have shown improved glucose sensitivity. Furthermore, incorporating insulin resistance vitamins along with specific supplements can enhance metabolic health and optimize the body’s response to glucose. Community support plays a vital role in preventing type 2 diabetes, fostering accountability and promoting healthier lifestyle choices.
Understanding the link between obesity and hormonal sensitivity is crucial, particularly as hormonal sensitivity increases among older populations. By addressing these factors through informed dietary choices and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can proactively enhance their health and mitigate risks associated with blood sugar issues. As Vibhu Parcha, M.D., points out, “The presence of hormonal imbalance is considered an indicator for the onset of diabetes and potentially life-threatening cardiovascular events such as heart attack, stroke, and cardiac mortality.” This statement emphasizes the importance of early intervention and lifestyle changes in managing blood sugar challenges.
Identify Key Vitamins for Managing Insulin Resistance
Key vitamins for managing insulin resistance include:
-
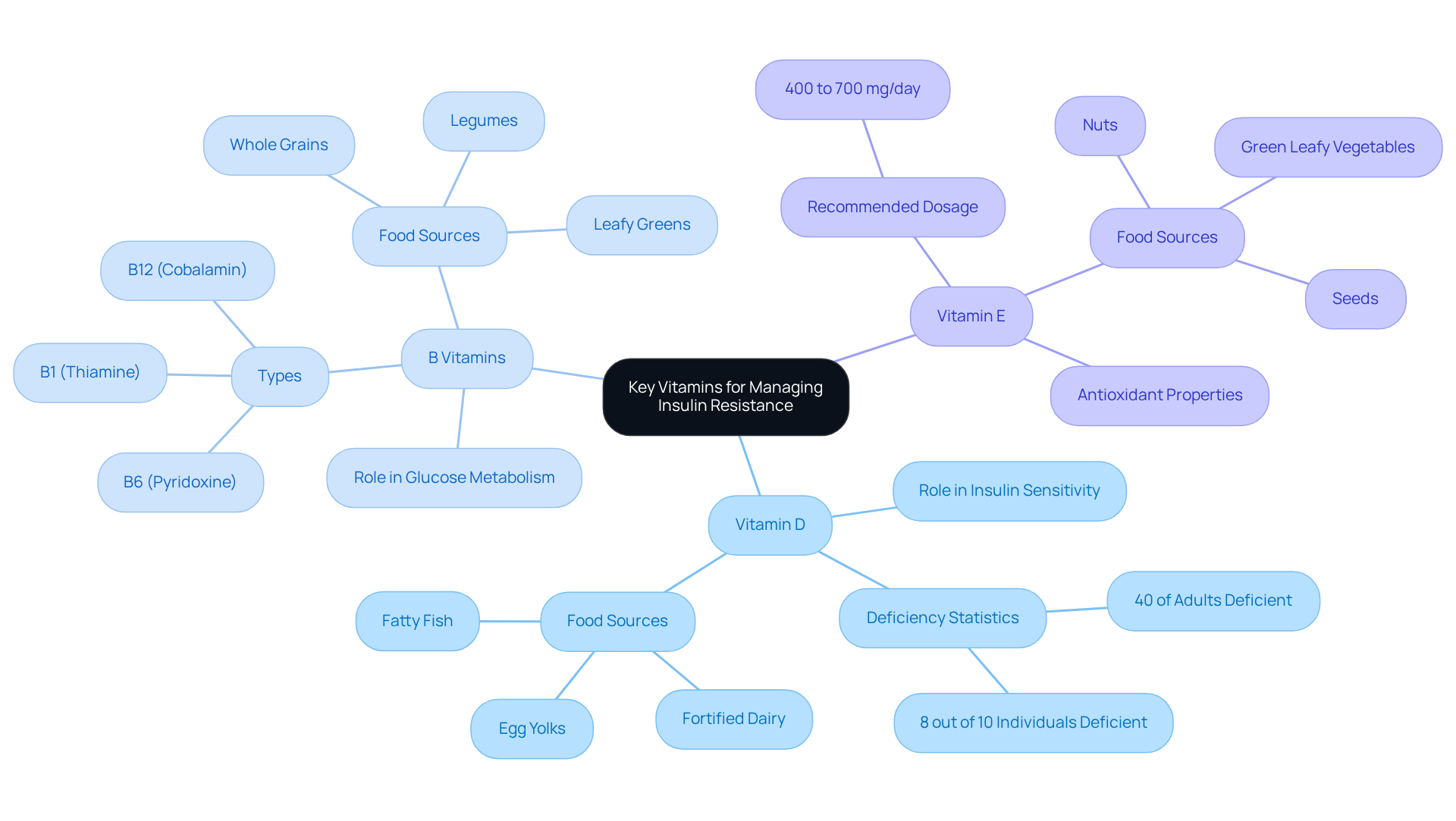
Vitamin D: This essential nutrient is crucial for insulin secretion and sensitivity. Research indicates that low levels of vitamin D are linked to heightened insulin resistance, making sufficient intake essential for metabolic health. In fact, a study discovered that 8 out of 10 individuals had vitamin D deficiency, highlighting its significance. Foods high in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, fortified dairy items, and egg yolks, can assist in sustaining optimal levels. Furthermore, clinical trials have demonstrated that vitamin D supplementation can lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, further emphasizing its importance in metabolic health.
-
B Vitamins: Vitamins B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), and B12 (cobalamin) are integral to glucose metabolism and energy production. Research indicates that these nutrients aid the body’s capacity to process glucose efficiently, with deficiencies associated with disrupted glucose metabolism. Including sources such as whole grains, legumes, and leafy greens can improve B vitamin intake.
-
Vitamin E: Recognized for its antioxidant characteristics, this nutrient may assist in reducing oxidative stress, a factor linked to glucose resistance. Clinical evidence indicates that vitamin E supplementation can result in substantial enhancements in glucose sensitivity and glycemic regulation. The suggested amount for vitamin E is between 400 to 700 mg/day for optimal effects. Nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables are excellent dietary sources of vitamin E.
Incorporating these vitamins through a balanced diet not only supports metabolic health but also enhances overall well-being, making it easier to manage insulin resistance effectively.
Examine the Impact of Vitamin Deficiencies on Insulin Resistance
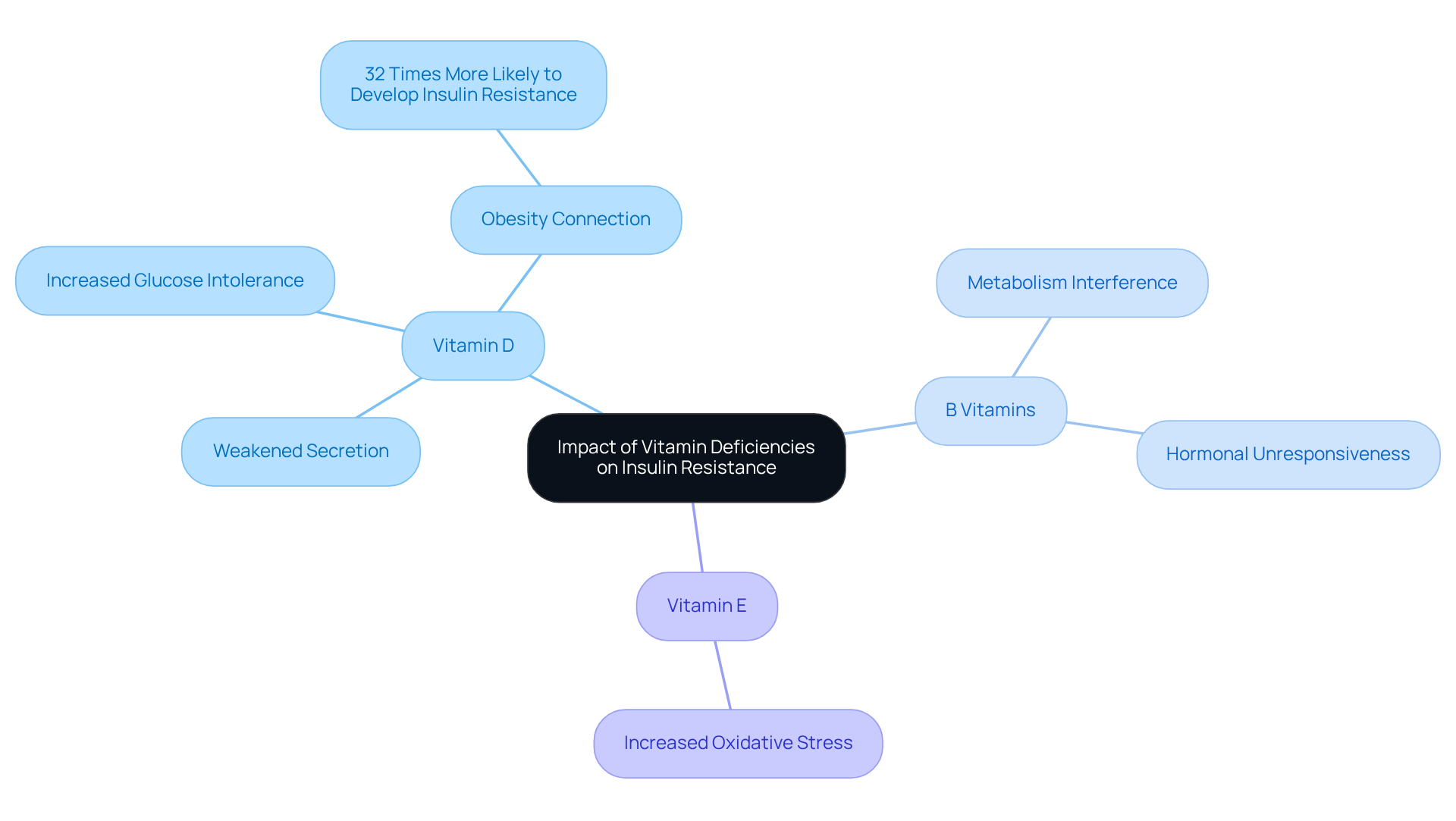
Vitamin shortages play a vital role in the formation of glucose intolerance. A significant instance is the lack of vitamin D, which has been associated with weakened secretion and increased challenges related to blood sugar regulation. Studies show that individuals with low levels of vitamin D are considerably more prone to encounter glucose intolerance, especially among those who are overweight. In fact, a study from Drexel University, which analyzed data from 5,806 respondents in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), found that obese individuals with low levels of vitamin D are about 32 times more likely to develop insulin resistance compared to the average population.
Furthermore, along with vitamin D, shortages in B vitamins can significantly interfere with glucose metabolism. These nutrients are crucial for different metabolic functions, and their deficiency can result in increased blood sugar levels. For example, B vitamin deficiencies have been demonstrated to adversely affect glucose metabolism, leading to hormonal unresponsiveness. Moreover, a lack of vitamin E may heighten oxidative stress, which can further worsen hormonal issues.
Addressing these deficiencies through dietary adjustments or supplementation is essential for those looking to improve their insulin resistance vitamins and enhance their sensitivity to glucose and overall metabolic health. With approximately 25.6 million adults in the U.S. affected by Type 2 diabetes, understanding the implications of vitamin deficiencies on insulin resistance is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding the critical role of insulin resistance vitamins is essential for maintaining metabolic health and preventing chronic diseases. These vitamins, particularly B vitamins, vitamin D, and vitamin E, are integral to enhancing glucose sensitivity and regulating blood sugar levels. By ensuring an adequate intake of these nutrients, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
The article highlights key insights into how deficiencies in vitamins can lead to increased insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. B vitamins are crucial for efficient glucose metabolism, while vitamin D plays a significant role in insulin secretion and sensitivity. Additionally, vitamin E’s antioxidant properties help mitigate oxidative stress, further supporting metabolic health. Lifestyle changes, including adopting a balanced diet rich in these vitamins, are vital for improving insulin sensitivity and overall well-being.
Ultimately, addressing vitamin deficiencies through dietary adjustments or supplementation is a proactive approach to managing insulin resistance. As awareness of the health implications associated with this condition grows, individuals are encouraged to prioritize their nutrient intake and engage in healthy lifestyle practices. By doing so, they can enhance their metabolic health and reduce the risks associated with insulin resistance, paving the way for a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are insulin resistance vitamins?
Insulin resistance vitamins are nutrients that play a critical role in the body’s ability to utilize glucose effectively, enhancing glucose sensitivity and regulating blood sugar levels.
Which vitamins are associated with insulin resistance?
Key vitamins associated with insulin resistance include B vitamins (particularly B1, B6, and B12), vitamin D, and vitamin E.
How do B vitamins affect blood sugar levels?
B vitamins, especially B1, B6, and B12, significantly improve blood sugar responsiveness and can lead to enhanced glucose metabolism and a reduced likelihood of metabolic issues.
What role does vitamin D play in glucose sensitivity?
Vitamin D is recognized for its role in improving glucose sensitivity, with sufficient levels associated with better glucose responses and lower fasting blood sugar levels.
What impact does vitamin E have on diabetes?
Vitamin E, particularly at doses between 400 to 700 mg/day, has been shown to reduce HbA1c levels, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR in diabetic patients, leading to improved glycemic control.
Are there any precautions for taking insulin resistance vitamins?
Yes, individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) and those suffering from diabetic nephropathy or neuropathy should exercise caution due to limited research on the effects of dietary supplementation in these groups.
Why is understanding insulin resistance vitamins important for health management?
Understanding insulin resistance vitamins is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and overall health, especially as individuals age, as these nutrients enhance glucose sensitivity and support metabolic health.
What is the recommended approach for intake of these vitamins?
Experts recommend a balanced intake of B vitamins, D, and E as part of a holistic health approach to effectively manage blood sugar levels and promote overall well-being.


