Understanding Rapamycin Longevity: Its Role and Mechanisms
Overview
Rapamycin plays a significant role in promoting longevity by inhibiting the mTOR pathway. This inhibition enhances autophagy and reduces the onset of age-related diseases. How does this work? The mechanisms of rapamycin improve:
- Cellular health
- Insulin sensitivity
- Inflammation
As a result, it positions itself as a promising candidate in anti-aging research and therapies.
In summary, exploring rapamycin’s potential could lead to groundbreaking advancements in longevity and healthspan. Its ability to target critical pathways in our cells makes it a key focus in the quest for effective anti-aging solutions.
Introduction
Rapamycin, a compound first discovered in the soil of Easter Island, has evolved from its initial role as an immunosuppressant to a central focus in longevity research, intriguing both scientists and wellness enthusiasts. Its remarkable ability to inhibit the mTOR pathway positions it as a potential game-changer in the pursuit of an extended healthspan, effectively mimicking the life-prolonging effects associated with caloric restriction. However, as excitement mounts regarding its anti-aging benefits, important questions emerge about the long-term implications and optimal usage of rapamycin. What does the future hold for this promising longevity agent?
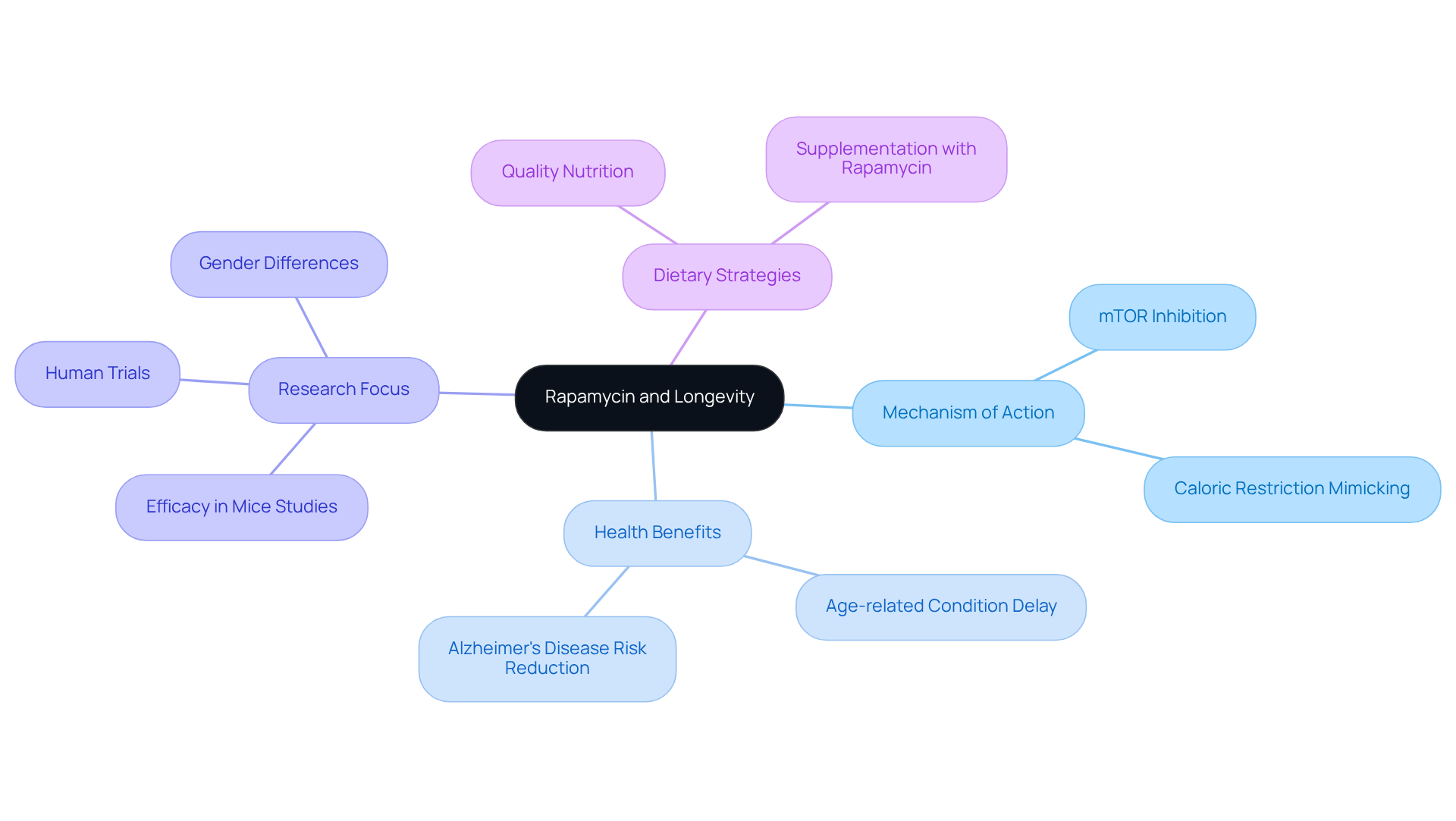
Define Rapamycin and Its Role in Longevity
Rapamycin, also known as sirolimus, is a macrolide compound first identified in the soil of Rapa Nui (Easter Island). Initially developed as an immunosuppressant for organ transplant patients, its primary mechanism involves inhibiting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a crucial regulator of cell growth and metabolism. Recent studies have highlighted the potential of this compound to enhance lifespan, contributing to rapamycin longevity by mimicking the effects of caloric restriction, which is recognized to prolong life across various species.
By modulating the mTOR pathway, the potential of rapamycin longevity may delay the onset of age-related conditions and improve overall healthspan, positioning it as a pivotal focus in anti-aging research. Ongoing investigations are exploring the efficacy of rapamycin longevity in reducing risks associated with Alzheimer’s and cardiac diseases, further solidifying its role in longevity therapies. Researchers emphasize that this compound’s ability to enhance cell longevity, particularly through mechanisms related to rapamycin longevity by decreasing cellular growth and reproduction, may help reduce disease-related waste accumulation, making it a promising option for future anti-aging strategies.
This aligns with broader investigations into dietary supplements in anti-aging, as noted in personal experiences shared by wellness enthusiasts who advocate for quality nutrition and innovative therapies, such as those discussed on ByKomi.com. Many health-conscious individuals have reported incorporating rapamycin into their routines alongside a diet rich in quality animal-based foods. This reflects a holistic approach to longevity that resonates with the principles of ByKomi.com.
Examine the Mechanisms of Rapamycin in Aging
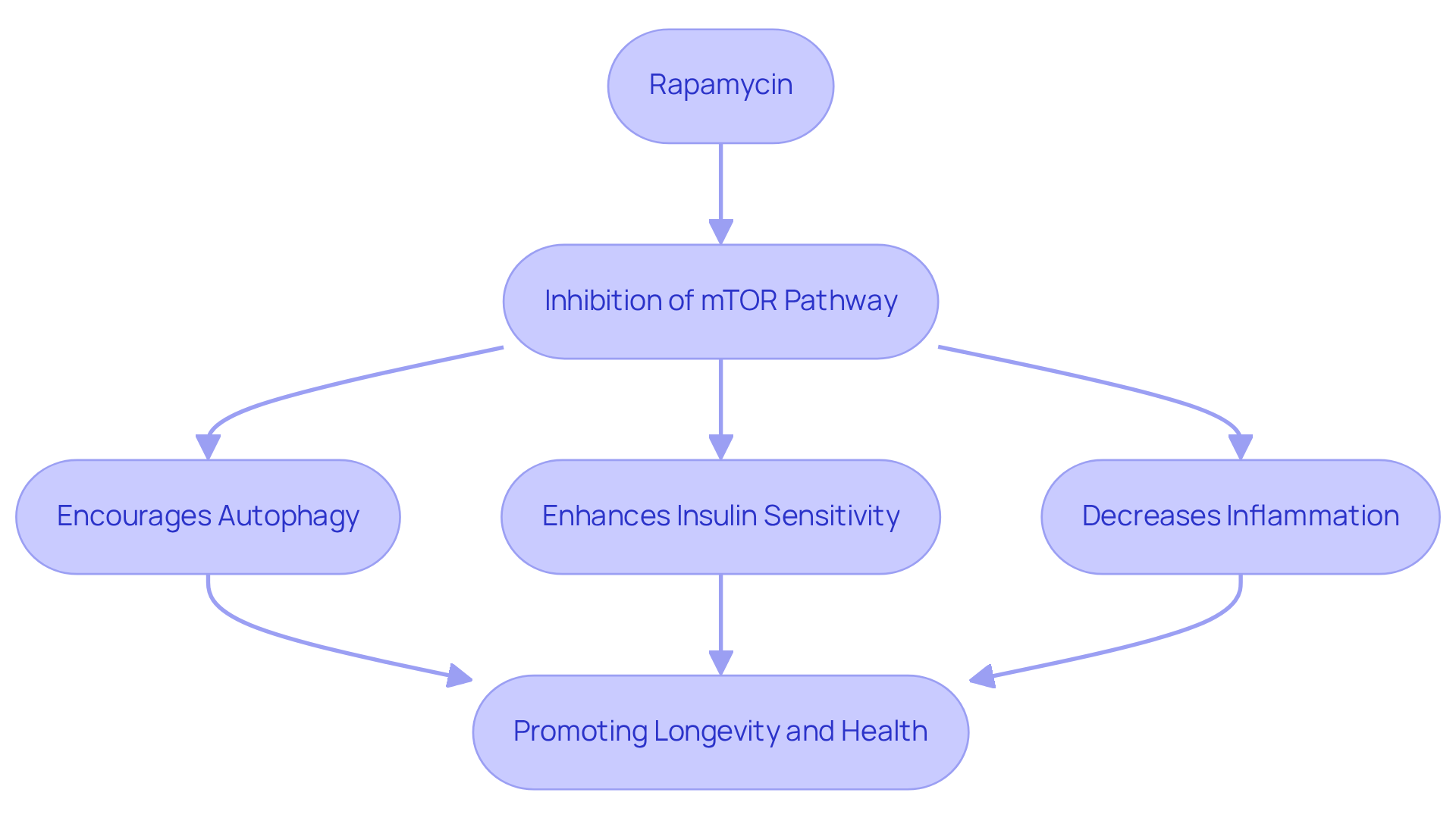
Rapamycin longevity is primarily influenced by its inhibition of the mTOR pathway, a crucial regulator of cellular growth, proliferation, and survival. This inhibition encourages autophagy, a critical cellular process that removes damaged organelles and proteins, thereby improving overall cellular well-being. Furthermore, this compound has been demonstrated to enhance insulin sensitivity, decrease inflammation, and improve mitochondrial function—essential elements in preserving health as people grow older.
Studies involving different animal models have shown that rapamycin longevity can be achieved by prolonging lifespan and postponing the emergence of age-related illnesses, such as cancer and heart diseases. Significantly, studies suggest that administering this compound during mid-life can promote rapamycin longevity, highlighting its potential as a geroprotective agent.
The insights gained from innovative interdisciplinary research, such as Dr. Dituri’s underwater experiments, suggest that combining a specific supplement with lifestyle interventions—like dietary modifications and exercise—could enhance its anti-aging effects. Overall, the effects of this compound on autophagy contribute significantly to its health benefits, making it a promising candidate for further exploration in the context of aging.
Discuss the Rising Popularity of Rapamycin in Anti-Aging Research
The growing popularity of this compound in anti-aging research is evident, fueled by persuasive results from animal studies and an increasing interest in rapamycin longevity science. Researchers are exploring this compound not only as a treatment for age-related diseases but also for its potential in promoting rapamycin longevity as a proactive approach to healthy aging. Its ability to mimic caloric restriction—a well-studied method for extending lifespan—has garnered significant attention from both researchers and wellness enthusiasts.
Initial studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that small amounts of this compound may enhance immune function and overall well-being in older adults. Consequently, discussions surrounding this compound are becoming integral to personalized longevity strategies, with many eager to incorporate it into their health routines.
However, despite the excitement regarding its potential, caution is advised as ongoing research aims to clarify the long-term effects and optimal dosing of rapamycin.
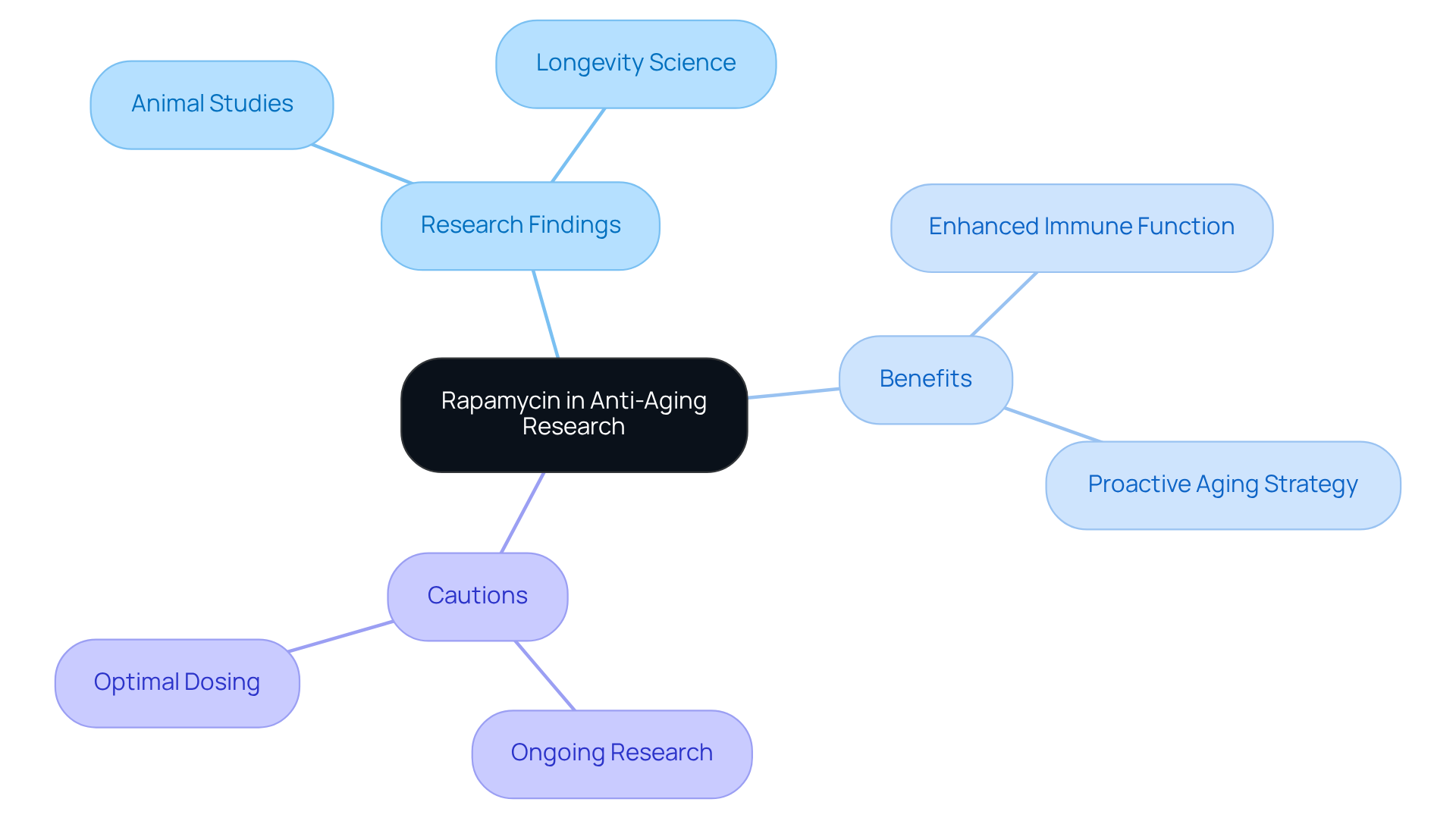
Conclusion
Rapamycin emerges as a groundbreaking compound in longevity research, showcasing its potential to significantly extend lifespan and enhance healthspan by modulating the mTOR pathway. By inhibiting this critical regulator of cell growth and metabolism, rapamycin mimics the effects of caloric restriction, a well-established method for promoting longevity across various species. This positions rapamycin not only as a treatment for age-related diseases but also as a proactive measure in the pursuit of healthy aging.
The article highlights key mechanisms through which rapamycin operates, including:
- Its ability to stimulate autophagy
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Reduce inflammation
These processes collectively contribute to delaying the onset of age-related conditions such as cancer and heart disease, making rapamycin a promising candidate for further exploration. As research progresses, the compound’s rising popularity in anti-aging discussions is evident, with many health enthusiasts integrating it into their routines alongside holistic dietary practices.
In light of the compelling evidence surrounding rapamycin’s benefits, it is crucial to approach its use with informed caution. Ongoing studies aim to clarify optimal dosing and long-term effects, ensuring that individuals can safely harness its potential. As the landscape of longevity science evolves, embracing innovative compounds like rapamycin could be key to unlocking healthier, longer lives. The journey toward understanding and utilizing rapamycin in the quest for longevity is just beginning, inviting further exploration and dialogue within the wellness community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is rapamycin and where was it first identified?
Rapamycin, also known as sirolimus, is a macrolide compound first identified in the soil of Rapa Nui (Easter Island).
What was the initial use of rapamycin?
It was initially developed as an immunosuppressant for organ transplant patients.
How does rapamycin work in the body?
Its primary mechanism involves inhibiting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which is a crucial regulator of cell growth and metabolism.
What potential benefits does rapamycin have in relation to longevity?
Recent studies suggest that rapamycin may enhance lifespan by mimicking the effects of caloric restriction, which is known to prolong life across various species.
How might rapamycin affect age-related conditions?
By modulating the mTOR pathway, rapamycin may delay the onset of age-related conditions and improve overall healthspan.
What diseases are researchers investigating rapamycin’s efficacy against?
Ongoing investigations are exploring rapamycin’s potential in reducing risks associated with Alzheimer’s and cardiac diseases.
How does rapamycin contribute to cell longevity?
Rapamycin enhances cell longevity by decreasing cellular growth and reproduction, which may help reduce disease-related waste accumulation.
What is the broader context of rapamycin in anti-aging research?
Rapamycin is positioned as a pivotal focus in anti-aging research, aligning with broader investigations into dietary supplements and innovative therapies for longevity.
How are wellness enthusiasts incorporating rapamycin into their routines?
Many health-conscious individuals report incorporating rapamycin into their routines alongside a diet rich in quality animal-based foods, reflecting a holistic approach to longevity.






