Understanding Why Is NMN Banned: Regulatory Insights and Impacts
Overview
The article delves into the complexities surrounding the regulatory status of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN). It specifically highlights why NMN is currently classified as banned by the FDA. This ban arises from NMN’s reclassification as a potential pharmaceutical drug due to safety concerns. As a result, there is significant confusion surrounding its status, which limits consumer access to NMN products. Legal challenges are currently underway to clarify this situation.
Introduction
The complex regulatory landscape surrounding Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has sparked significant debate. As the FDA navigates its shifting classification from a nutritional aid to a potential pharmaceutical, stakeholders are left seeking clarity. The agency’s recent pause on enforcing its ban has left consumers and manufacturers grappling with uncertainty about NMN’s legal status and its implications for health and wellness.
Furthermore, as clinical trials and legal challenges continue, the pressing question remains: what does the future hold for NMN? Will it ultimately be recognized for its potential benefits, or will it remain shrouded in regulatory ambiguity? This uncertainty calls for a closer examination of NMN’s journey through the regulatory process and its potential impact on health and wellness.
Examine the Regulatory Landscape Surrounding NMN
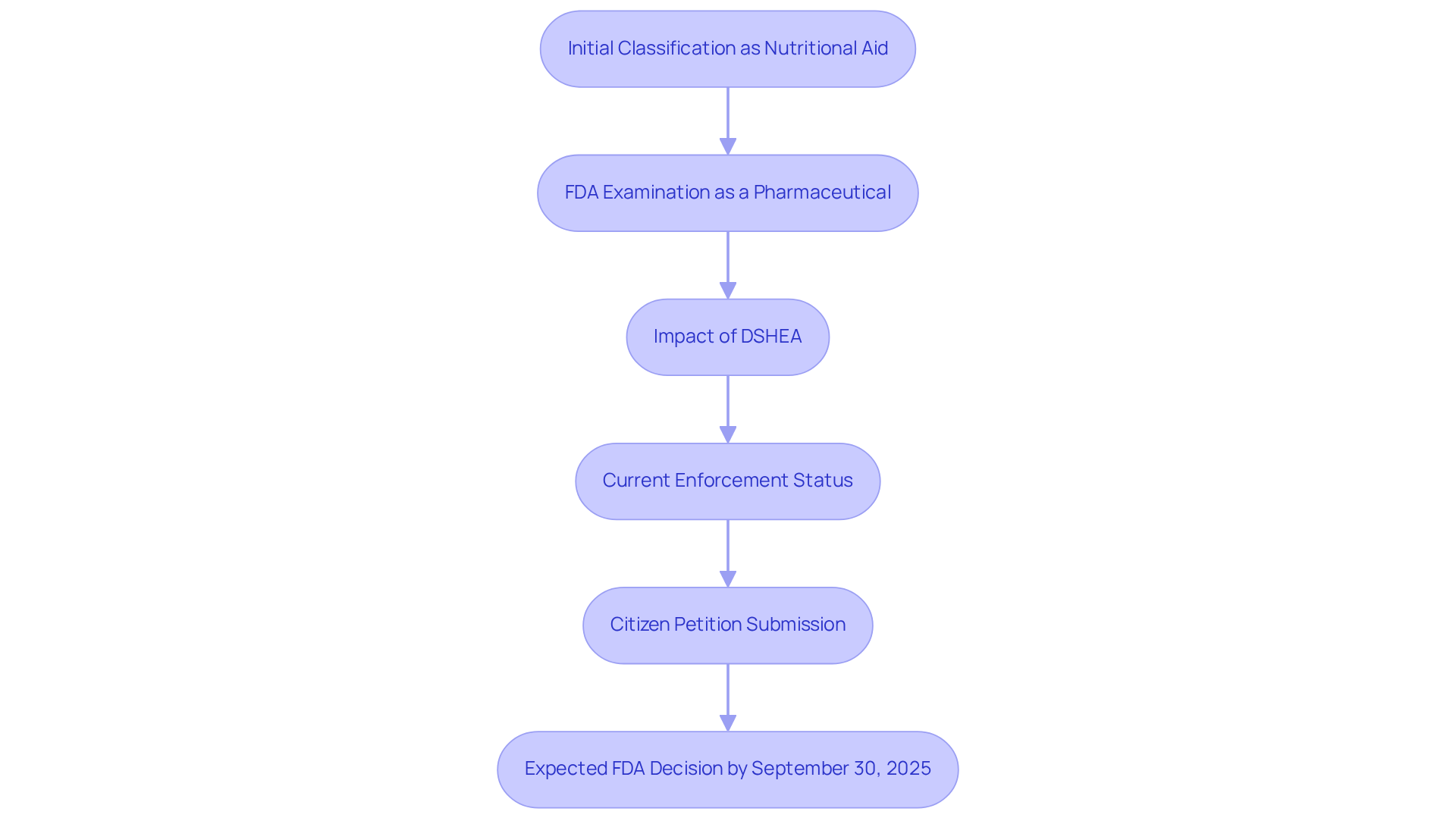
The regulatory landscape for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established guidelines that regulate the classification and promotion of nutritional products. Initially recognized as a nutritional aid, NMN’s classification shifted when the FDA began examining it as a potential pharmaceutical medication. This change stems from the Dietary Ingredient Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which prohibits substances under drug investigation from being marketed as nutritional products. This legal framework has sparked considerable confusion and debate within the health and wellness community, particularly among consumers and manufacturers advocating for NMN’s potential benefits. Currently, the FDA has paused enforcement of its ban on NMN, leading to questions about whether NMN is banned, pending further review of its classification and adding another layer of uncertainty to its regulatory status.
In March 2023, the National Products Association (NPA) and the Alliance for Natural Health (ANH) submitted a citizen petition requesting regulatory clarity on NMN as a food additive. Recent developments suggest that the FDA is expected to issue a final decision on this petition by September 30, 2025. This decision may establish a precedent for how the agency manages other nutritional products in the future. The ongoing discussions surrounding NMN raise the important question of whether NMN is banned, highlighting the necessity for clarity in regulatory guidelines, especially as numerous clinical trials are underway to assess NMN’s safety and efficacy. For instance, studies indicate that NMN supplementation can significantly enhance metabolic health and physical performance in older adults, suggesting its potential as an anti-aging agent. However, the FDA’s earlier categorization of NMN as an investigational new drug complicates its availability and promotion as a nutritional product. Furthermore, the FDA’s reduction in force (RIF) has impacted the agency’s ability to respond to the NMN petition, further delaying regulatory decisions. As the regulatory environment continues to evolve, stakeholders in the health and wellness sector remain vigilant, advocating for a clearer understanding of NMN’s benefits and risks.
Analyze FDA’s Concerns and Rationale for the Ban
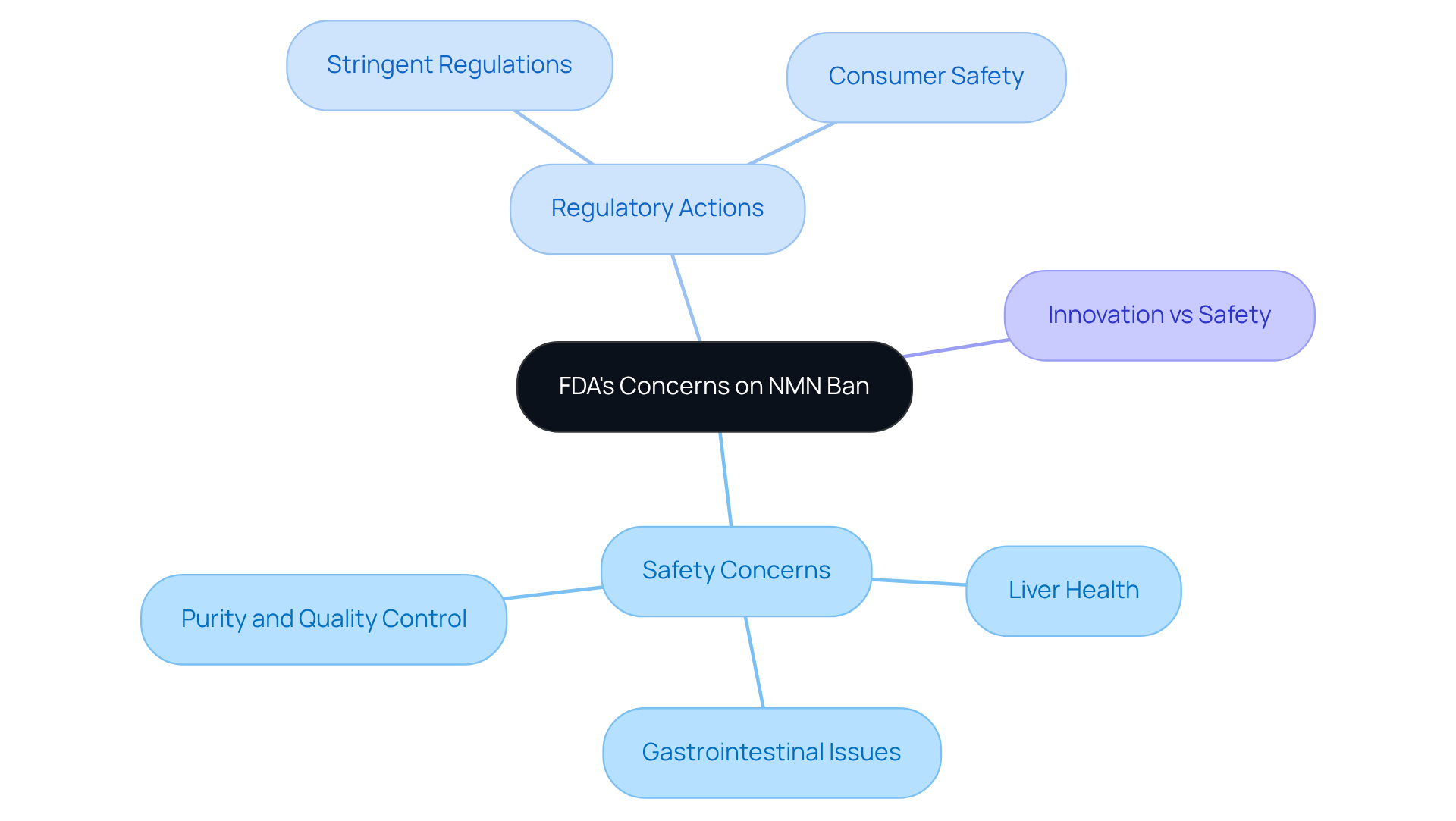
The FDA’s decision to prohibit NMN as a nutritional product raises the question of whether NMN is banned due to safety concerns related to its potential adverse effects on liver and stomach health. Preliminary research suggests that high doses of NMN may lead to gastrointestinal issues and liver toxicity, prompting questions about whether NMN is banned among health regulators. Furthermore, this scrutiny is compounded by ongoing investigations into whether the question of NMN being banned as a pharmaceutical product has sparked worries regarding the purity and quality control of NMN in its formulated form.
The FDA’s actions reflect a growing trend toward stringent regulation in the health product industry, particularly for items that claim significant health benefits. By prioritizing consumer safety, the FDA seeks to protect individuals from potentially harmful substances, even as the scientific community continues to explore NMN’s therapeutic potential. This cautious approach underscores the delicate balance between fostering innovation in nutritional products and adhering to regulatory standards designed to safeguard public health.
Discuss the Impact of NMN Ban on Consumers and the Supplement Market
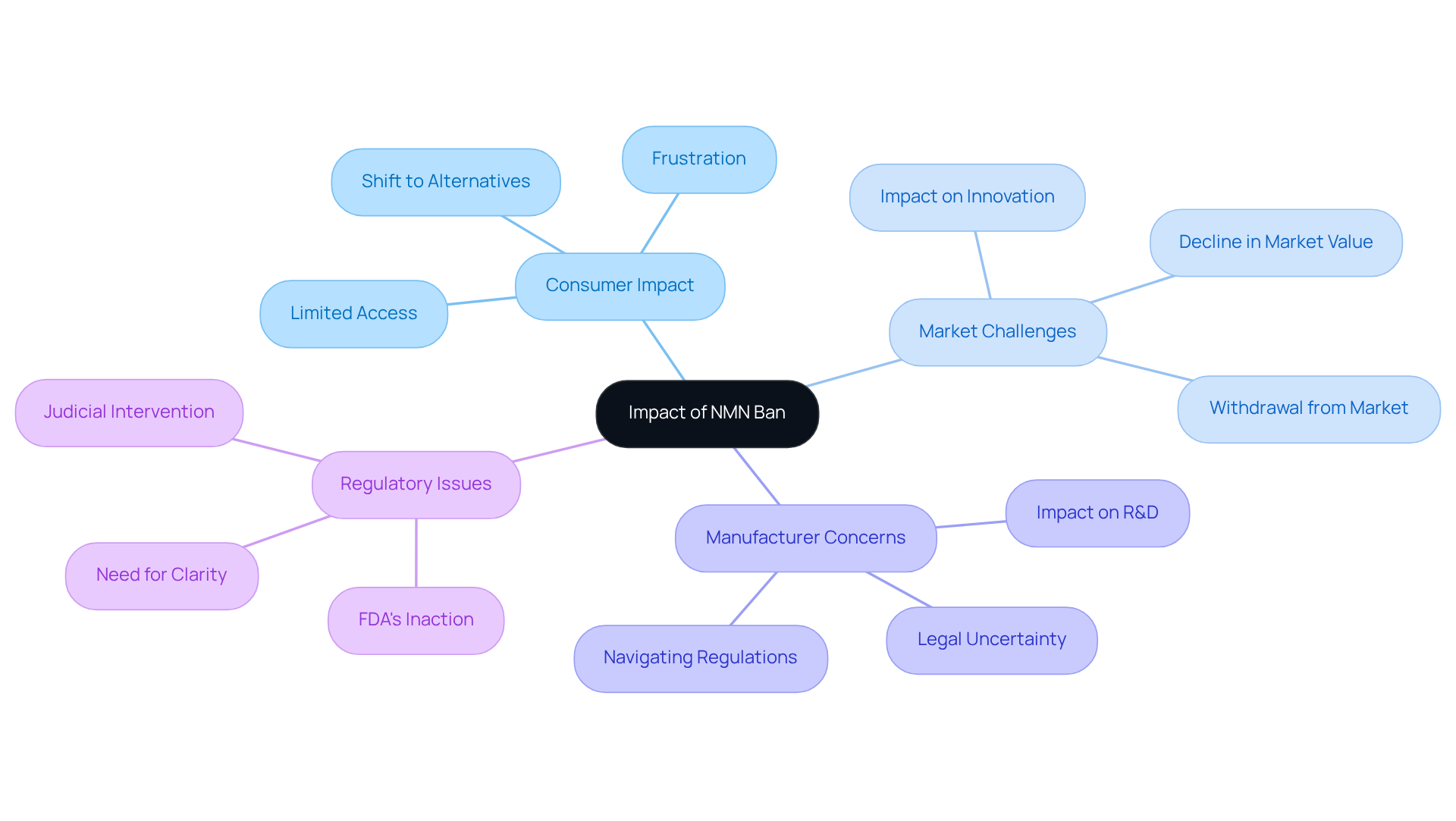
The question of whether NMN is banned has significant repercussions for both consumers and the market for dietary aids. For health-conscious individuals, this restriction greatly limits access to a well-known product that many believe offers anti-aging advantages. This has led to palpable frustration among consumers who rely on NMN for its purported effects on energy levels and overall vitality, especially with the question of whether NMN is banned. The uncertainty surrounding NMN’s legal status has created a climate of apprehension among retailers. As a result, many have removed NMN products from shelves and major online platforms like Amazon, where it is NMN banned since March 2023. This withdrawal not only reduces consumer options but also hinders innovation within the wellness industry.
Manufacturers now face the daunting task of navigating a landscape where the legality of their products remains uncertain. The NMN market, previously estimated at around $280.2 million in 2022, is now facing a decline as consumers increasingly opt for alternative products or seek unregulated sources. Daniel Fabricant, President and CEO of the Natural Products Association, has expressed concerns that the FDA’s inaction on the NMN petition could prolong this situation, raising the question of whether NMN is banned and emphasizing the need for judicial intervention to protect consumer access to NMN.
This situation highlights the delicate balance between regulatory supervision and consumer access to health products, raising essential questions about whether NMN is banned and its implications for similar health aids. In summary, the ongoing legal challenges and the current regulatory landscape pose significant hurdles for both consumers and manufacturers, underscoring the urgent need for clarity and resolution in the NMN market.
Explore Alternative Views and Future of NMN Regulation
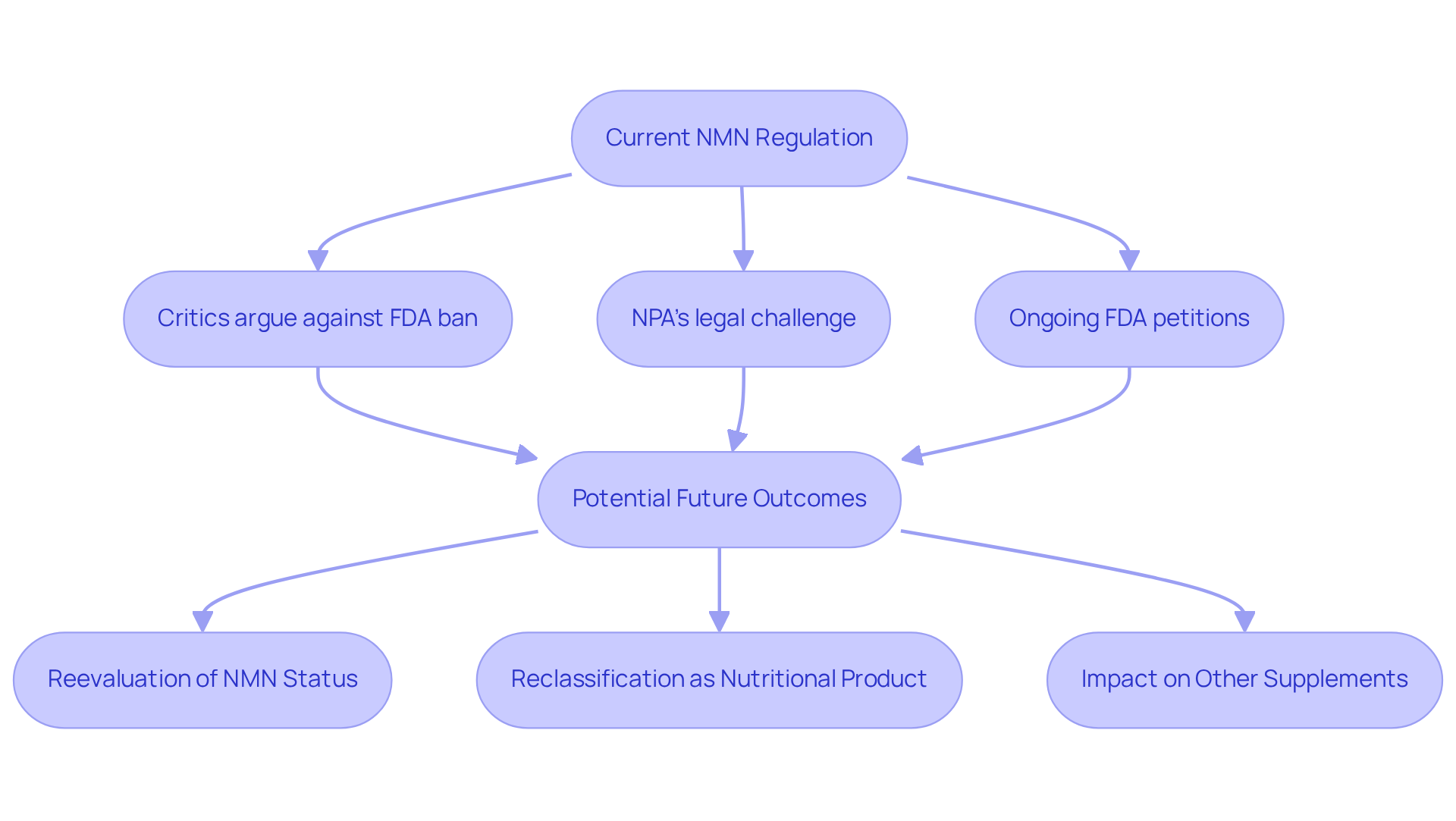
The discourse on NMN regulation remains contentious, with various stakeholders advocating for divergent outcomes. Critics of the FDA’s ban argue that it is excessively cautious and fails to align with the growing body of scientific evidence supporting that NMN is banned despite its safety and efficacy. Numerous studies highlight NMN’s potential benefits, indicating minimal adverse effects. This suggests a need for the regulatory framework to evolve in response to new research findings.
Furthermore, the Natural Products Association (NPA) has begun legal proceedings against the FDA, challenging the exclusion of NMN from nutritional product classification. This legal challenge could spark a reevaluation of NMN’s status, potentially aiding its reclassification as a nutritional product in the future. As the FDA navigates ongoing petitions and legal disputes, it remains unclear whether NMN is banned in the future of NMN regulation.
The outcomes of these proceedings are poised to not only affect NMN’s market availability but also establish precedents for the regulation of other dietary supplements within the dynamic health and wellness sector.
Conclusion
The ongoing debate surrounding the regulatory status of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) encapsulates a critical intersection of consumer health, scientific inquiry, and regulatory oversight. With the FDA’s current classification of NMN as an investigational new drug, the pivotal question of whether NMN is banned significantly affects its availability and the broader landscape of dietary supplements. The evolving nature of NMN’s regulatory framework underscores the necessity for clarity and consistency in the guidelines governing nutritional products.
Key insights from the discussion reveal the complexities of NMN’s classification, the FDA’s concerns about potential safety risks, and the substantial impact on consumers and the supplement market. As stakeholders advocate for regulatory reform, the tension between innovation in health products and the imperative of consumer safety emerges as a central theme. Furthermore, the legal challenges posed by organizations like the Natural Products Association signal a potential shift in NMN’s future, which could redefine its status and influence the regulation of similar dietary aids.
In light of these developments, it is essential for consumers, manufacturers, and regulators to engage in informed dialogue about NMN’s benefits and risks. The outcomes of ongoing petitions and legal actions will not only shape the future of NMN but also set important precedents for the regulation of dietary supplements. Advocating for transparency and scientific rigor in the regulatory process will ultimately empower consumers to make informed health choices while fostering innovation in the wellness industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current regulatory status of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) in the United States?
The regulatory status of NMN is complex and evolving. Initially recognized as a nutritional aid, NMN’s classification changed when the FDA began examining it as a potential pharmaceutical medication. Currently, the FDA has paused enforcement of its ban on NMN, leading to confusion regarding its status.
Why did the FDA change its classification of NMN?
The FDA’s classification of NMN changed due to the Dietary Ingredient Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which prohibits substances under drug investigation from being marketed as nutritional products. This shift has sparked considerable debate within the health and wellness community.
What actions have been taken to seek regulatory clarity on NMN?
In March 2023, the National Products Association (NPA) and the Alliance for Natural Health (ANH) submitted a citizen petition requesting regulatory clarity on NMN as a food additive. The FDA is expected to issue a final decision on this petition by September 30, 2025.
What implications could the FDA’s decision on the NMN petition have?
The FDA’s decision may establish a precedent for how the agency manages other nutritional products in the future, potentially impacting the availability and promotion of NMN and similar substances.
Are there any ongoing studies related to NMN?
Yes, numerous clinical trials are underway to assess NMN’s safety and efficacy. Some studies suggest that NMN supplementation can significantly enhance metabolic health and physical performance in older adults, indicating its potential as an anti-aging agent.
How has the FDA’s reduction in force affected NMN’s regulatory process?
The FDA’s reduction in force (RIF) has impacted the agency’s ability to respond to the NMN petition, further delaying regulatory decisions and contributing to the uncertainty surrounding NMN’s status.